The Kahraman Maraş earthquake sequence, Turkey/Syria, 2023
Two large earthquakes occurred within hours of each other on 6 February 2023.
14/02/2023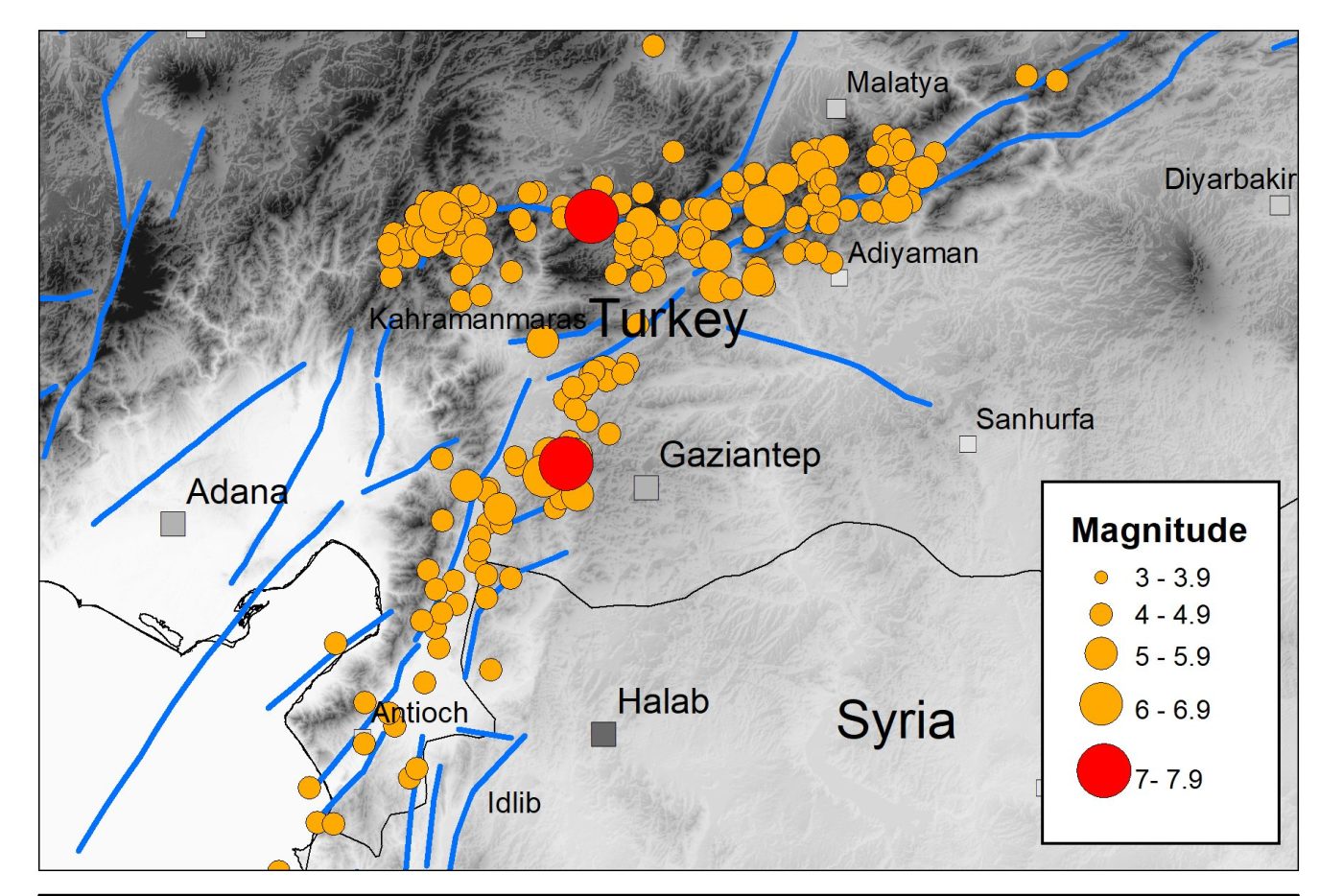
The devastating Kahraman Maraş earthquake sequence has caused widespread destruction and terrible loss of life across a large part of southern Turkey and northern Syria, with the collapse of thousands of buildings in populated areas throughout the region.
The earthquake sequence
The sequence started with a magnitude 7.8 earthquake at 01:17 UTC on 6 February 2023, rupturing a 200 km section of the north-east to south-west trending fault system that forms the boundary between the Anatolian and the Arabian tectonic plates. These plates are moving horizontally relative to each other at a speed of around 13 mm per year.
The earthquake took about 30 seconds to reach a maximum slip of around 3 m and resulted in intense shaking that lasted over a minute. Recorded ground accelerations at some sites close to the fault rupture exceeded 1.0 g. A few hours later, a magnitude 7.5 event occurred on a nearby branch of the fault system that trends east to west. This caused further strong ground shaking and destruction.
Previous seismicity in the area
The magnitude 7.8 earthquake was approximately 2.5 times bigger than the magnitude 7.4 Izmit earthquake in Turkey in 1999, which killed over 17 000 people, and was the same size as the magnitude 7.8 Erzincan earthquake in north-east Turkey in 1939, which killed over 32 000 people. The latter is considered the deadliest natural disaster in Turkey in the 20th century.
Although the earthquake risk in this part of southern Turkey was generally considered to be less than along the well-known Northern Anatolian Fault in northern Turkey, large and damaging earthquakes have struck here in the past. The city of Aleppo in northern Syria has been destroyed by several earthquakes in the last thousand years, including an earthquake in 1822 with over 20 000 fatalities.
The continuing hazard
Aftershocks are expected to cause moderate to severe ground shaking over a 300 to 500 km region for months to come. Some of these earthquakes may be several hundred kilometres away from other aftershocks and may be large enough to cause further damage, particularly to buildings that have already been weakened.
There have already been several aftershocks with a magnitude larger than 6.0. Our current understanding of the statistics of the aftershock process suggests that there may be several tens of earthquakes of this size or greater.
Over a period of months to years, the frequency of triggered seismicity (aftershocks) will reduce, with earthquake activity gradually returning to previous levels. Until then, earthquake hazard and risk in the region will remain heightened. This means that increased seismic hazard in the region where the two large earthquakes occurred is transient in nature, whilst longer seismic hazard estimates continue to be relevant.
Earthquake cascades
It is well established that large earthquakes can trigger seismicity on other nearby faults as the Earth’s Crust adjusts to the sudden change in stress. Both the permanent deformation caused by the initial earthquake and the passage of seismic waves through the Earth can trigger these subsequent earthquakes.
Other recent examples of this triggering process include the Kumamoto sequence on the island of Kyushu, Japan, in 2016, when a magnitude 6.5 earthquake was followed almost a day later by a magnitude 7.3 event. In Europe, the magnitude 6.0 Amatrice earthquake that occurred in Italy in 2016 was followed by the magnitude 6.5 Norcia earthquake two months later.
Although such cascading sequences of large-magnitude earthquake within short periods of time are relatively rare, investigation and analysis of these may promote a new understanding of the earthquake process.
Further information
About the authors

Dr Brian Baptie
Seismologist
Dr Margarita Segou
Earthquake seismologist
Relative topics
Related news

Funding awarded to UK/Canadian critical mineral research projects
08/07/2025
BGS is part of a groundbreaking science partnership aiming to improve critical minerals mining and supply chains.
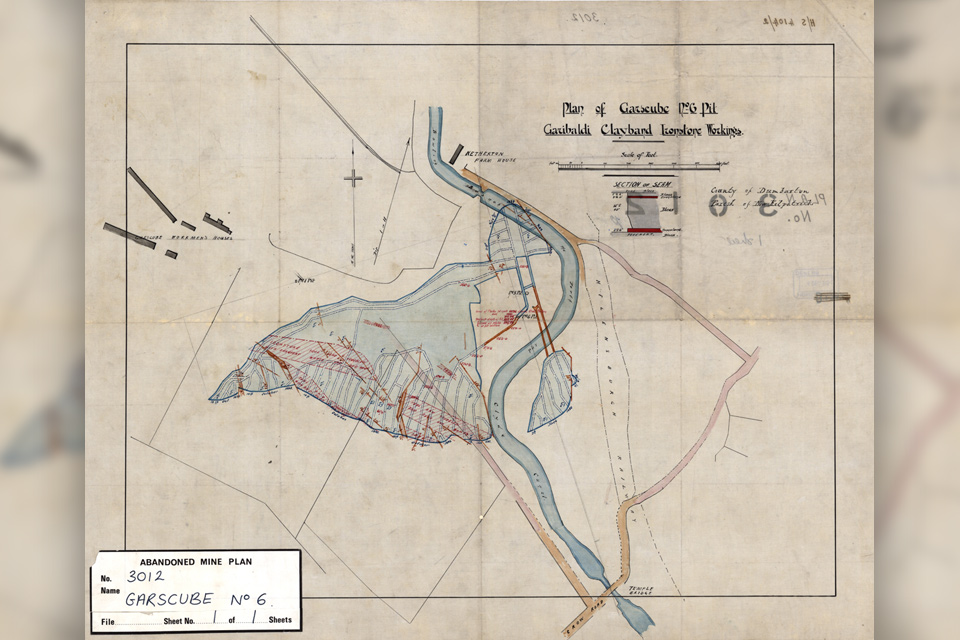
Release of over 500 Scottish abandoned-mine plans
24/06/2025
The historical plans cover non-coal mines that were abandoned pre-1980 and are available through BGS’s plans viewer.

New collaboration aims to improve availability of real-time hazard impact data
19/06/2025
BGS has signed a memorandum of understanding with FloodTags to collaborate on the use of large language models to improve real-time monitoring of geological hazards and their impacts.

Modern pesticides found in UK rivers could pose risk to aquatic life
17/06/2025
New research shows that modern pesticides used in agriculture and veterinary medicines have been found for the first time in English rivers.

Goldilocks zones: ‘geological super regions’ set to drive annual £40 billion investment in jobs and economic growth
10/06/2025
Eight UK regions identified as ‘just right’ in terms of geological conditions to drive the country’s net zero energy ambitions.
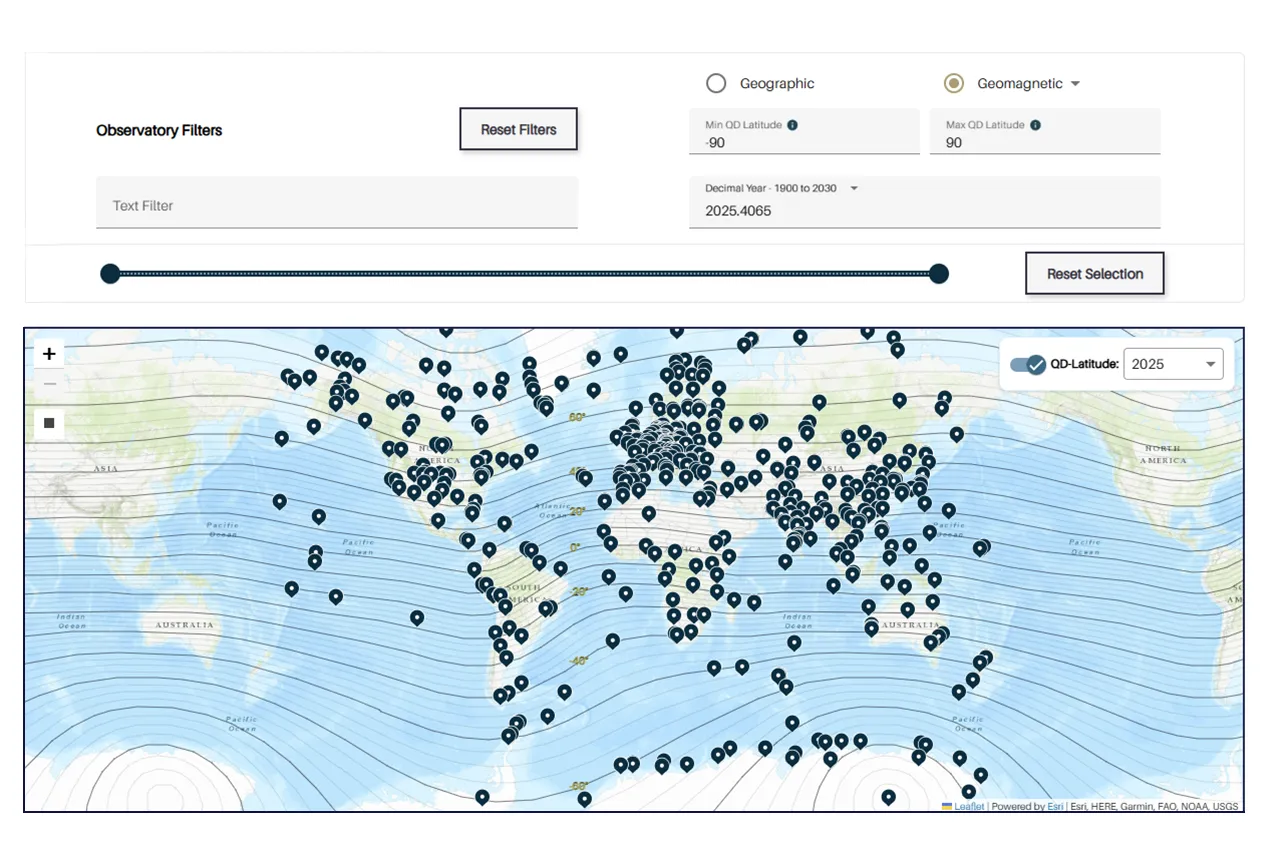
Upgraded web portal improves access to geomagnetism data
02/06/2025
BGS’s geomagnetism portal, which holds data for over 570 observatories across the world, has received a significant update.
BGS digital geology maps: we want your feedback
29/05/2025
BGS is asking for user feedback on its digital geological map datasets to improve data content and delivery.

What is the impact of drought on temperate soils?
22/05/2025
A new BGS review pulls together key information on the impact of drought on temperate soils and the further research needed to fully understand it.

UK Minerals Yearbook 2024 released
21/05/2025
The annual publication provides essential information about the production, consumption and trade of UK minerals up to 2024.

BGS scientists join international expedition off the coast of New England
20/05/2025
Latest IODP research project investigates freshened water under the ocean floor.

New interactive map viewer reveals growing capacity and rare earth element content of UK wind farms
16/05/2025
BGS’s new tool highlights the development of wind energy installations over time, along with their magnet and rare earth content.

UKRI announce new Chair of the BGS Board
01/05/2025
Prof Paul Monks CB will step into the role later this year.


