For many years, energy policy in the UK has been framed by the requirement for:
- security of supply
- energy that is affordable
- sources of low-carbon energy
Globally, the requirements of the COP21 (‘Paris Agreement’) on climate change are to reduce temperature rises to two degrees by 2050. However, there are significant environmental advantages to keeping the rise in temperature to less than two degrees; a rise restricted to just 1.5 degrees would lead to a reduced rise in sea level, maintain some coral communities and keep more Arctic sea ice.
It is thought that restricting the temperature rise to two degrees requires a reduction in carbon emissions of 70–90 per cent worldwide; the UK has adopted an emissions reduction target of 80 per cent by 2050. Furthermore, the UK has pledged to be carbon-neutral by 2050 (with Scotland aiming to achieve this by 2045).
Renewable energy
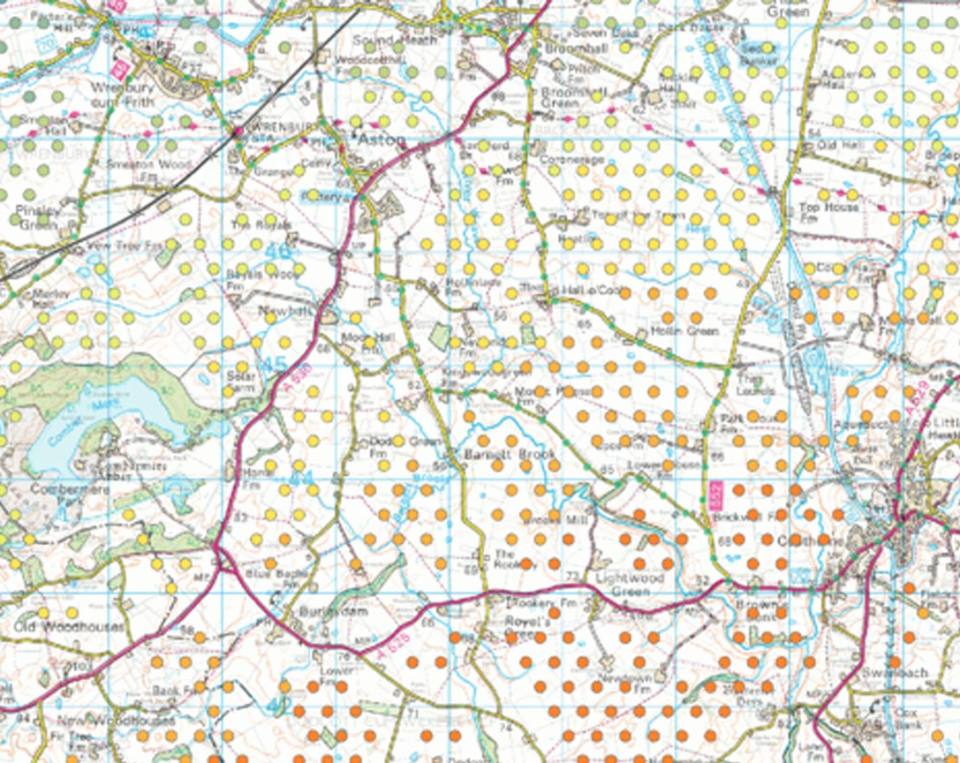
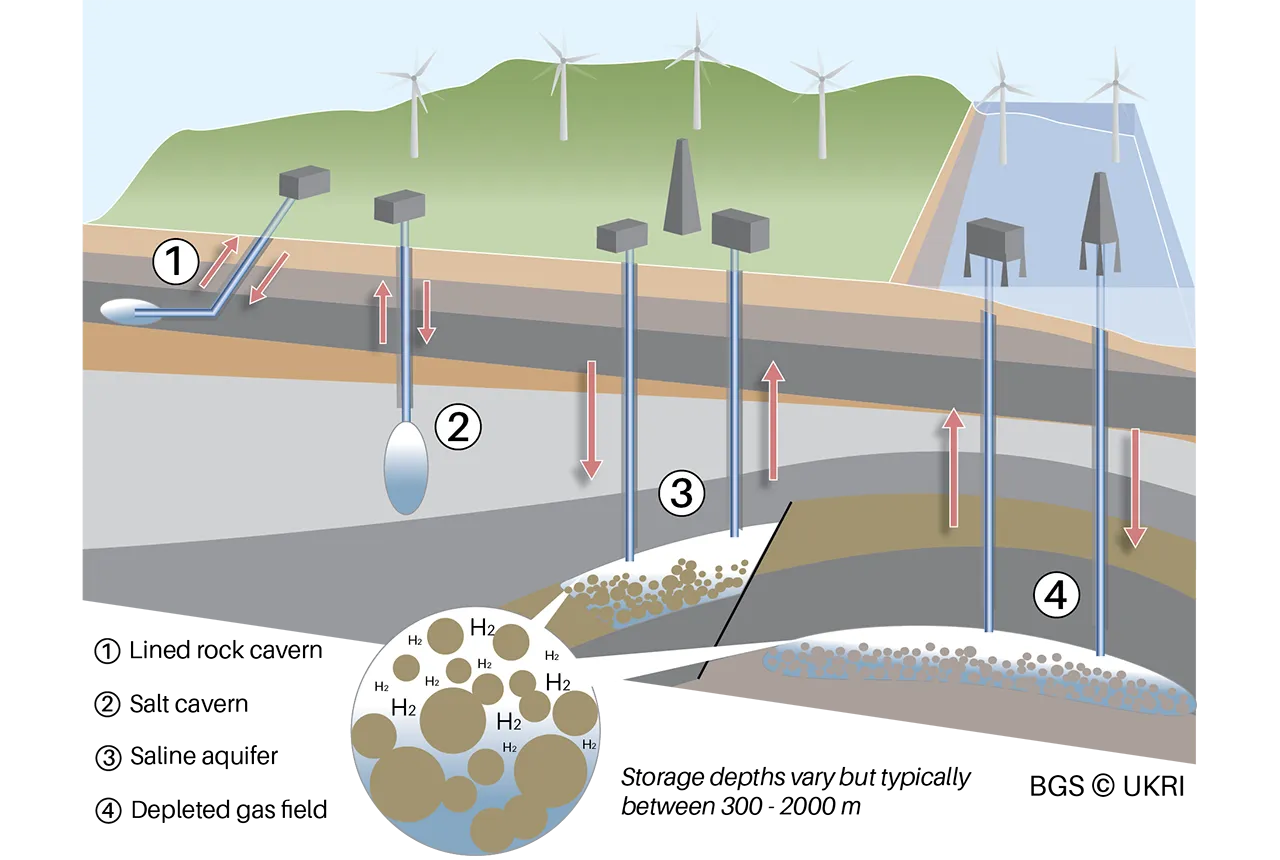
As well as mapping potential locations for gas storage caverns, we have also calculated the energy that can be stored in individual caverns, allowing planners and developers to understand the variation in the amount of energy that can be stored in different parts of the UK. Contains Ordnance Survey data © Crown Copyright and database rights 2020.
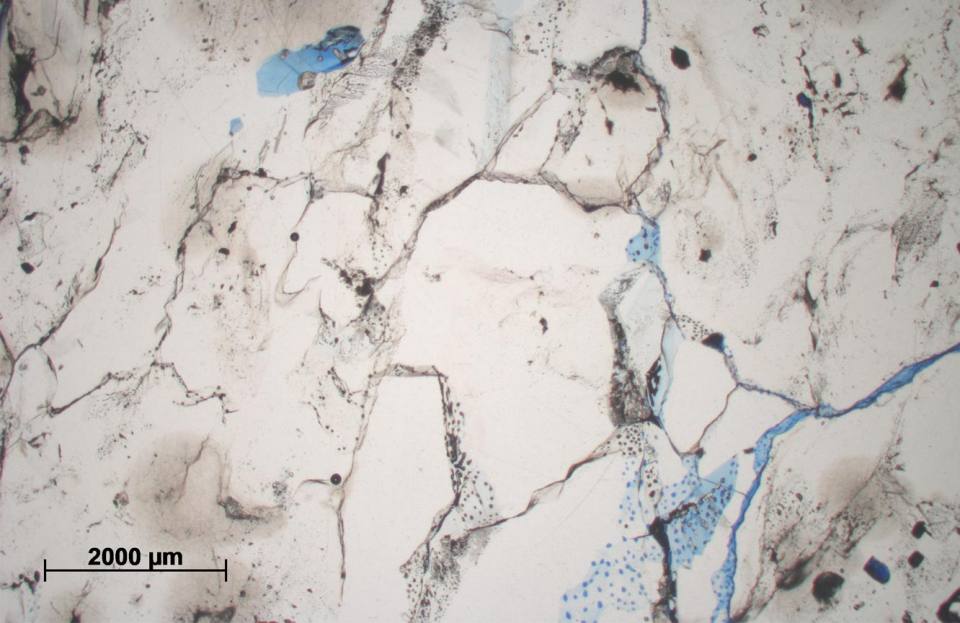
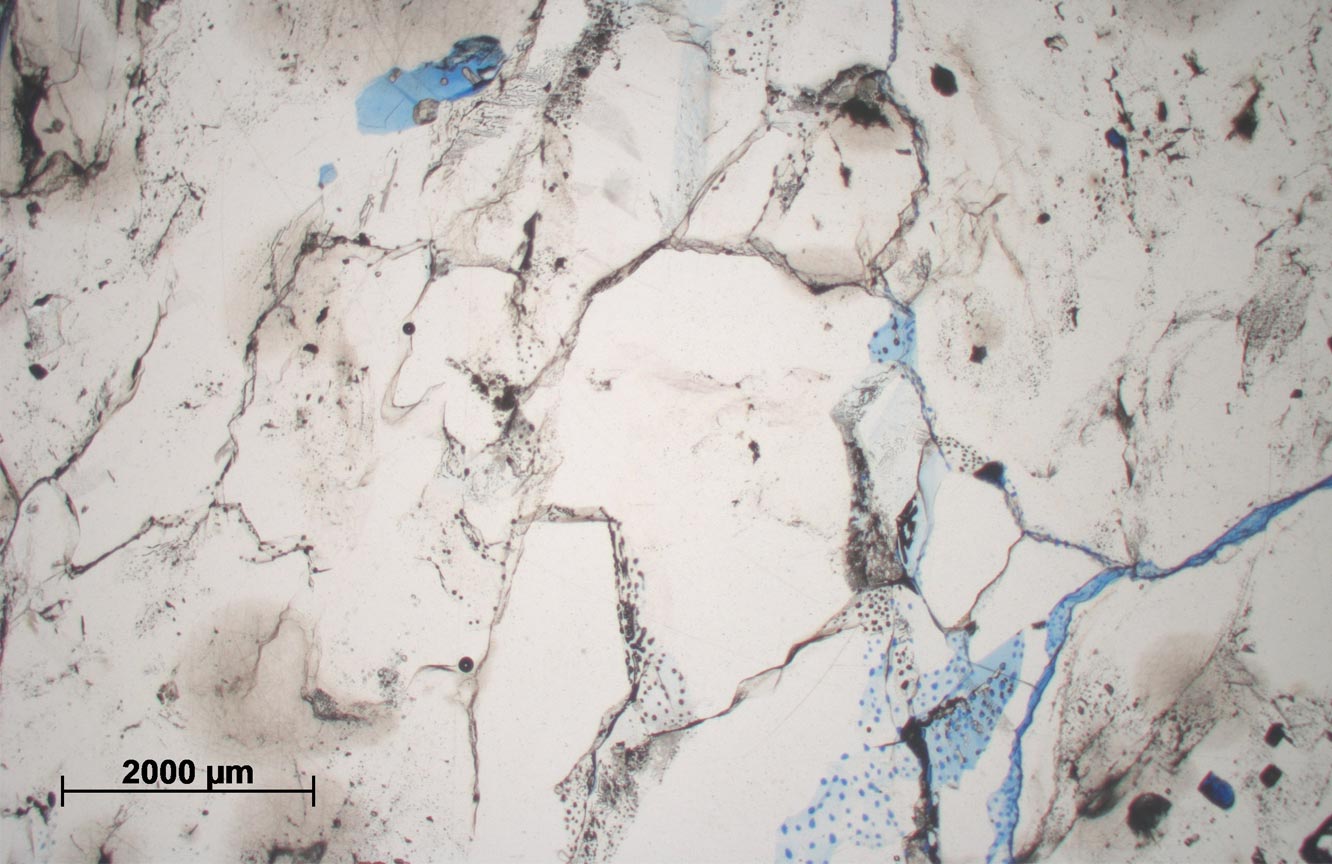
Halite is a complex, crystalline rock that is viscoplastic, meaning it flows naturally in the subsurface and can self-heal fractures over geological time. Halite is also soluble. These properties mean that large voids in the subsurface can be created by solution mining, resulting in storage space that is gas-tight and suitable for the storage of natural gas, compressed air and hydrogen, three principal energy carriers. © BGS/UKRI.
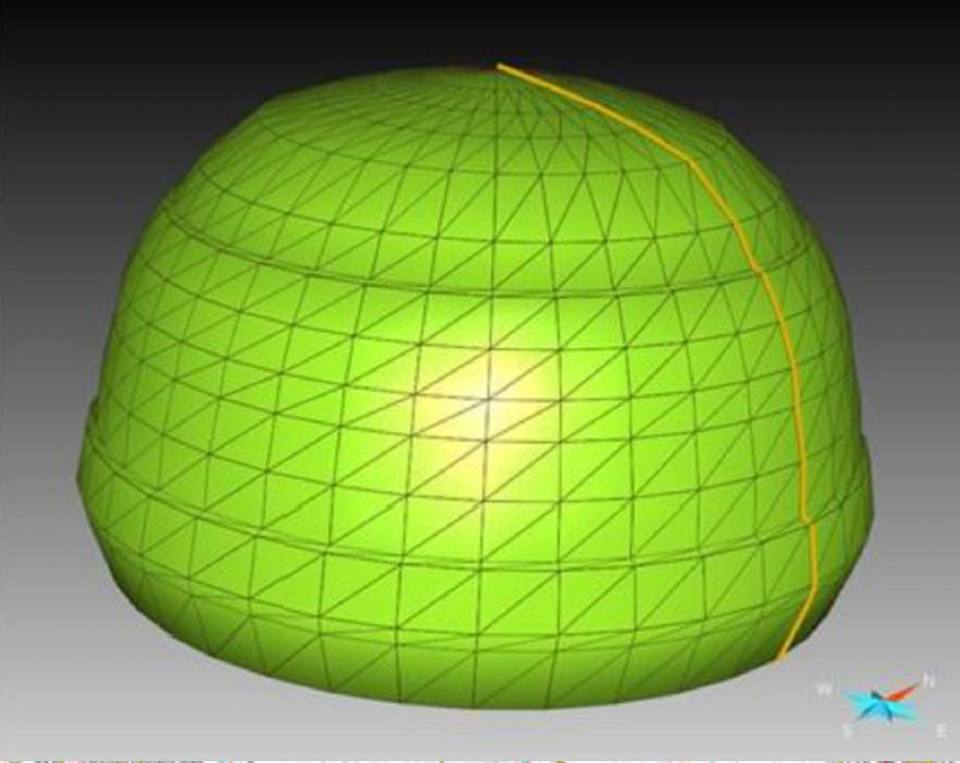
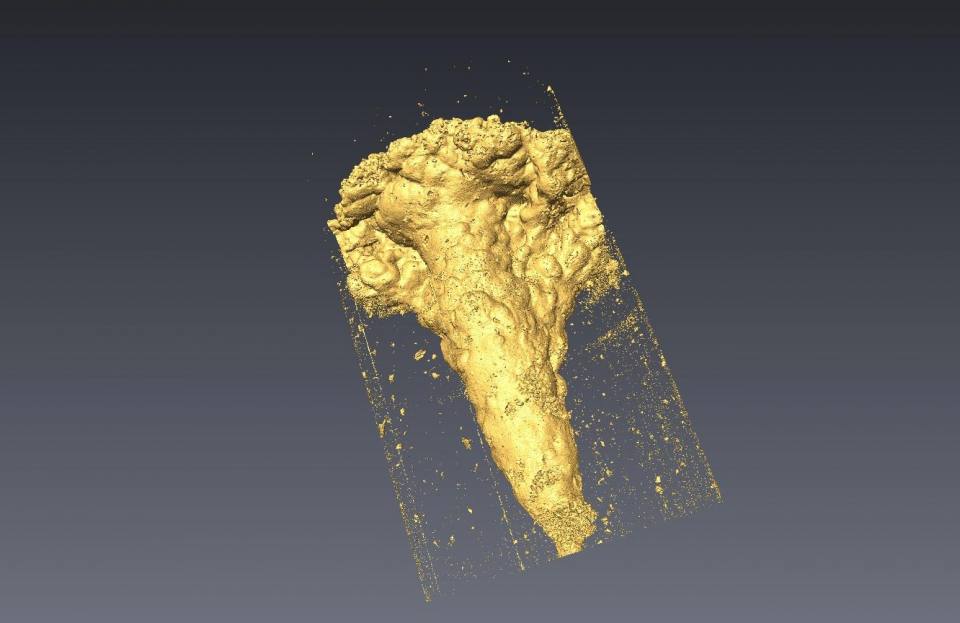
This is a 3D model of an engineered gas storage cavern in solution-mined halite. This cavern is over 500 m below the ground surface, with approximate dimensions of 80 m high and 50 m diameter and 300 000 m3 in volume. Our research has mapped out the areas where these caverns could potentially be developed. © BGS/UKRI.
One way to achieve these ambitious targets is to increase the use of renewable energy. However, to address the issue of intermittent supply of energy (e.g. days with little sunshine or wind) energy has to be stored at time of surplus for use at times where demand outstrips supply.
Technologies for energy storage
Large-scale energy storage is possible via various technologies.
- The largest potential energy stores in the UK are pumped hydro schemes, which account for over 90 per cent of current storage capacity in the UK
- Underground storage is operated commercially in several parts of the UK, where large caverns in halite have been developed and store various products including natural gas and hydrogen. There is the potential for energy to be stored in similar caverns as compressed air
- Heat and cool can be stored in a multitude of ways in the subsurface, including being stored and retrieved in the pore space of depleted hydrocarbon reservoirs and aquifers. There are also opportunities to store heat as molten salt and in hot rocks and cool in the production of ice when demand for electricity is low
- The pore space in depleted hydrocarbon reservoirs and aquifers can also be a target for the storage of fluids including natural gas, hydrogen and fuel
- We have contributed to a Europe-wide review of energy storage options
Hydrogen as an energy source
A second route to meeting the temperature rise targets may be to increase the use of hydrogen as an energy source or carrier. Hydrogen could decarbonise domestic heating, transport and areas of industry.
Hydrogen can be produced from methane; it produces water and no carbon dioxide (CO2) on combustion. However, commercial production of hydrogen is energy intensive, with the steam methane reformation process being more carbon-intensive than combustion, so carbon capture and storage (CCS) is required to lessen the carbon impact. Hydrogen can also be produced by electrolysis from water, but to date this is not commercially viable.
The role of geology
Geology is key to the success of the hydrogen economy as a source of methane, as a sink for CO2 and to provide underground storage for large quantities of hydrogen. The underground geology can also provide the host for the underground energy-storage techniques that could potentially be developed in the UK. Our rich geological heritage includes thick beds of halite that can be developed for cavern storage, depleted hydrocarbon fields that have held large amounts of oil and gas over geological time and aquifers with pore space that could be utilised for energy storage.
There are also novel uses of the underground for energy storage such as lined tunnels for compressed air, abandoned mines for heat storage and permeable rocks/caverns for underground pumped hydro projects.
The UK Government, through the Industrial Strategy, has identified energy storage as one of eight technologies where the UK is set to become a global leader.
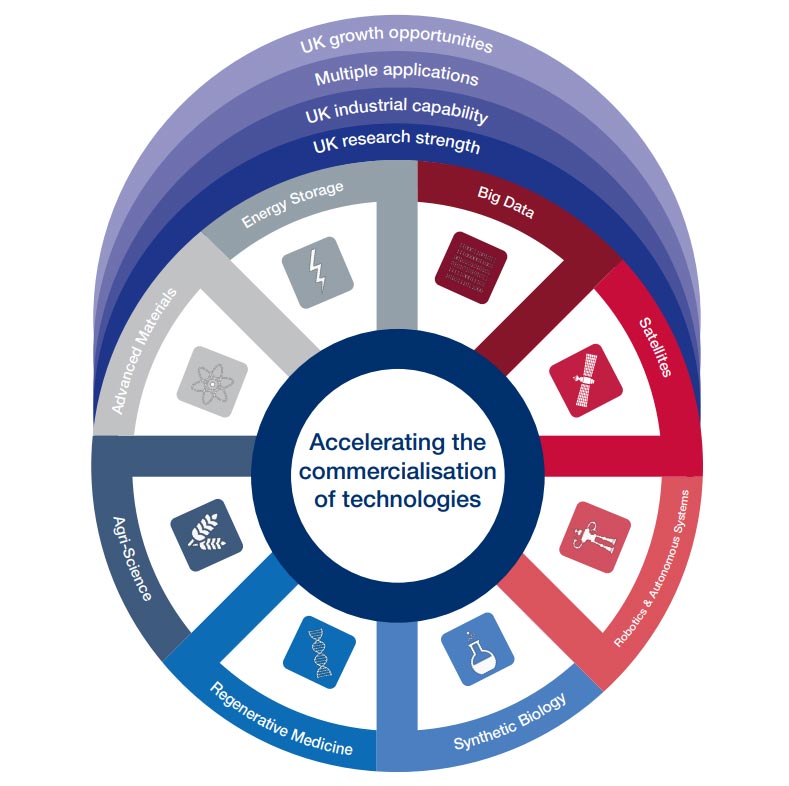
Eight great technologies in which the UK is set to be a global leader. Source: gov.uk
We have a sustained track record of research in this area, which will underpin future laboratory, field and GIS-based activities and commissions.
References
Bérest, P, Réveillère, A, Evans, D J, and Stöwer, M. 2019. Review and analysis of historical leakages from storage salt caverns wells. Oil & Gas Science and Technology — Revue d’IFP Energies Nouvelles, Vol. 74, 27. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2516/ogst/2018093
Crotogino, F, Schneider, G-S, and Evans, D J. 2017. Renewable energy storage in geological formations. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part A: Journal of Power and Energy, Vol. 232,(1). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0957650917731181
Evans, D J. 2009. A review of underground fuel storage events and putting risk into perspective with other areas of the energy supply chain. 173–216 in Underground Energy Storage: worldwide experiences and future development in the UK and Europe. Evans, D J, and Chadwick, R A (editors). Geological Society Special Publication 313. (London: Geological Society.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1144/SP313.12
Evans, D J. 2008. Accidents at UFS sites and risk relative to other areas of the energy supply chain, with particular reference to salt cavern storage. SMRI Fall 2008 Technical Conference, 13–14 October 2008, Austin, USA.
Evans, D J, and Chadwick, R A (editors). 2009. Underground Energy Storage: worldwide experiences and future development in the UK and Europe. Geological Society Special Publication 313. (London: Geological Society.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1144/SP313.0
Evans, D, and Chadwick, R A. 2009. Underground gas storage: an introduction and UK perspective. 1–11 in Underground Energy Storage: worldwide experiences and future development in the UK and Europe. Evans, D J, and Chadwick, R A (editors). Geological Society Special Publication 313. (London: Geological Society.) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1144/SP313.1
Evans, D J, and Holloway, S. 2009. A review of onshore UK salt deposits and their potential for underground gas storage. 39–80 in Underground Energy Storage: Underground Energy Storage: worldwide experiences and future development in the UK and Europe. Evans, D J, and Chadwick, R A (editors). Geological Society Special Publication 313. (London: Geological Society.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1144/SP313.5
Evans, D J, and West, J M. 2008. An appraisal of underground gas storage technologies and incidents, for the development of risk assessment methodology. Health and Safety Executive (HSE) Research Report RR605. Available via https://www.hse.gov.uk/research/rrhtm/rr605.htm
Evans, D J, Carpenter, G, and Farr, G. 2019. Mechanical systems for energy storage-scale and environmental issues: pumped hydroelectric and compressed air energy storage. 42–114 in Energy Storage Options and their Environmental Impact. Hester, R E, and Harrison, R M (editors). (London, UK: Royal Society of Chemistry.) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/9781788015530-00042
Evans, D J, Kingdon, A, Hough, E, Reynolds, W, and Heitmann, N. 2012. First account of resistivity borehole micro-imaging (FMI) to assess the sedimentology and structure of the Preesall Halite, NW England: implications for gas storage and wider applications in CCS caprock assessment. Journal of the Geological Society, Vol. 169(5), 587–592. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1144/0016-76492011-14
Evans, D J, Williams, J D O, Hough, E, and Stacey, A. 2011. The stratigraphy and lateral correlations of the Northwich and Preesall halites from the Cheshire Basin-East Irish Sea areas: implications for sedimentary environments, rates of deposition and the solution mining of gas storage caverns. SMRI Fall 2011 Technical Conference, 3–4 October 2011, York, UK.
Evans, D J, Stephenson, M H, and Shaw, R. 2009. The present and future use of ‘land’ below ground. Land Use Policy, Vol. 265(1), S302–S316. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2009.09.015
Evans, D J, Reay, D M, Riley, N J, Mitchell, W I, and Busby, J. 2006. Appraisal of underground energy storage potential in Northern Ireland. British Geological Survey Internal Report, IR/06/095.
Evans, D J, Holloway, S, and Riley, N J. 2004. The case for underground gas storage (UGS): a report submitted by the BGS to the House of Lords inquiry into European Union energy policy: gas supply and access. British Geological Survey Occasional Publication, 5. (Nottingham, UK: British Geological Survey.) (Unpublished.)
Field, L P, Milodowski, A E, Evans, D J, Palumbo-Roe, B, Hall, M R, Marriott, A L, Barlow, T, and Devez, A. 2017. Determining constraints imposed by salt fabrics on the morphology of solution mined cavities in relation to CAES, through dissolution experiments using brine and seawater in halite. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology and Hydrogeology, Vol. 52, 240–254. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1144/qjegh2018-072
Field, L P, Palumbo-Roe, B, Milodowski, A E, Hall, M R, Parkes, D, and Evans, D. 2015. Dissolution experiments in halite cores: comparisons in cavity shape and controls between brine and seawater experiments. In Goldschmidt 2015, Prague, Czech Republic, 16–21 August. (Unpublished.) Available at http://nora.nerc.ac.uk/id/eprint/510575/
Garvey, S D, Eames, P C, Wang, J H, Pimm, A J, Waterson, M, MacKay, R S, Giuliette, M, Flatley, L C, Thomson, M, Barton, J, Evans, D J, Busby, J, and Garvey, J E. 2015. On generation-integrated energy storage. Energy Policy, Vol. 86, 544–551. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2015.08.001
He, W, Luo, X, Evans, DJ, Busby, J, Garvey, S, Parkes, D, and Wang, J. 2017. Exergy storage of compressed air in cavern and cavern volume estimation of the large-scale compressed air energy storage system. 2017. Applied Energy, Vol. 208, 745–757. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.09.074
Hough, E, and Evans, D J. 2016. Primary sedimentary structures in bedded halite- indicators of depositional conditions from the mid-Triassic of the UK. In: 55th British Sedimentological Research Group Annual Meeting, Cambridge, UK, 18–20 December 2016. (Unpublished.) Available at http://nora.nerc.ac.uk/id/eprint/515998/
Hough, E, and Evans, D J. 2011. Cheshire Basin field workshop for SMRI Fall 2011 Technical Conference. SMRI Fall 2011 Technical Conference, 5–6 October, York, UK.
Hough, E, Evans, D J, and Williamson, J P. 2011. A geological reappraisal of the Preesall Saltfield, Lancashire, United Kingdom: recognising geological factors relevant to gas storage. SMRI Fall 2011 Technical Conference, 3–4 October 2011, York, UK.
Kingdon, A, and Evans, D J. 2013. Use of processed resistivity borehole imaging to assess the insoluble content of the massively bedded Preesall Halite NW England. In: EGU General Assembly 2013, Vienna, Austria, 7–12 April 2013 (unpublished).
Kingdon, A, Evans, D J, Hough, E, Heitmann, N, and Reynolds, W. 2011. Use of resistivity borehole imaging to assess the structure, sedimentology and insoluble content of the massively bedded Preesall Halite NW England. SMRI Fall 2011 Technical Conference, 3–4 October 2011, York, UK. (Unpublished.)
Milodowski, A E, Field, L P, Palumbo-Roe, B, Hall, M R, Parkes, D, and Evans, D J. 2014 Dissolution experiments in halite cores: initial findings. In: UKES2014: UK Energy Storage Conference, Warwick, UK, 25–27 November 2014 (unpublished).
Parkes, D, Evans, D J, Dooner, M, He, W, Busby, J, and Garvey, S. 2019. Estimating potential for CAES (compressed air energy storage) in the bedded halites of the UK. Geophysical Research Abstracts 21, EGU 2019–4205.
Parkes, D, Evans, D J, Williamson, J P, and Williams, J D O. 2018. Estimating available salt volume for potential CAES development: a case study using the Northwich Halite of the Cheshire Basin. Journal of Energy Science, Vol. 18, 50–61.
Related news

Funding awarded to UK/Canadian critical mineral research projects
08/07/2025
BGS is part of a groundbreaking science partnership aiming to improve critical minerals mining and supply chains.

Goldilocks zones: ‘geological super regions’ set to drive annual £40 billion investment in jobs and economic growth
10/06/2025
Eight UK regions identified as ‘just right’ in terms of geological conditions to drive the country’s net zero energy ambitions.

New interactive map viewer reveals growing capacity and rare earth element content of UK wind farms
16/05/2025
BGS’s new tool highlights the development of wind energy installations over time, along with their magnet and rare earth content.

Latest mineral production statistics for 2019 to 2023 released
28/04/2025
More than 70 mineral commodities have been captured in the newly published volume of World Mineral Production.
Making the case for underground hydrogen storage in the UK
03/04/2025
A new BGS science briefing note focuses on the potential of hydrogen storage to support the UK energy transition.

Exploring Scotland’s hidden energy potential with geology and geophysics: fieldwork in the Cairngorms
31/03/2025
BUFI student Innes Campbell discusses his research on Scotland’s radiothermal granites and how a fieldtrip with BGS helped further explore the subject.

Future projections for mineral demand highlight vulnerabilities in UK supply chain
13/03/2025
New Government-commissioned studies reveal that the UK may require as much as 40 per cent of the global lithium supply to meet anticipated demand by 2030.

Could underground disposal of carbon dioxide help to reduce India’s emissions?
28/01/2025
BGS geologists have partnered with research institutes in India to explore the potential for carbon capture and storage, with an emphasis on storage.

Prehistoric power: 250-million-year-old rocks could contain secrets to net zero future
05/12/2024
BGS has completed a comprehensive scan of Mercia Mudstone rocks that could hold geological secrets of the UK’s past and provide a boost for net zero.

The challenge of assessing the UK economy’s dependence on mineral supply
28/11/2024
Critical, essential, or just plain important? Dr Gavin Mudd, director of the Critical Minerals Intelligence Centre, discusses the findings and new methodology featured in the 2024 UK Criticality Assessment.
UK 2024 Criticality Assessment published
28/11/2024
The latest UK Criticality Assessment, produced by the UK Critical Minerals Intelligence Centre, shows that growing diversification brings an increasing vulnerability in terms of disruption to supply.

Criticality Assessment 2024 launch webinar
Event on 28/11/2024
A special live webinar with the team from the Critical Minerals Intelligence Centre to accompany the launch the latest UK Criticality Assessment. A recording is now available to watch online
You may also be interested in

Geothermal energy
Investigating geothermal energy — energy stored in the form of heat beneath the surface of the solid Earth.

Carbon capture and storage
Studying carbon dioxide storage as a recognised European centre of excellence in a number of research areas.