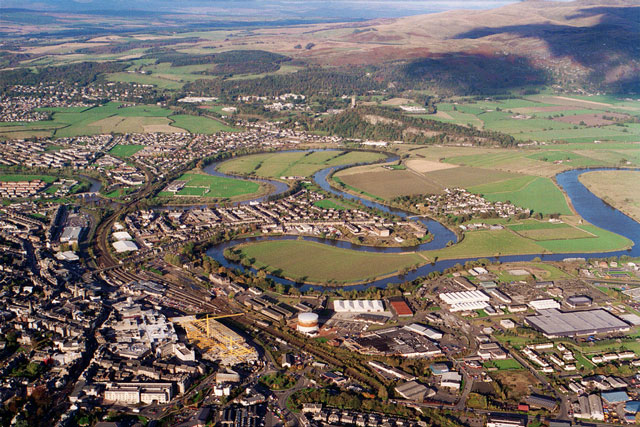
Landforms are features on the Earth’s surface that make up the terrain, such as mountains, valleys, plains or plateaux. They also include coastal features, such as peninsulas or bays, and underwater features, such as ocean basins and mid-ocean ridges.

A BGS scientist collecting samples from Mt Holt, Antactica, for cosmogenic dating to help determine the rate of thinning of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet since the Last Glacial Maximum. BGS © UKRI.
Landforms are categorised by their physical attributes, such as:
- elevation
- orientation
- slope
- rock exposure
- soil type
They can also be organised by the processes that create them. Here are some examples of landforms and the different ways they can be created.
Sand dunes
A sand dune is an ‘aeolian’ landform; this means it is formed by the wind.

Sand dunes at Prestatyn, North Wales. BGS © UKRI.
Peninsulas
A peninsula is a type of coastal landform. It is a piece of land almost entirely surrounded by water but connected to the mainland on one side.

Charleshill Peninsula, Braefoot Bay, Fife. BGS © UKRI.
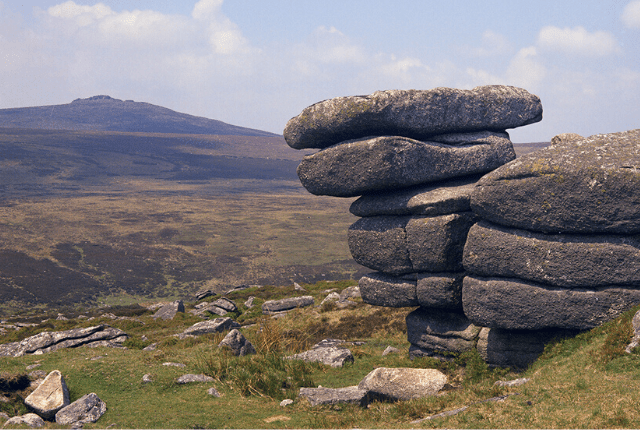
Buttes
A butte, an isolated hill with steep sides, is a type landform created by erosion and weathering.

Monitor and Merrimac Buttes, Utah, USA. Source: BGS © UKRI
Impact craters
An impact crater, a depression formed by a collision of a large object with the Earth’s surface, is a type of impact landform.
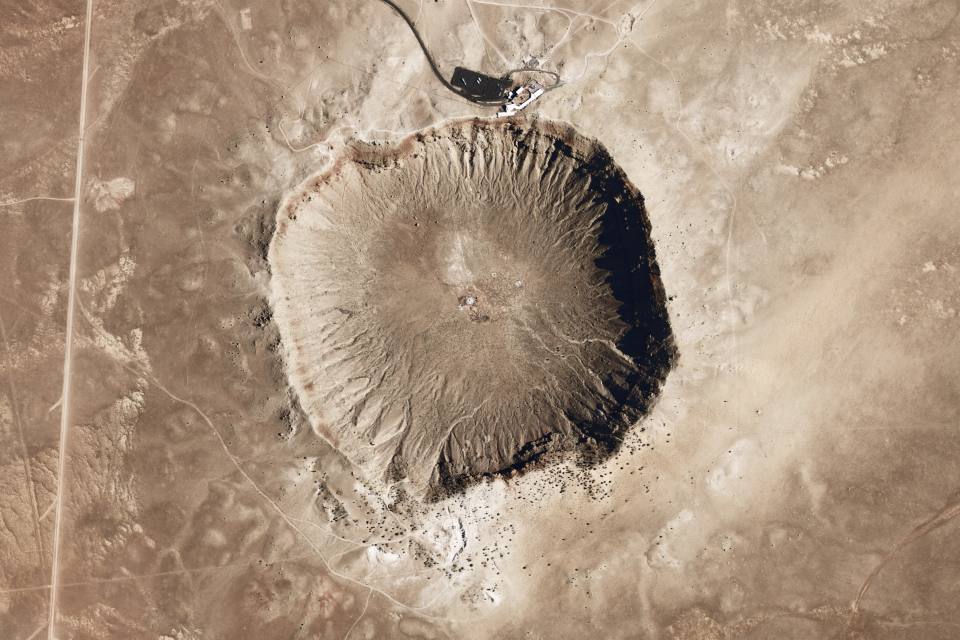

Meteor Crater, Arizona, USA. © NASA.
Valleys
A U-shaped valley is an example of a glacial landform, carved by slowly moving glaciers.
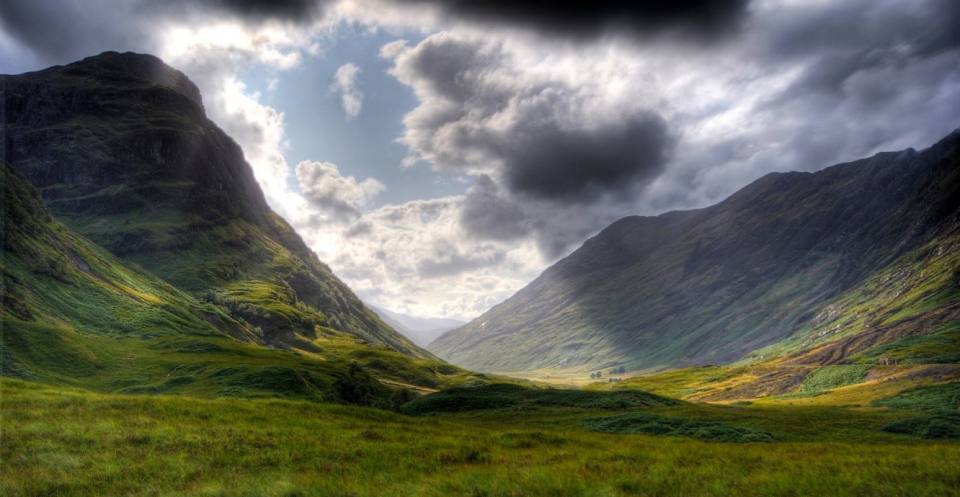

Glencoe, Scotland, is a U-shaped valley. © Gil Cavalcanti, Wikimedia Commons.
Ocean trenches
Deep oceanic trenches are a type of tectonic landform, formed where one tectonic plate is subducted beneath another.
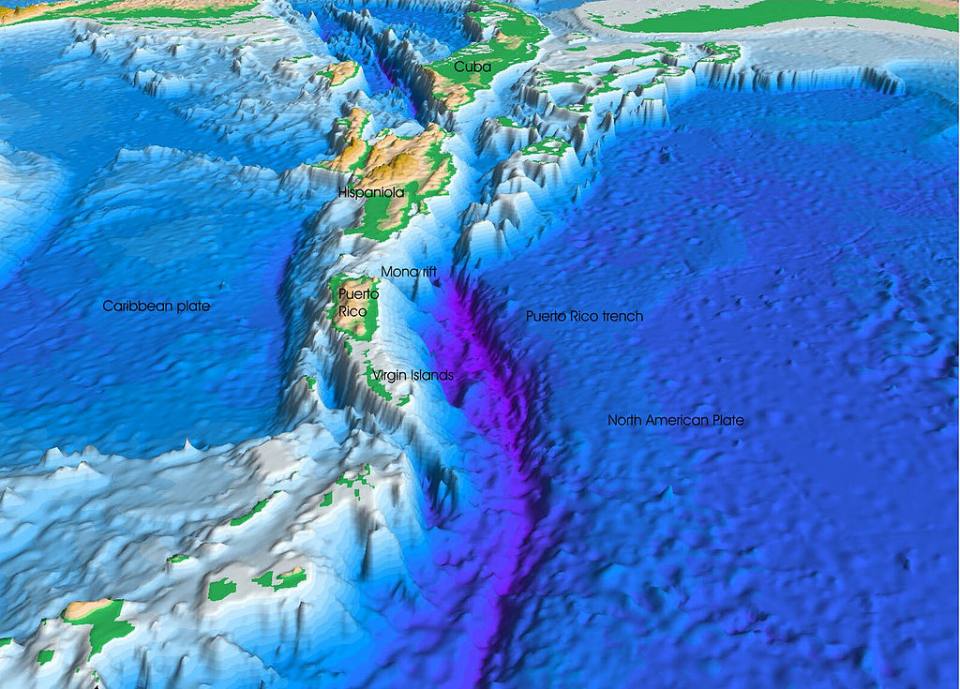
The Puerto Rico Trench to the east of the Caribbean. Credit: U.S. Geological Survey, Department of the Interior/USGS.
Volcanic cones
A volcanic cone is the most recognisable volcanic landform, built from the materials erupted from a volcanic vent.
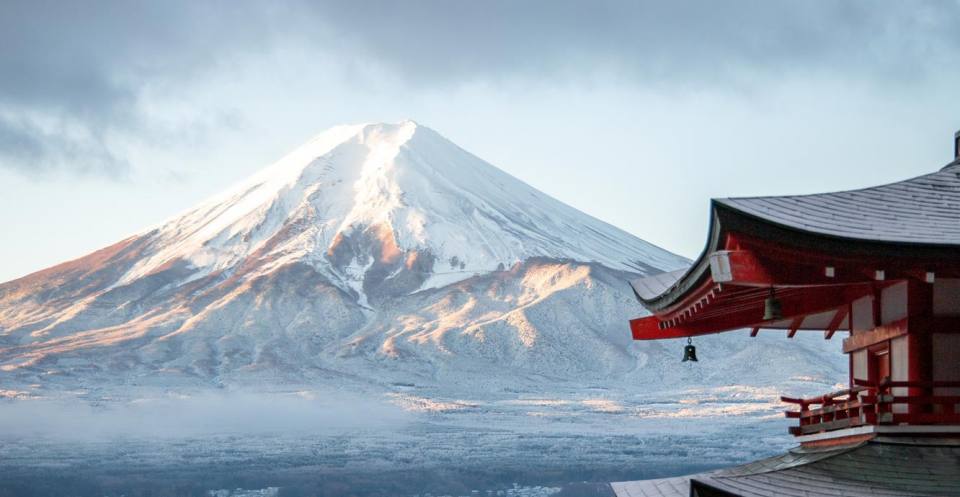

The volcanic cone of Mount Fuji, Japan. © Tomáš Malík / Pexels
You may also be interested in

Discovering Geology
Discovering Geology introduces a range of geoscience topics to school-age students and learners of all ages.

Geological processes
Planet Earth is dynamic with a surface that is always changing. Find out about the processes that cause these changes.
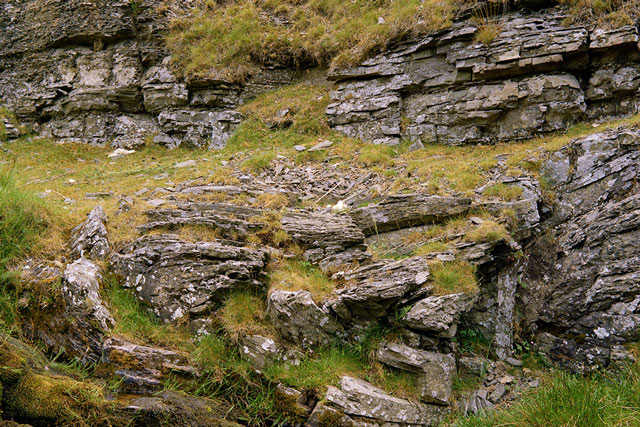

Weathering
Weathering is the wearing down or breaking of rocks while they are in place.

Deposition
Deposition is the laying down of sediment carried by wind, water, or ice.





