Mining hazard data (not including coal) from BGS
Great Britain has over 250 000 documented mining sites and the underground voids resulting from past mining activity pose a possible hazard. Knowledge of the distribution of former mining areas will help us to plan for future development and ongoing maintenance.
17/05/2022 By BGS Press
Mine workings range from small-scale, local workings, such as graphite mining in the Lake District or jet mined in Whitby, to large-scale, national resources such as salt extraction in Cheshire. While modern mine workings meet stringent safety standards, many old, disused or abandoned sites are gradually decaying, leaving a long-forgotten legacy that poses potential problems to infrastructure and property. It is therefore essential we have knowledge of the distribution of former mining areas, helping us to plan for future development and ongoing maintenance.
What is a mining hazard?
The voids resulting from past underground mining activity pose a possible hazard. Former underground workings, particularly where shallow, may collapse and cause surface settlement.
Mining hazards in Great Britain can take on various different forms, including surface impacts like ground instability, gradual subsidence, cover collapse and groundwater contamination. As our climate changes, new climate conditions may exacerbate ground conditions further, leading to more incidents of this nature.
Armed with knowledge about potential hazards, preventative steps can be put in place to alleviate the impact of the hazard on people and property. The cost of such prevention may be very low and is often many times lower than the repair bill following ground movement.
Mining hazard examples
- An old mining substructure at Burrow Lead Mine in Derbyshire decayed, leading to a tunnel collapse and propagation to the surface. In turn, this caused roadside subsidence in 2011, which disrupted infrastructure
- Ferniehill in Edinburgh has seen issues where movement in old limestone workings has caused property damage
- Former chalk workings opened up, causing potential risk to life, at Gillingham in Kent (2014) and St Albans, Hertfordshire (2018)
- Ten million gallons of contaminated water flowed out of old mine workings at Wheal Jane tin mine, Cornwall, in 1992. The workings became flooded and the groundwater contaminated with heavy metal pollution; when an underground structure failed, a sudden outrush occurred
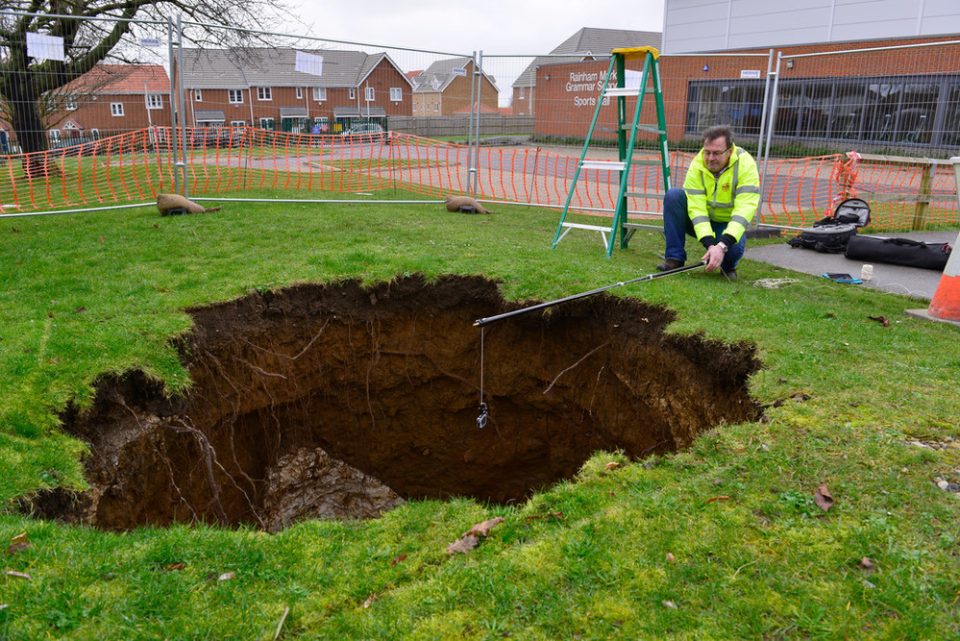

Denehole at Rainham Mark Grammar School, Gillingham, Kent (2014). Deneholes are medieval chalk extraction pits; characteristically they comprise a narrow shaft with a number of chambers radiating from the base. The depth of the features reflects the depth to the underlying chalk bedrock. The shaft width was commonly in the order of 2–3 m, widening out into galleries at depth. BGS © UKRI.
New research incorporated into our mining hazard data product
Currently. approximately two per cent of the land area of Great Britain is identified as having high susceptibility to mining hazard. The BGS Mining Hazard (not including coal) data product identifies areas affected by non-coal mining, providing a general assessment of hazard potential, thereby indicating areas at risk of possible subsidence associated with voids resulting from mine workings.
The newly released version of the BGS Mining Hazard data product also introduces a series of derived ‘zones of influence’ (ZOI) for evaporites (e.g. salt; gypsum; anhydrite), oil shales and building stone (e.g. limestone; sandstone; slate).
(Mining of coal is specifically excluded from this dataset. Enquiries on past coal mining should be directed to the Coal Authority.)
What is a zone of influence?
Zones of influence are areas indicating the potential surface extent that may be affected by underground workings. Calculations evaluate a number of criteria, including:
- seam thickness
- depth and dip of seam
- competence of roof and floor
- age of working
By integrating ZOIs into the product, a clearer picture of the surface area of legacy mining on property, people and pursuits can be established.
- Learn more about our mining hazard (not including coal) data
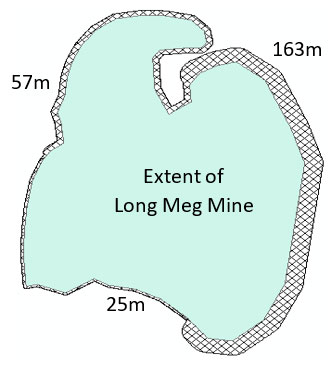
Case study: Long Meg Mine, Cumbria
- Worked for gypsum and anhydrite; approximately five million tonnes were extracted
- Mining was from horizontal adits and drifts driven from the side of the Eden Valley
- The mining method was pillar-and-stall, once underground
Try our open data option for free
BGS offers a generalised 1 km ‘hexgrid’ version of the data in ESRI shapefile format under the Open Government Licence to enable users to get a feel for our mining hazard (not including coal) data.
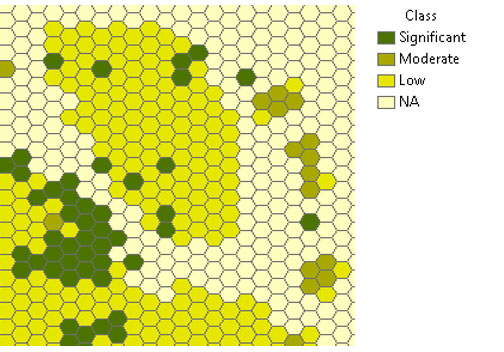
Mining hazard hexgrid example. BGS © UKRI.
Further information
For further information please contact digitaldata@bgs.ac.uk.
Relative topics
Related news

Funding awarded to UK/Canadian critical mineral research projects
08/07/2025
BGS is part of a groundbreaking science partnership aiming to improve critical minerals mining and supply chains.
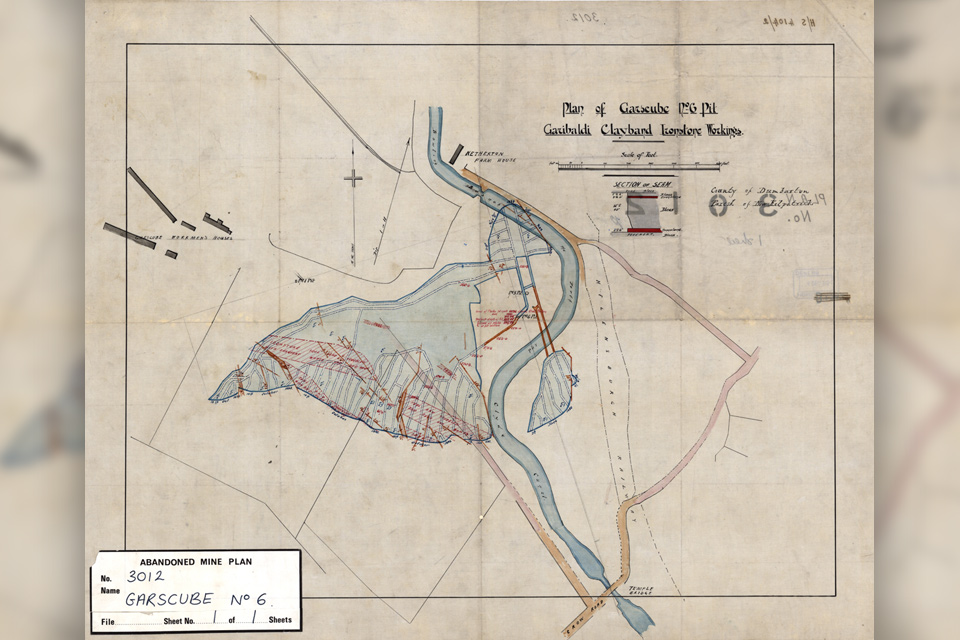
Release of over 500 Scottish abandoned-mine plans
24/06/2025
The historical plans cover non-coal mines that were abandoned pre-1980 and are available through BGS’s plans viewer.

New collaboration aims to improve availability of real-time hazard impact data
19/06/2025
BGS has signed a memorandum of understanding with FloodTags to collaborate on the use of large language models to improve real-time monitoring of geological hazards and their impacts.

Modern pesticides found in UK rivers could pose risk to aquatic life
17/06/2025
New research shows that modern pesticides used in agriculture and veterinary medicines have been found for the first time in English rivers.

Goldilocks zones: ‘geological super regions’ set to drive annual £40 billion investment in jobs and economic growth
10/06/2025
Eight UK regions identified as ‘just right’ in terms of geological conditions to drive the country’s net zero energy ambitions.
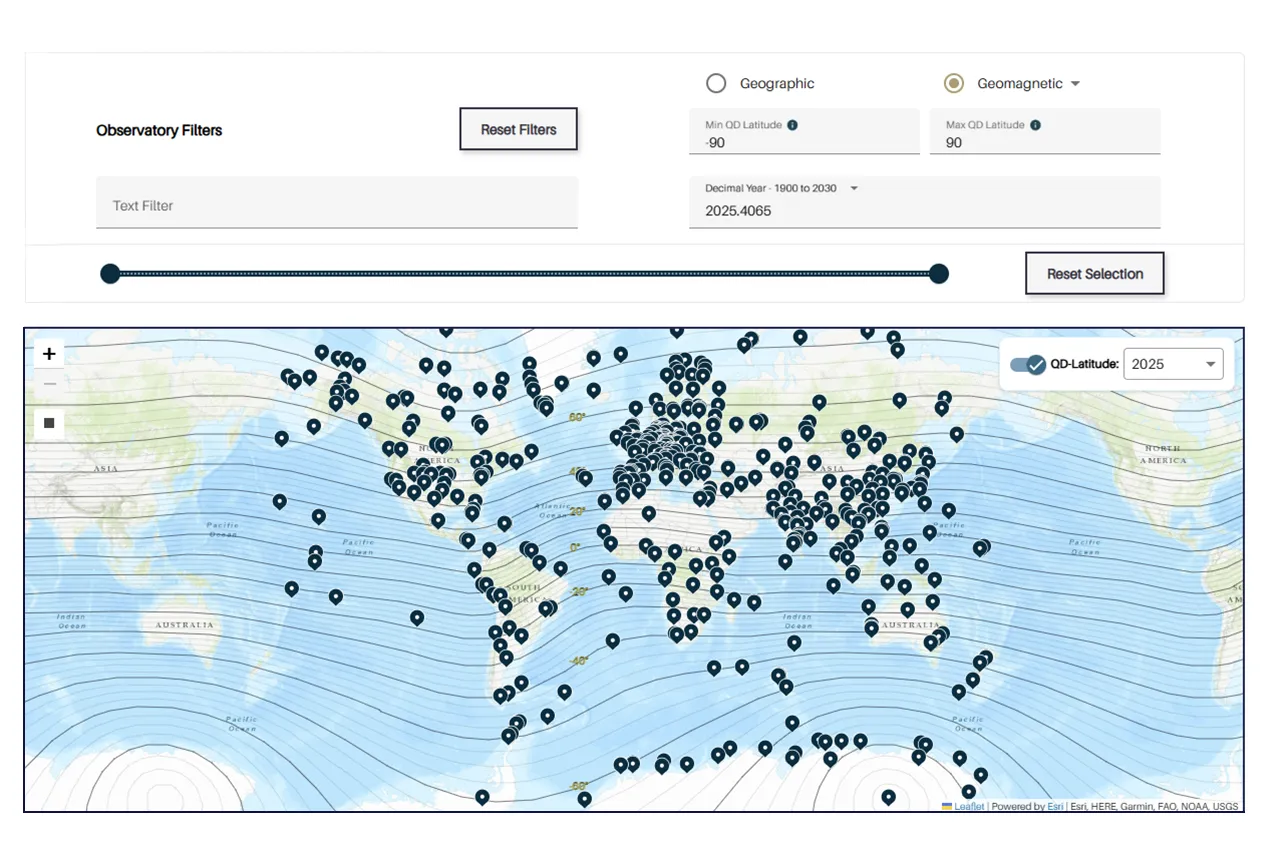
Upgraded web portal improves access to geomagnetism data
02/06/2025
BGS’s geomagnetism portal, which holds data for over 570 observatories across the world, has received a significant update.
BGS digital geology maps: we want your feedback
29/05/2025
BGS is asking for user feedback on its digital geological map datasets to improve data content and delivery.

What is the impact of drought on temperate soils?
22/05/2025
A new BGS review pulls together key information on the impact of drought on temperate soils and the further research needed to fully understand it.

UK Minerals Yearbook 2024 released
21/05/2025
The annual publication provides essential information about the production, consumption and trade of UK minerals up to 2024.

BGS scientists join international expedition off the coast of New England
20/05/2025
Latest IODP research project investigates freshened water under the ocean floor.

New interactive map viewer reveals growing capacity and rare earth element content of UK wind farms
16/05/2025
BGS’s new tool highlights the development of wind energy installations over time, along with their magnet and rare earth content.

UKRI announce new Chair of the BGS Board
01/05/2025
Prof Paul Monks CB will step into the role later this year.