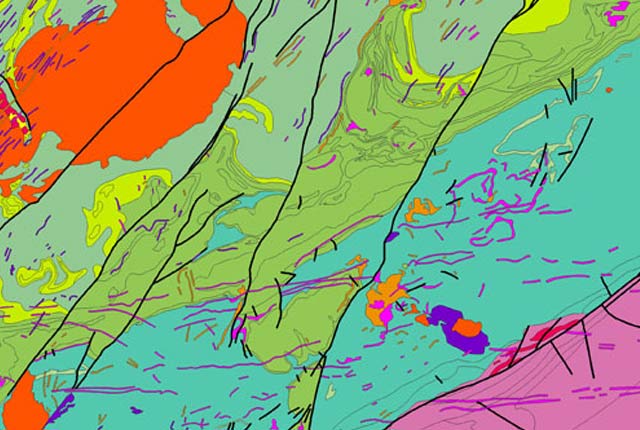
Key information
Scale:
1:50 000Coverage:
Great BritainAvailability:
LicensedFormat:
GIS polygon data (ESRI, MapInfo, others available by request)Price:
£0.34 per km2. Subject to number of users, licence fee and data preparation fee.
Uses:
Local-level useGet data
Free access
Our free data is available under the Open Government Licence. Please acknowledge reproduced BGS materials.
Sample mapsSupporting documents
Shrinking and swelling of the ground (often reported as subsidence) is one of the most damaging geohazards in Britain today, costing the economy an estimated £3 billion over the past decade.
Many soils contain clay minerals that absorb water when wet (making them swell) and lose water as they dry (making them shrink). Many of us see this in our gardens when the ground becomes cracked during the summer, yet becomes ‘heavy’ in the winter. This ‘shrink–swell’ behaviour is controlled by the type and amount of clay in the soil and by seasonal changes, related to rainfall and local drainage, in the soil moisture content .


In this video we can see the effect of a clay swelling due to water ingress and the subsequent damage to the house above, known as ‘heave’. BGS © UKRI.
Ground moisture variations may be related to a number of factors, including:
- weather variations
- vegetation, particularly growth or removal of trees
- human activity
Variation in ground moisture can cause ground movement, particularly in the upper two metres of the ground, which may affect building foundations, pipes or services.
The potential for shrink–swell to be a hazard has been assessed using 1:50 000-scale digital maps of superficial and bedrock deposits. These have been combined with information from the BGS superficial thickness dataset, scientific and engineering reports. The detailed digital data illustrated in the map is available as attributed vector polygons, as raster grids and in spreadsheet format.
You may also be interested in
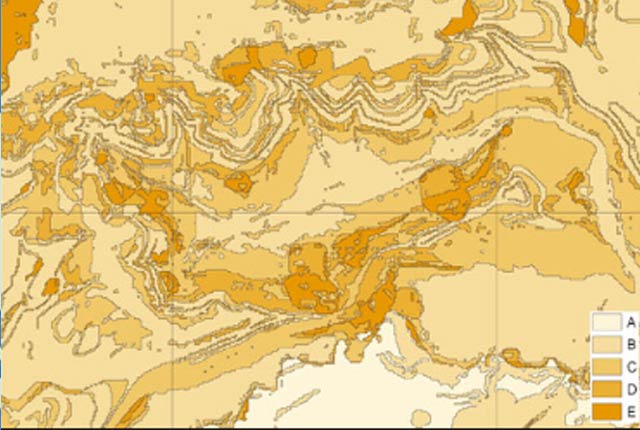
BGS GeoSure
The BGS GeoSure datasets identify areas of potential hazard and, therefore, potential natural ground movement, in Great Britain.

Shrink–swell: property hazard information
If active clay shrinkage/swelling appears to be affecting your property, inform your insurance company, mortgage lender or landlord.
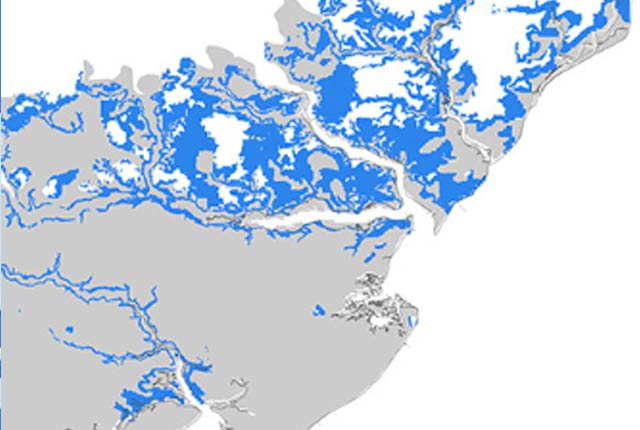
BGS GeoSure: shrink–swell subsurface
This is a single data layer that identifies areas of potential shrink–swell hazard that are underneath another solid formation and therefore hidden from the surface.
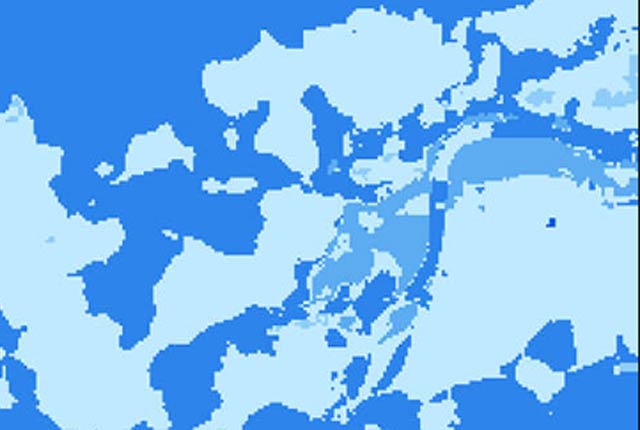
BGS GeoSure: shrink–swell 3D for London and Thames Valley
The shrink–swell 3D data is a regional hazard susceptibility map that identifies areas of potential shrink–swell hazard in 3D at intervals down to 20 m in the London and Thames Valley area.