Key information
Scale:
1:50 000Coverage:
Great BritainAvailability:
LicensedFormat:
GIS polygon data (ESRI, MapInfo, others available by request)Price:
All six themes: £0.88 per km2
Shrink-swell: £0.34 per km2
Landslides including Debris Flow Model: £0.34 per km2
Soluble rocks: £0.17 per km2
Collapsible deposits: £0.06 per km2
Compressible ground: £0.22 per km2
Running sands: £0.22 per km2
Subject to number of users, licence fee and data preparation fee.
Uses:
Local-level useGet data
Free access
Our free data is available under the Open Government Licence. Please acknowledge reproduced BGS materials.
Sample mapsSupporting documents
The BGS GeoSure national datasets provide geological information about potential ground movement or subsidence that can help planning decisions. This data also provides essential information for the BGS Natural Ground Stability GeoReport.
BGS GeoSure data gives you information about:
- collapsible deposits:
- compressible ground:
- landslides:
- running sand
- shrink–swell:
- soluble rocks:
- debris flow susceptibility model:
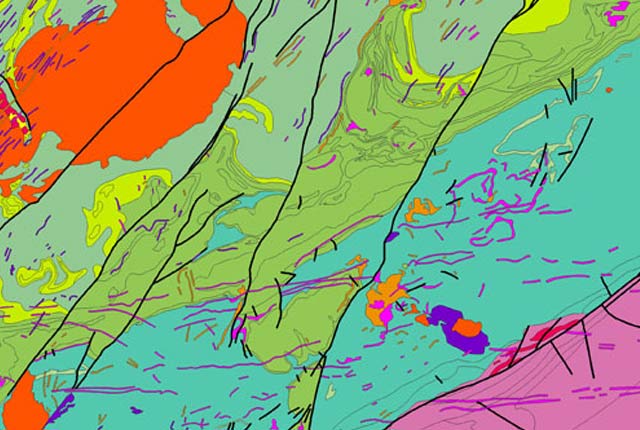
BGS GeoSure sample map. BGS © UKRI.
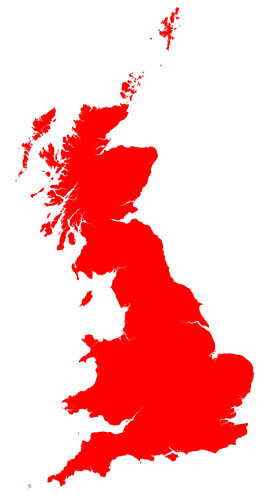
BGS GeoSure UK coverage. BGS © UKRI – Contains OS data © Crown copyright 2020.
Download GeoSure sample data
You may also be interested in

BGS GeoSure: collapsible deposits
The potential for collapsible ground to be a hazard has been assessed using 1:50 000 scale digital maps of superficial deposits.

BGS GeoSure: compressible ground
The potential for compressible ground to be a hazard has been assessed using 1:50 000-scale digital maps of superficial and bedrock deposits.
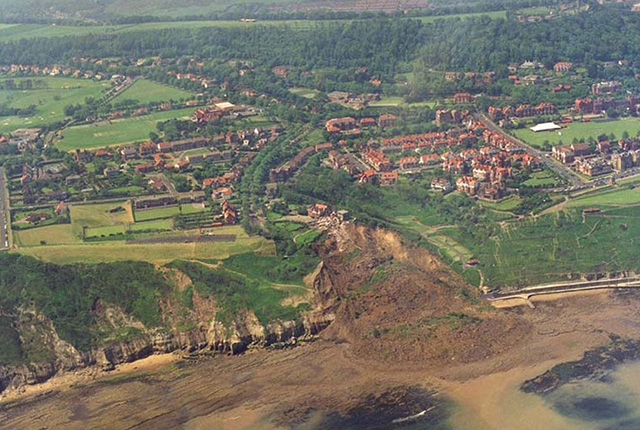

BGS GeoSure: landslides
The potential for landsliding (slope instability) to be a hazard has been assessed using 1:50 000 scale digital maps of superficial and bedrock deposits. These have been combined with information from the BGS National Landslide Database and scientific and engineering reports.

BGS GeoSure: running sand
The potential for running sand to be a hazard has been assessed using 1:50 000-scale digital maps of superficial and bedrock deposits.

BGS GeoSure: shrink–swell
Many soils contain clay minerals that absorb water when wet (making them swell), and lose water as they dry (making them shrink). Many of us see this in our gardens when the ground becomes cracked during the summer, yet becomes ‘heavy’ in the winter.

BGS GeoSure: soluble rocks
Ground dissolution occurs when water passing through soluble rocks produces underground cavities and cave systems. These cavities reduce support to the ground above and can cause localised collapse of the overlying rocks and deposits.