Six ways to prepare your home for climate change related subsidence
Subsidence caused by shrinking and swelling of the ground can lead to financial loss. How can you mitigate against it?
19/05/2021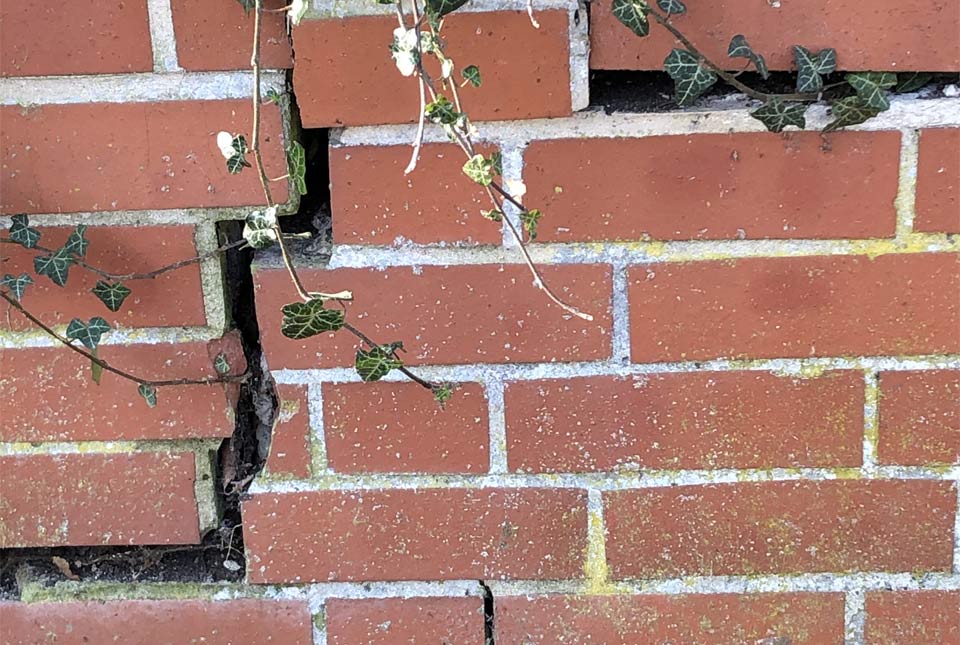
Shrinking and swelling of the ground, often reported as subsidence, is already one of the most damaging geohazards in Britain, costing the economy an estimated £3 billion over the past decade. Subsidence may lead to financial loss for anyone involved in the ownership or management of property, including developers, homeowners or local government. These costs could include increased insurance premiums, depressed house prices and in some cases, engineering works to stabilise land or property.
How does climate change affect shrink–swell?
Many soils contain clay minerals that absorb water when wet (making them swell) and lose water as they dry (making them shrink). Dry weather and high temperatures have been found to be a major factor in the emergence of subsidence in clay soils. However, every summer can be completely different to the last; summer 2018 had the hottest, driest June for years whereas summer 2019 had one of the wettest Junes on record. Looking to the future, warmer, drier summers and increases in annual temperature and rainfall variability are suggested for the UK. What is considered a heat wave today may be the norm in the 2050s and cool in the 2080s!
What does the data show?
The rock formations most susceptible to shrink–swell behaviour are found mainly in the south-east of Britain. Here, many of the clay formations are too young to have been changed into stronger mudrocks, leaving them still able to absorb and lose moisture. Superficial deposits, such as alluvium, peat and laminated clays, can also be susceptible to soil subsidence and heave (e.g. in the Vale of York and the Cheshire Basin).
Clay rocks elsewhere in the country are older, hardened by burial deep in the Earth and less able to absorb water. In some areas (e.g. around The Wash and under the Lancashire Plain) they are deeply buried beneath other soils that are not susceptible to shrink–swell behaviour.
By combining the BGS GeoSure dataset and applying the UK Climate Projections (UKCP) scenarios for rainfall and temperature changes in the UK for the next century, maps have been produced for Great Britain showing areas with varying vulnerability to shrink–swell and thus subsidence in the future due to climate change. The maps show that areas with clay soils that shrink and swell with changes in moisture are going to become increasingly susceptible in the coming century and beyond.
The BGS GeoClimate UKCP18 datasets show an obvious increase in the amount of shrink–swell potential across the south-east of England, due to climate change. Of particular interest are the clay-rich formations that are currently of low-moderate susceptibility. Buildings on these rock types might not have the robust foundations suitable to withstand subsidence hazard.
How might this affect my home?
As reported by the Association of British Insurers (2018), the effects of subsidence in a property can usually be seen as cracks in walls that:
- are more than 3 mm thick
- run diagonally across the wall
- are wider from top to bottom
- are visible from inside and outside
- occur near doors and windows
- cause rippling in wallpaper
What can I do about it?
If you are in an area that shows an increased susceptibility under future climate conditions, you should get specialist advice from a suitably qualified expert such as a structural surveyor, geotechnical engineer or chartered engineering geologist.
If active clay shrinkage or swelling is not affecting your property but the area has shrink–swell clay potential, this should be taken into account before planning new buildings, extensions or modifications, or any other changes in land use.
- Take specialist advice before starting major building work.
- Consider the effect of laying impermeable drives, paths or hardstanding on the rainfall reaching the soil below and changing its moisture content.
- Seek expert advice before planting trees near to a house. The safe planting distance will depend on the tree species, the type of foundation and soil composition.
- Ensure foundations of new constructions or extensions are designed for any shrinkable clay soil conditions that could be present or forecast under future climate conditions.
- Do not plant potentially large trees next to a house.
- Do not remove mature trees that pre-date the construction of the house before taking advice. Tree management by crown reduction or thinning may be better than removal because it will maintain a stable soil moisture profile.
About the author

Kathryn Lee
Geologist and BGS Informatics product portfolio manager
Relative topics
Latest blogs

AI and Earth observation: BGS visits the European Space Agency
02/07/2025
The newest artificial intelligence for earth science: how ESA and NASA are using AI to understand our planet.

Geology sans frontières
24/04/2025
Geology doesn’t stop at international borders, so BGS is working with neighbouring geological surveys and research institutes to solve common problems with the geology they share.

Celebrating 20 years of virtual reality innovation at BGS
08/04/2025
Twenty years after its installation, BGS Visualisation Systems lead Bruce Napier reflects on our cutting-edge virtual reality suite and looks forward to new possibilities.

Exploring Scotland’s hidden energy potential with geology and geophysics: fieldwork in the Cairngorms
31/03/2025
BUFI student Innes Campbell discusses his research on Scotland’s radiothermal granites and how a fieldtrip with BGS helped further explore the subject.

Could underground disposal of carbon dioxide help to reduce India’s emissions?
28/01/2025
BGS geologists have partnered with research institutes in India to explore the potential for carbon capture and storage, with an emphasis on storage.

Carbon and oxygen isotope analysis of carbonates and the development of new reference materials
18/12/2024
Dr Charlotte Hipkiss and Kotryna Savickaite explore the importance of standard analysis when testing carbon and oxygen samples.

Studying oxygen isotopes in sediments from Rutland Water Nature Reserve
20/11/2024
Chris Bengt visited Rutland Water as part of a project to determine human impact and environmental change in lake sediments.

Celebrating 25 years of technical excellence at the BGS Inorganic Geochemistry Facility
08/11/2024
The ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation is evidence of technical excellence and reliability, and a mark of quality assurance.

Electromagnetic geophysics in Japan: a conference experience
23/10/2024
Juliane Huebert took in the fascinating sights of Beppu, Japan, while at a geophysics conference that uses electromagnetic fields to look deep into the Earth and beyond.

Exploring the role of stable isotope geochemistry in nuclear forensics
09/10/2024
Paulina Baranowska introduces her PhD research investigating the use of oxygen isotopes as a nuclear forensic signature.

BGS collaborates with Icelandic colleagues to assess windfarm suitability
03/10/2024
Iceland’s offshore geology, geomorphology and climate present all the elements required for renewable energy resources.

Mining sand sustainably in The Gambia
17/09/2024
BGS geologists Tom Bide and Clive Mitchell travelled to The Gambia as part of our ongoing work aiming to reduce the impact of sand mining.
You may also be interested in
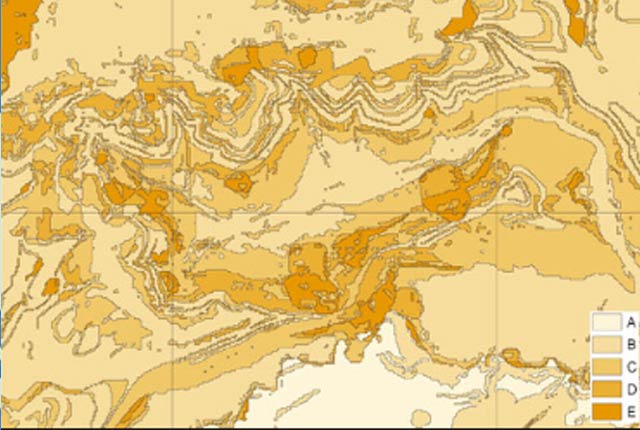
BGS GeoSure
The BGS GeoSure datasets identify areas of potential hazard and, therefore, potential natural ground movement, in Great Britain.
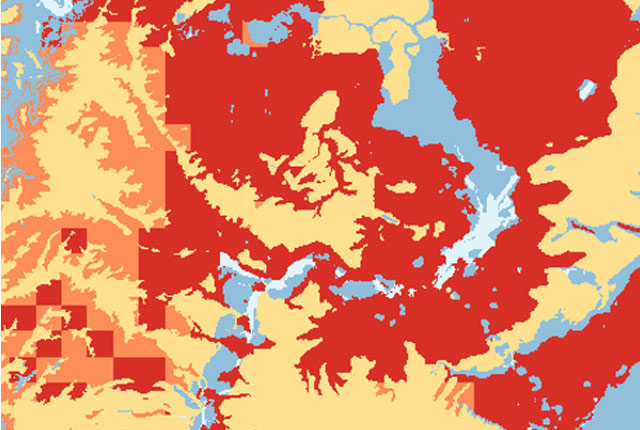
GeoClimate UKCP09 and UKCP18
BGS has developed a suite of products, including maps and data, which show potential change in subsidence due to UKCP climate change scenarios

Swelling and shrinking soils
Shrink–swell, or expansive, soils are one of the most costly and widespread geological hazards globally, with costs estimated to run into several billion pounds annually.


