Moving stones: faults, slopes and sediments
Fractured rock along faults affects sediment movement on slopes with implications for the design of infrastructure.
12/01/2024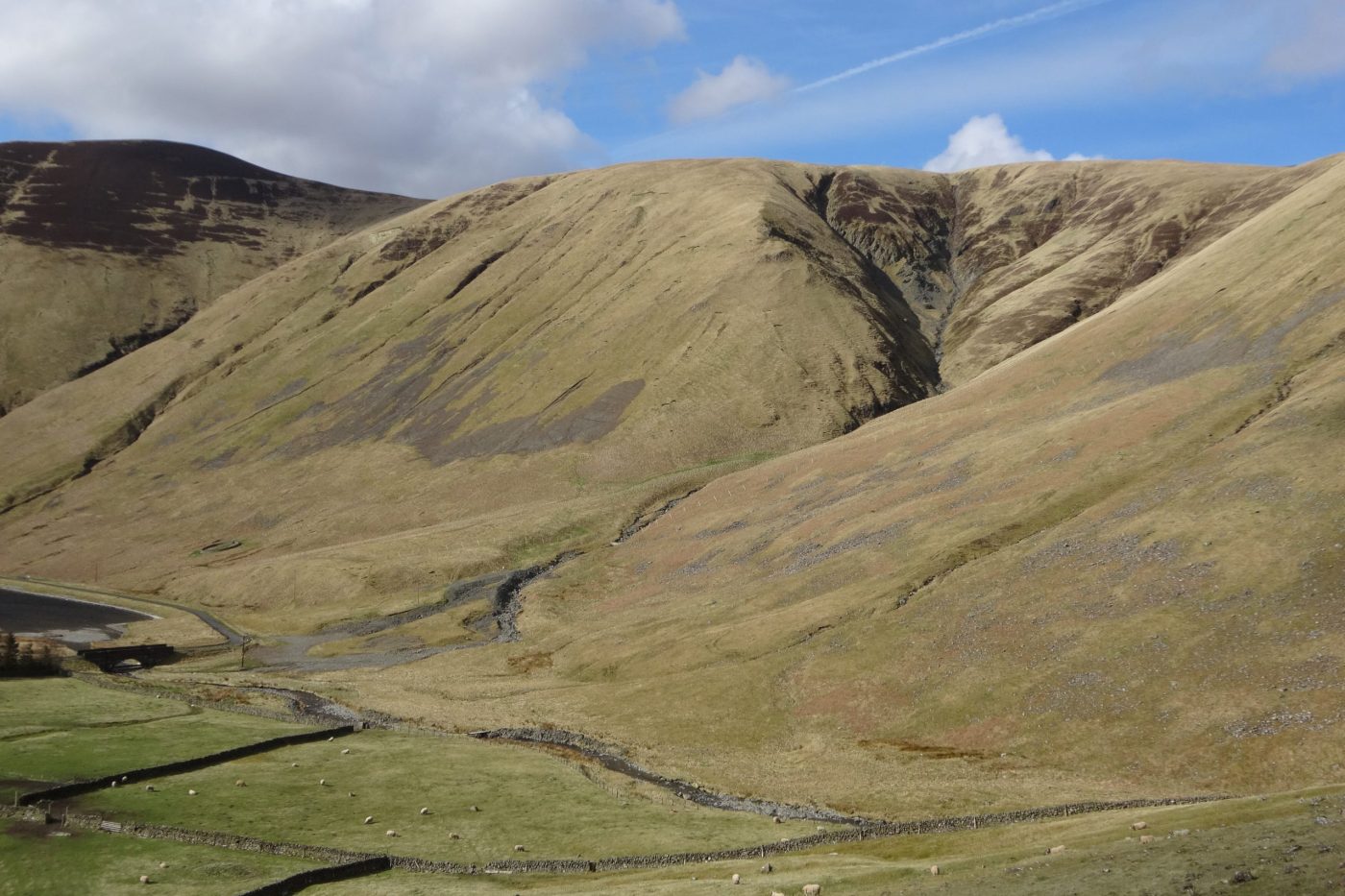
Deposits on upland hillslopes are formed by a range of processes like debris flows, rock falls, slope wash and soil creep. The movement of sediment by these processes occurs over days, years or decades and can have far-reaching implications. Over geological timescales it can influence the relief of mountain ranges, but on human timescales it is also a potential geohazard affecting roads, bridges, and reservoirs, and a key factor in managing river habitats and water quality.
Faults are important geological features, even when they are no longer active tectonic structures. They are often associated with highly fractured ‘damage zones’ that are relatively weak, providing abundant source material for slope processes and acting as conduits for groundwater flow. We investigated how faults control the types of deposits that are produced on upland slopes by weathering and erosion, and how the direction of a fault’s intersection with a hillside influences the way sediment is mobilised and transported to rivers and reservoirs.
Study area: Tweedsmuir Hills, Scotland
In the Tweedsmuir Hills, in Scotland’s Southern Uplands, the rolling upland landscape is bisected by a series of brittle faults comprising highly fractured damage zones in the otherwise hard, metasedimentary rocks. The study area, at the head of the Talla Reservoir, provides a prime opportunity to compare the geomorphological imprint of slope-oblique faults that traverse across a slope at a low angle (roughly perpendicular to the slope direction) with that of slope-parallel faults (roughly parallel to the slope direction).
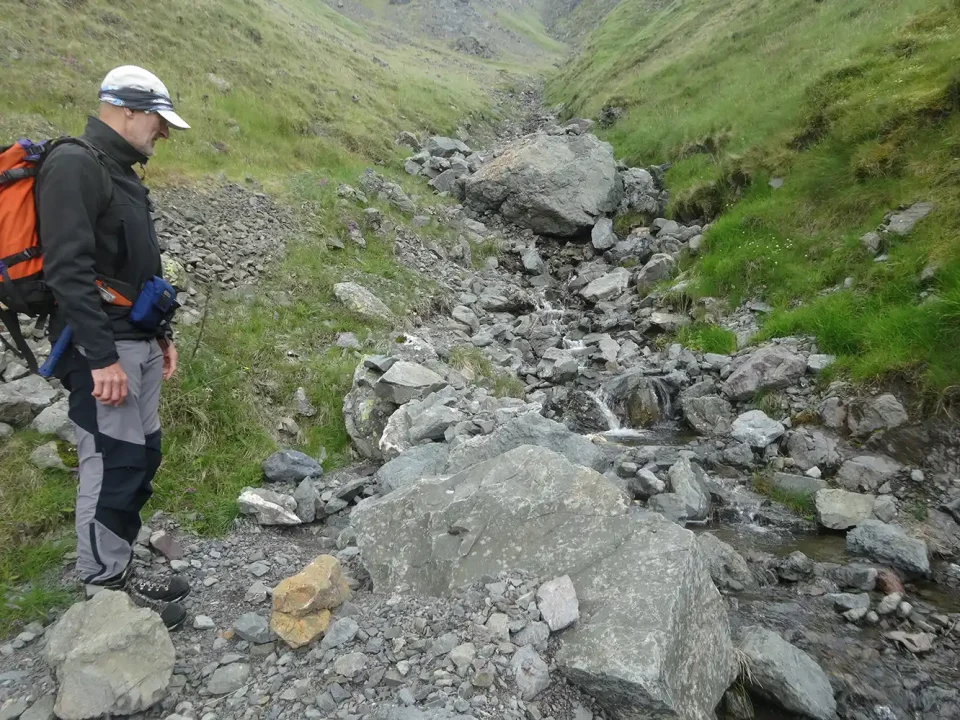

Examining debris flow deposits in the Codleteth Burn, Talla, Southern Uplands. BGS © UKRI.
Faults that traverse slopes at low angles are associated with enhanced regolith (weathered bedrock) production, which forms a more-or less continuous spread of colluvial deposits (loose sediments that move downslope under gravity) across the slope. Sediment transfer to the valley floor is limited because topographical breaks associated with the slope-crossing structures disrupt gully systems and inhibit sediment ‘flow’ downslope.
By contrast, slope-parallel faults are associated with more focused erosion along fault zones, giving rise to a deep and well-connected gully system. The alignment of slope and fault directions creates positive feedback, which enhances downslope erosion and transport to the valley floor. This feedback has resulted in approximately 20 times more rock being eroded per metre of fault length than in the slope-oblique fault system.
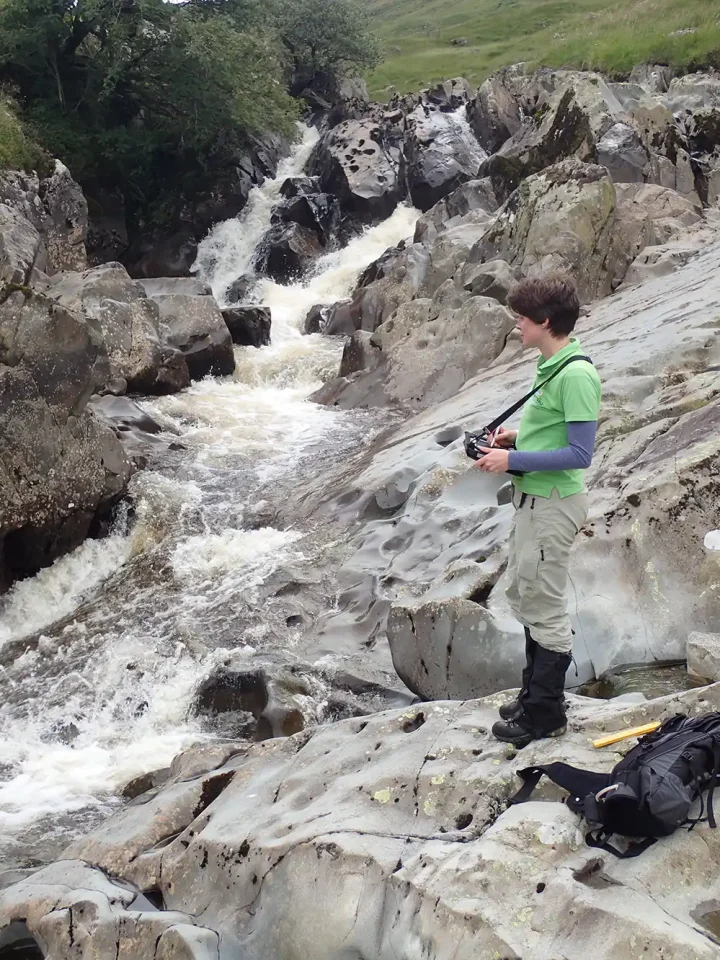

Observing the sparsely fractured (unfaulted) wacke sandstone in the bed of the Gameshope Burn. BGS © UKRI.
Influence on infrastructure design
The movement of sediment is associated with geohazards such as debris flows and rock falls as well as slope instability that can damage upland transport, energy and water infrastructure. However, sediment movement on slopes is a natural part of how our landscape behaves and interrupting or altering the flow of sediment from hillslopes into streams can affect river environments and habitats, and influence water quality in reservoirs.
Understanding the mechanisms of active slope processes and their distributions within the landscape is necessary to ensure we can design effective approaches for managing both the impact of moving sediment on our built infrastructure, and the effect this infrastructure has on our rivers and reservoirs.
Another way of looking at it is that every slope has its own story. Our work in Talla demonstrates how geomorphological mapping and quantitative field analysis can be used to help understand the dynamics of slope systems, adding to our knowledge of the ‘language’ of slopes. By understanding how their past geological history influences their present processes, we can learn to better ‘read’ slopes and ensure we develop more positive relationships with them.
About the authors

Dr Katie Whitbread
Survey geologist
Relative topics
Reference
Whitbread, K, Thomas, C, and Finlayson, A. 2023. The influence of bedrock faulting and fracturing on sediment availability and Quaternary slope systems, Talla, Southern Uplands, Scotland, UK. Proceedings of Geologists’ Association, in press. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pgeola.2023.11.003
Latest news

Funding awarded to UK/Canadian critical mineral research projects
08/07/2025
BGS is part of a groundbreaking science partnership aiming to improve critical minerals mining and supply chains.
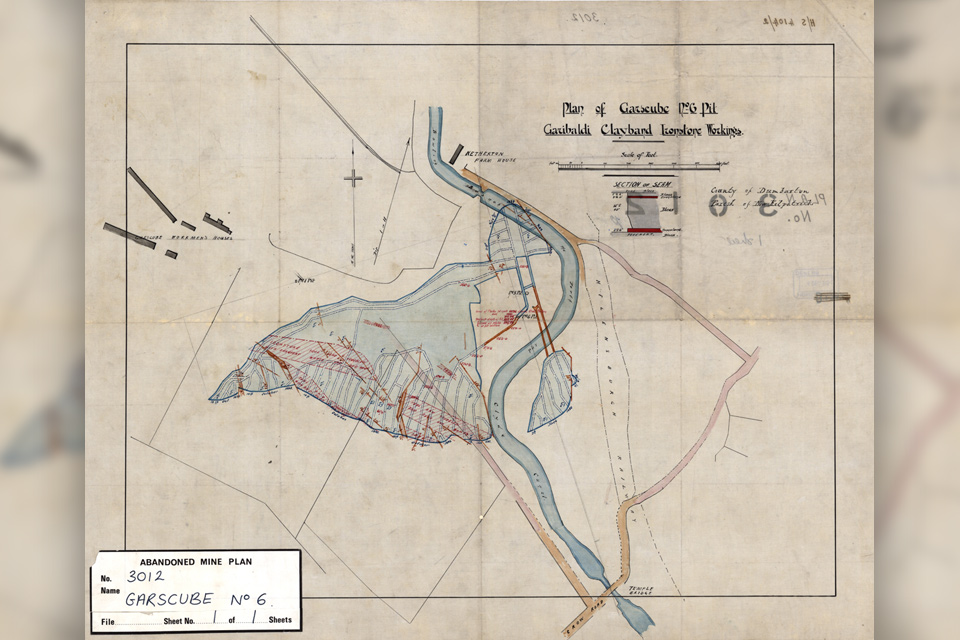
Release of over 500 Scottish abandoned-mine plans
24/06/2025
The historical plans cover non-coal mines that were abandoned pre-1980 and are available through BGS’s plans viewer.

New collaboration aims to improve availability of real-time hazard impact data
19/06/2025
BGS has signed a memorandum of understanding with FloodTags to collaborate on the use of large language models to improve real-time monitoring of geological hazards and their impacts.

Modern pesticides found in UK rivers could pose risk to aquatic life
17/06/2025
New research shows that modern pesticides used in agriculture and veterinary medicines have been found for the first time in English rivers.

Goldilocks zones: ‘geological super regions’ set to drive annual £40 billion investment in jobs and economic growth
10/06/2025
Eight UK regions identified as ‘just right’ in terms of geological conditions to drive the country’s net zero energy ambitions.
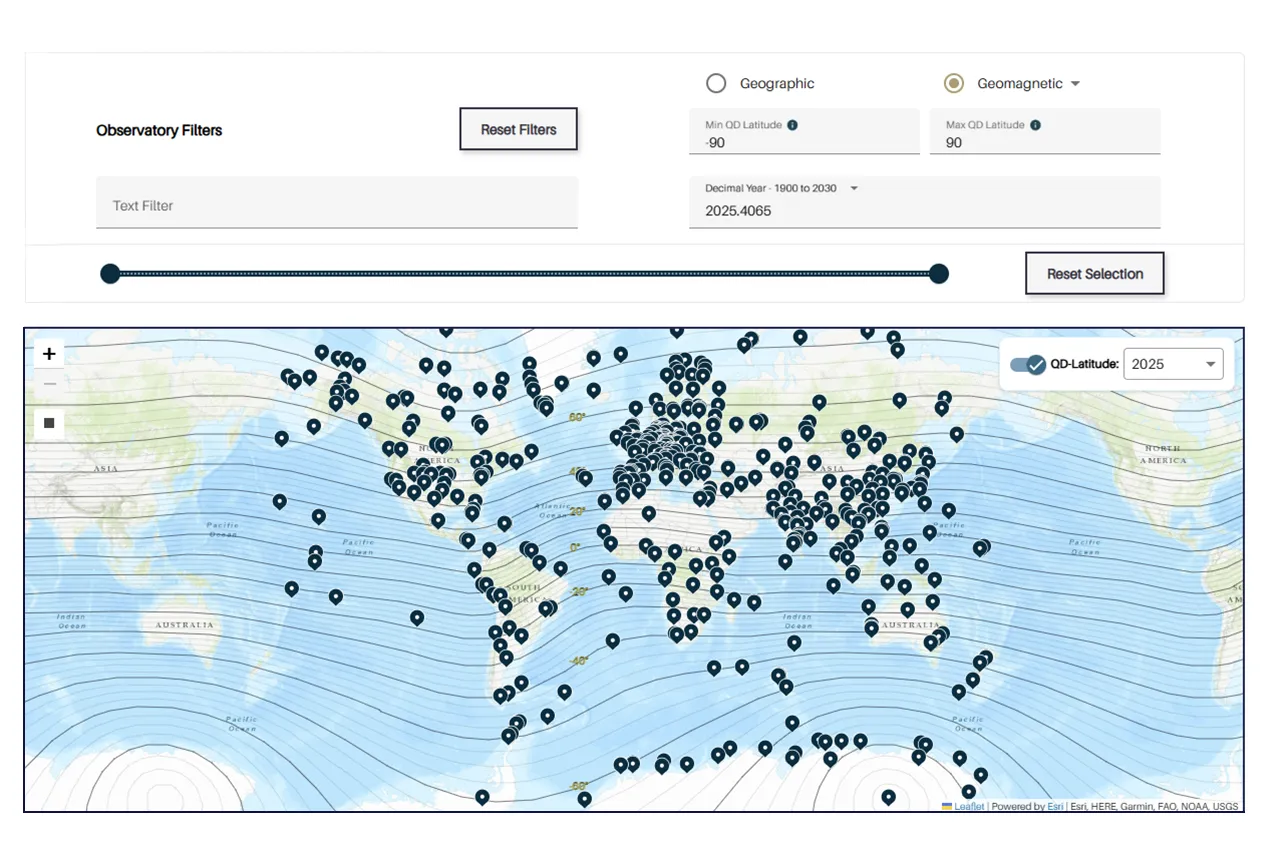
Upgraded web portal improves access to geomagnetism data
02/06/2025
BGS’s geomagnetism portal, which holds data for over 570 observatories across the world, has received a significant update.
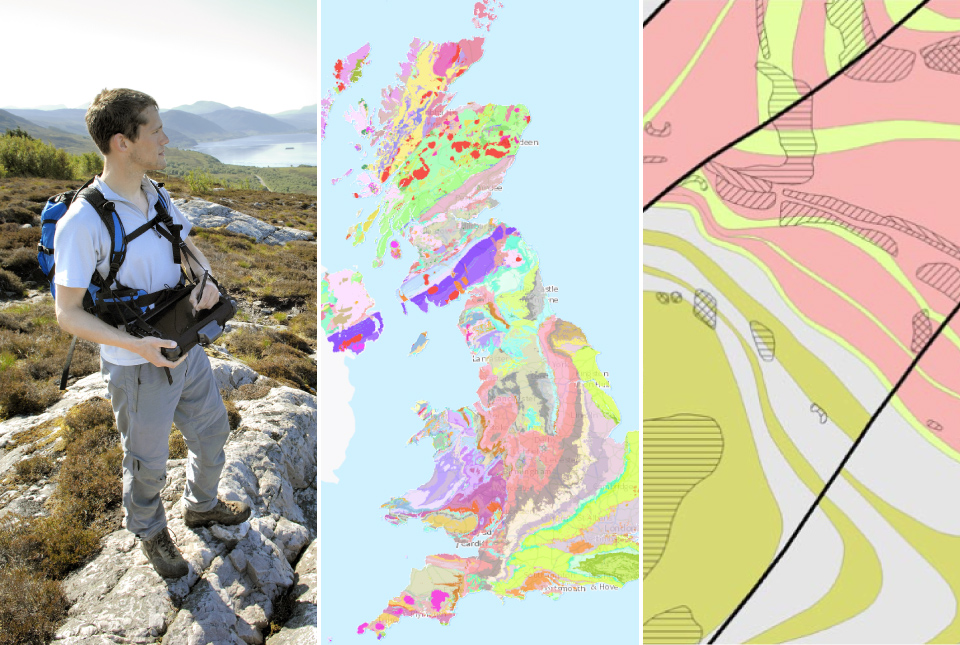
BGS digital geology maps: we want your feedback
29/05/2025
BGS is asking for user feedback on its digital geological map datasets to improve data content and delivery.

What is the impact of drought on temperate soils?
22/05/2025
A new BGS review pulls together key information on the impact of drought on temperate soils and the further research needed to fully understand it.

UK Minerals Yearbook 2024 released
21/05/2025
The annual publication provides essential information about the production, consumption and trade of UK minerals up to 2024.

BGS scientists join international expedition off the coast of New England
20/05/2025
Latest IODP research project investigates freshened water under the ocean floor.

New interactive map viewer reveals growing capacity and rare earth element content of UK wind farms
16/05/2025
BGS’s new tool highlights the development of wind energy installations over time, along with their magnet and rare earth content.

UKRI announce new Chair of the BGS Board
01/05/2025
Prof Paul Monks CB will step into the role later this year.


