The Kahraman Maraş earthquake sequence, Turkey/Syria, 2023
Two large earthquakes occurred within hours of each other on 6 February 2023.
14/02/2023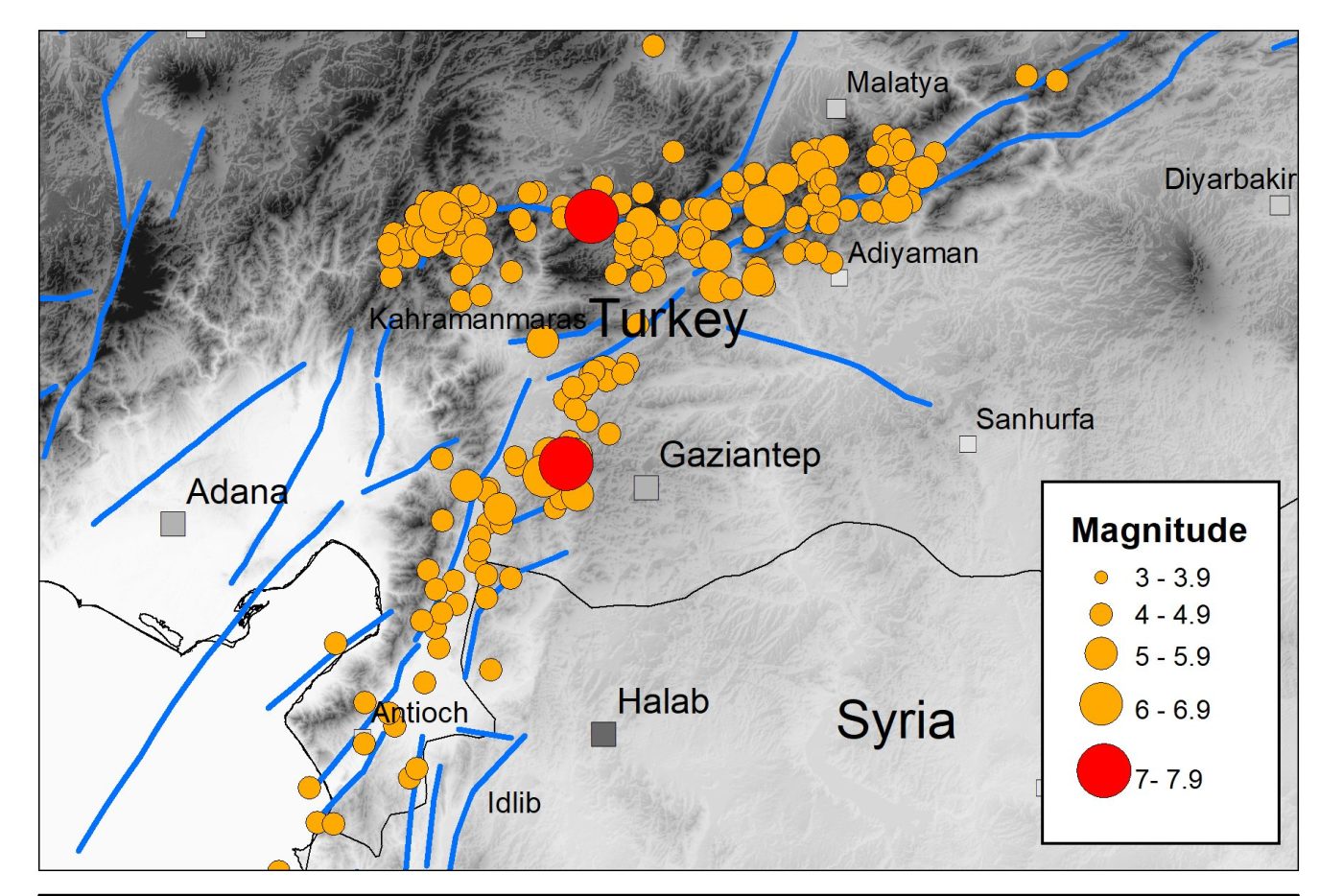
The devastating Kahraman Maraş earthquake sequence has caused widespread destruction and terrible loss of life across a large part of southern Turkey and northern Syria, with the collapse of thousands of buildings in populated areas throughout the region.
The earthquake sequence
The sequence started with a magnitude 7.8 earthquake at 01:17 UTC on 6 February 2023, rupturing a 200 km section of the north-east to south-west trending fault system that forms the boundary between the Anatolian and the Arabian tectonic plates. These plates are moving horizontally relative to each other at a speed of around 13 mm per year.
The earthquake took about 30 seconds to reach a maximum slip of around 3 m and resulted in intense shaking that lasted over a minute. Recorded ground accelerations at some sites close to the fault rupture exceeded 1.0 g. A few hours later, a magnitude 7.5 event occurred on a nearby branch of the fault system that trends east to west. This caused further strong ground shaking and destruction.
Previous seismicity in the area
The magnitude 7.8 earthquake was approximately 2.5 times bigger than the magnitude 7.4 Izmit earthquake in Turkey in 1999, which killed over 17 000 people, and was the same size as the magnitude 7.8 Erzincan earthquake in north-east Turkey in 1939, which killed over 32 000 people. The latter is considered the deadliest natural disaster in Turkey in the 20th century.
Although the earthquake risk in this part of southern Turkey was generally considered to be less than along the well-known Northern Anatolian Fault in northern Turkey, large and damaging earthquakes have struck here in the past. The city of Aleppo in northern Syria has been destroyed by several earthquakes in the last thousand years, including an earthquake in 1822 with over 20 000 fatalities.
The continuing hazard
Aftershocks are expected to cause moderate to severe ground shaking over a 300 to 500 km region for months to come. Some of these earthquakes may be several hundred kilometres away from other aftershocks and may be large enough to cause further damage, particularly to buildings that have already been weakened.
There have already been several aftershocks with a magnitude larger than 6.0. Our current understanding of the statistics of the aftershock process suggests that there may be several tens of earthquakes of this size or greater.
Over a period of months to years, the frequency of triggered seismicity (aftershocks) will reduce, with earthquake activity gradually returning to previous levels. Until then, earthquake hazard and risk in the region will remain heightened. This means that increased seismic hazard in the region where the two large earthquakes occurred is transient in nature, whilst longer seismic hazard estimates continue to be relevant.
Earthquake cascades
It is well established that large earthquakes can trigger seismicity on other nearby faults as the Earth’s Crust adjusts to the sudden change in stress. Both the permanent deformation caused by the initial earthquake and the passage of seismic waves through the Earth can trigger these subsequent earthquakes.
Other recent examples of this triggering process include the Kumamoto sequence on the island of Kyushu, Japan, in 2016, when a magnitude 6.5 earthquake was followed almost a day later by a magnitude 7.3 event. In Europe, the magnitude 6.0 Amatrice earthquake that occurred in Italy in 2016 was followed by the magnitude 6.5 Norcia earthquake two months later.
Although such cascading sequences of large-magnitude earthquake within short periods of time are relatively rare, investigation and analysis of these may promote a new understanding of the earthquake process.
Further information
About the authors

Dr Brian Baptie
Seismologist
Dr Margarita Segou
Earthquake seismologist
Relative topics
Related news
Call for new members and Chair to join the NERC facilities steering committees
25/02/2026
New members are needed to join the committees over the next four years.

Your views wanted – developing a ‘Geothermal energy subsurface data portfolio’
24/02/2026
BGS is aiming to support the growth of the sector by providing the best-available, location-specific geothermal and ground source heat information as an accessible product or service.
Map of BGS BritPits showing the distribution of worked mineral commodities across the country
18/02/2026
BGS’s data scientists have generated a summary map of the most commonly extracted mineral commodities by local authority area, demonstrating the diverse nature of British mineral resources.

Funding awarded to map the stocks and flows of technology metals in everyday electronic devices
12/02/2026
A new BGS project has been awarded Circular Electricals funding from Material Focus to investigate the use of technology metals in everyday electrical items.

New UK/Chile partnership prioritises sustainable practices around critical raw materials
09/02/2026
BGS and Chile’s Servicio Nacional de Geología y Minería have signed a bilateral scientific partnership to support research into critical raw materials and sustainable practices.

Extensive freshened water confirmed beneath the ocean floor off the coast of New England for the first time
09/02/2026
BGS is part of the international team that has discovered the first detailed evidence of long-suspected, hidden, freshwater aquifers.

Funding secured to help mitigate ground risk in UK construction sector
05/02/2026
The BGS Common Ground project has been awarded new funding to help unlock the value of ground investigation data.

Can sandstones under the North Sea unlock the UK’s carbon storage potential?
02/02/2026
For the UK to reach its ambitious target of storing 170 million tonnes of carbon dioxide per year by 2050, it will need to look beyond the current well-studied geographical areas.
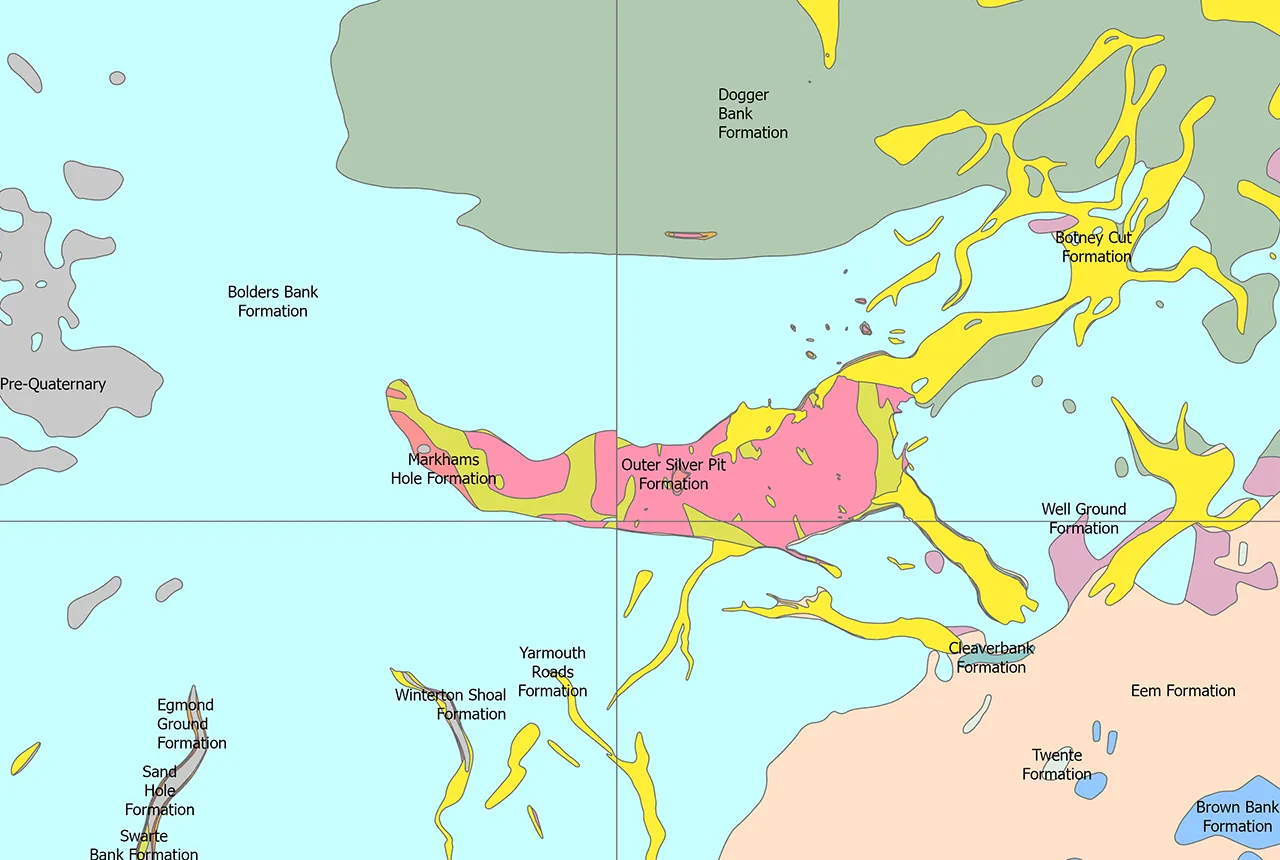
Quaternary UK offshore data digitised for the first time
21/01/2026
The offshore wind industry will be boosted by the digitisation of a dataset showing the Quaternary geology at the seabed and the UK’s shallow subsurface.
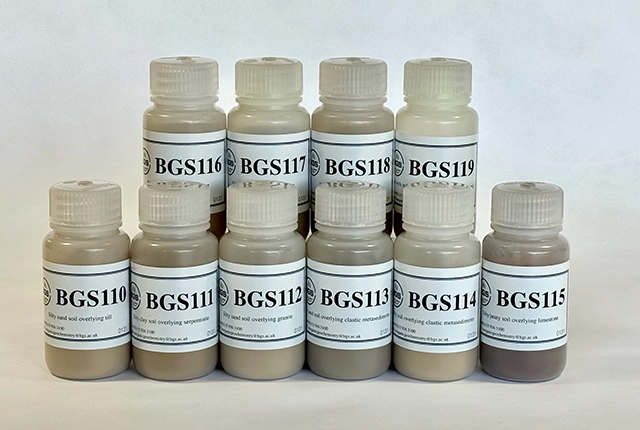

Suite of ten new soil reference materials released
02/01/2026
BGS has a longstanding track record of producing high-quality reference materials and has released ten new soil reference materials.
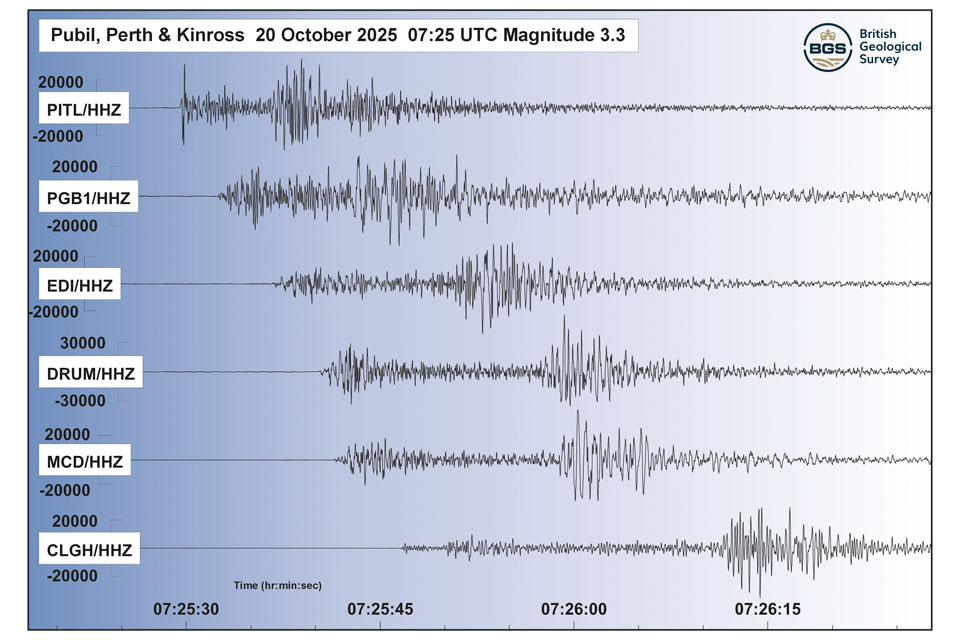
Perth and Kinross tops the UK’s earthquake activity charts for 2025
29/12/2025
Seismologists at BGS have published data on the number of seismic events over the past 12 months with over 300 earthquakes recorded.

BGS awarded funding to support Malaysia’s climate resilience plan
17/12/2025
The project, funded by the Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office, will focus on minimising economic and social impacts from rainfall-induced landslides.


