BGS partners with Arcadis in £70 000 research programme to support brownfield development
New research will explore microorganisms with the potential to breakdown hazardous chemicals in the environment.
15/10/2020 By BGS Press
New research will explore microorganisms with the potential to breakdown hazardous chemicals in the environment.
The British Geological Survey (BGS) will take part in a novel £70 000 research programme to support the clean up of brownfield sites using natural biological processes, in partnership with Arcadis, a leading global design and consultancy organisation for natural and built assets.
The research will be used to understand and evaluate how microorganisms naturally present in contaminated soil and groundwater can be used to bioremediate the chemical 1,4-dioxane, an emerging contaminant that is increasingly detected in groundwater and recognised as a potential risk to human health and the environment around the world.
The project is being funded by the Environmental Biotechnology Network (EBNet), with a contribution from Arcadis, and is expected to take around twelve months to complete.
We need to better understand the wide range of legacy chemicals present in post-industrial brownfield land. Many of these emerging contaminants have either previously not been looked for or detected, but they are hazardous to people and to the environment.
The more we understand them, the better we can make decisions about how to remove them from post-industrial land to make sites safe and suitable for redevelopment.
BGS microbiologist Simon Gregory.
Reported health problems from short-term exposure to 1,4-dioxane include breathing problems, vertigo, drowsiness, headaches and skin irritation. Long-term exposure can lead to kidney and liver damage, and can even be fatal.
Due to its high solubility and low degradability under some conditions, 1,4-dioxane can be a challenge to remove from soil and groundwater. However, it is known that it can be degraded by soil microorganisms possessing some types of monooxygenase enzymes, a family of enzymes that can help to breakdown a wide range of chemicals including many organic pollutants.
Dr Monica Heintz, a geoscientist at Arcadis specialising in natural attenuation and bioremediation, said: ‘While biodegradation of 1,4-dioxane has been demonstrated, the microorganisms responsible for this process remain under-characterised. This research will increase our understanding of microorganisms responsible for 1,4-dioxane biodegradation and will lead to genetic surveys that can be used to assess biodegradation of 1,4-Ddoxane at sites around the world.’
BGS and Arcadis will gather information using a range of DNA-based techniques to quantify and explore the diversity of organisms that produce monooxygenase enzymes in contaminated sites and understand which enzymes are most effective at biodegradation.
This approach to characterising natural attenuation mechanisms will allow confidence in the ability of microorganisms to detoxify 1,4-dioxane and provide a sustainable, cost-effective management solution for brownfield stakeholders.
Dr Ian Ross, Senior Technical Director at Arcadis UK.
Relative topics
For further information please contact:
Call: +44 (0)7790 607 010.
(Please do not text this number. We accept calls or email only.)
Email: bgspress@bgs.ac.uk
Notes
- A brownfield site is an area that has been used before and is typically disused or derelict Such sites are usually abandoned areas in towns and cities that have been used previously for industrial and commercial purposes.
- Historical industrial processes often produced harmful byproducts, residues and wastes that were poorly managed. The chemicals contained in these legacy materials can threaten human health and the environment.
- Examples of land uses highly likely to have resulted in contamination include chemical works, landfill sites and textile mills.
- Funding for the project is being awarded by the Environmental Biotechnology Network (EBNet), one of 6 Phase II networks in industrial biotechnology and bioenergy funded primarily by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) with additional funding from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC).
British Geological Survey
The British Geological Survey (BGS) is a world-leading applied geoscience research centre that is part of UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) and affiliated to the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC). BGS core science provides objective and authoritative geoscientific data, information and knowledge to inform UK Government on the opportunities and challenges of the subsurface. It undertakes national and public good research to understand earth and environmental processes in the UK and globally. Please see www.bgs.ac.uk
Arcadis
Arcadis is the leading global design and consultancy firm for natural and built assets. Applying our deep market sector insights and collective design, consultancy, engineering, project and management services, we work in partnership with our clients to deliver exceptional and sustainable outcomes throughout the lifecycle of their natural and built assets. We are 28 000 people, active in over 70 countries, that generate €3.5 billion in revenues. We support UN-Habitat with knowledge and expertise to improve the quality of life in rapidly growing cities around the world. Please see www.arcadis.com/en/global/
Related news

Funding awarded to UK/Canadian critical mineral research projects
08/07/2025
BGS is part of a groundbreaking science partnership aiming to improve critical minerals mining and supply chains.
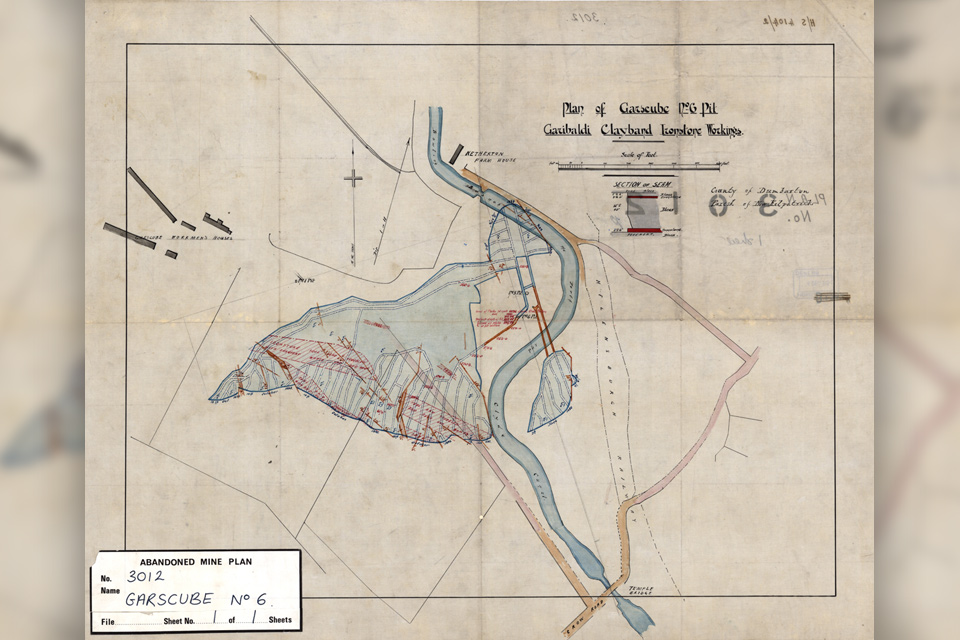
Release of over 500 Scottish abandoned-mine plans
24/06/2025
The historical plans cover non-coal mines that were abandoned pre-1980 and are available through BGS’s plans viewer.

New collaboration aims to improve availability of real-time hazard impact data
19/06/2025
BGS has signed a memorandum of understanding with FloodTags to collaborate on the use of large language models to improve real-time monitoring of geological hazards and their impacts.

Modern pesticides found in UK rivers could pose risk to aquatic life
17/06/2025
New research shows that modern pesticides used in agriculture and veterinary medicines have been found for the first time in English rivers.

Goldilocks zones: ‘geological super regions’ set to drive annual £40 billion investment in jobs and economic growth
10/06/2025
Eight UK regions identified as ‘just right’ in terms of geological conditions to drive the country’s net zero energy ambitions.
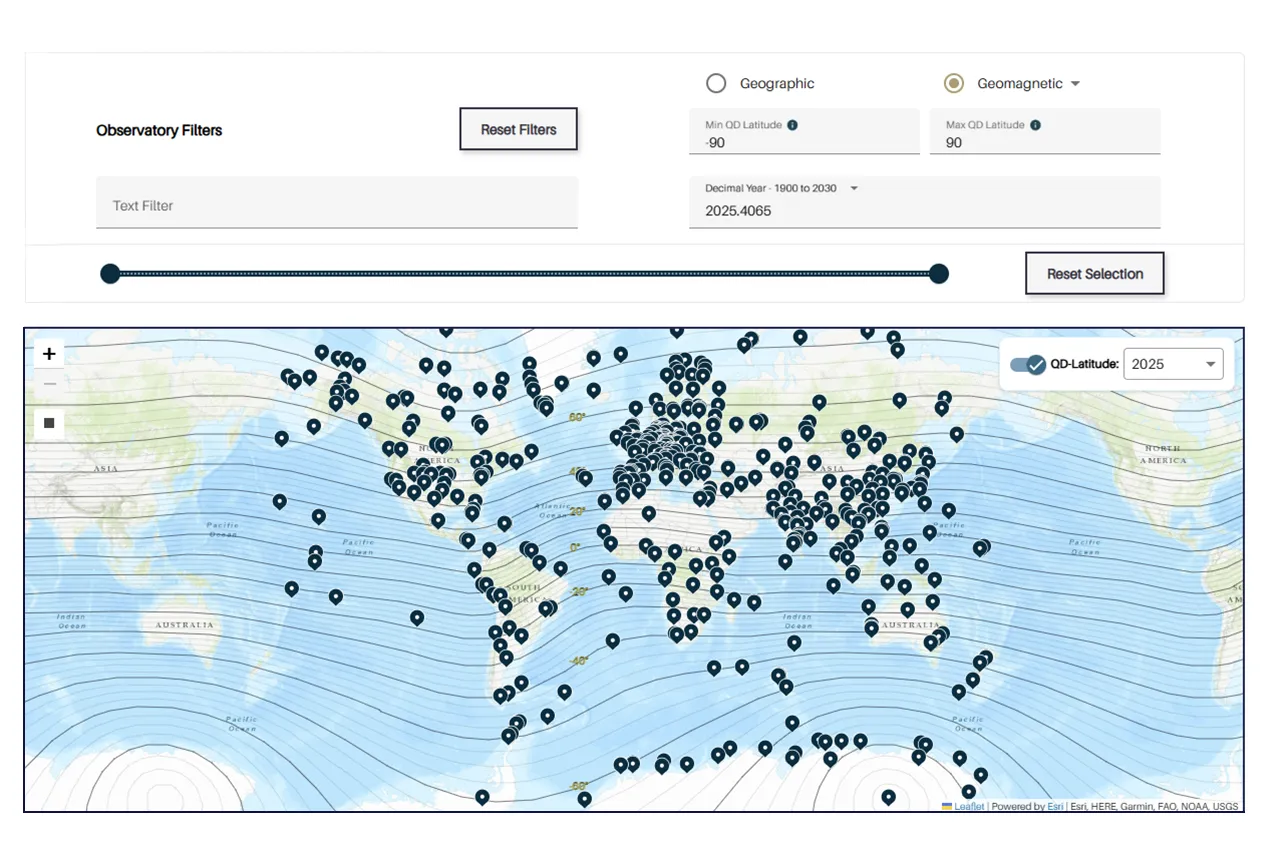
Upgraded web portal improves access to geomagnetism data
02/06/2025
BGS’s geomagnetism portal, which holds data for over 570 observatories across the world, has received a significant update.
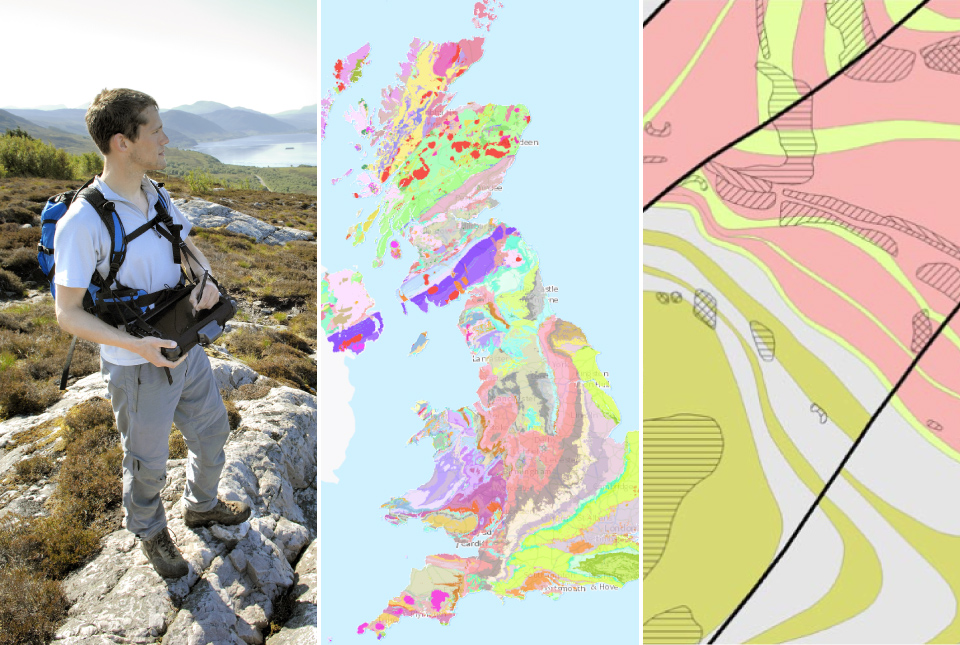
BGS digital geology maps: we want your feedback
29/05/2025
BGS is asking for user feedback on its digital geological map datasets to improve data content and delivery.

What is the impact of drought on temperate soils?
22/05/2025
A new BGS review pulls together key information on the impact of drought on temperate soils and the further research needed to fully understand it.

UK Minerals Yearbook 2024 released
21/05/2025
The annual publication provides essential information about the production, consumption and trade of UK minerals up to 2024.

BGS scientists join international expedition off the coast of New England
20/05/2025
Latest IODP research project investigates freshened water under the ocean floor.

New interactive map viewer reveals growing capacity and rare earth element content of UK wind farms
16/05/2025
BGS’s new tool highlights the development of wind energy installations over time, along with their magnet and rare earth content.

UKRI announce new Chair of the BGS Board
01/05/2025
Prof Paul Monks CB will step into the role later this year.



