UK’s geomagnetic blind spots tackled with new observatories
Three new geomagnetic observatories have been installed across the UK to fill in the country’s 'blind spots' and tackle the risk posed by space weather.
28/07/2022 By BGS Press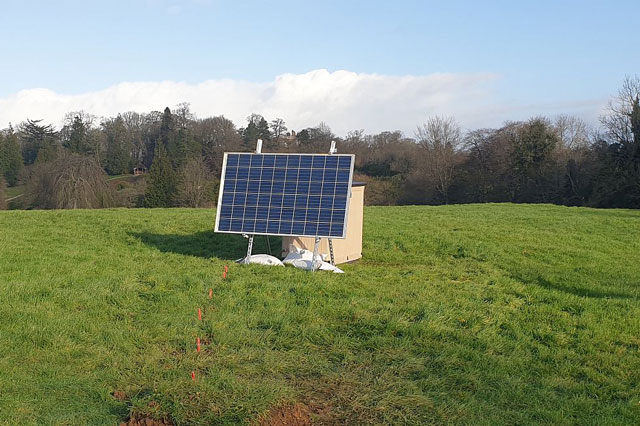
Three new underground geomagnetic observatories in County Fermanagh, Leicestershire and Sussex will detect and eventually help predict space weather, which can potentially disrupt power grids, satellite communications and the GPS on smartphones.
They were installed underground in quiet, rural locations by the BGS Geomagnetism team. The solar-powered observatories will collect data about Earth’s natural magnetic field and send it back to BGS in real-time, using the mobile phone network.
Why do we need new geomagnetic observatories?
Intense geomagnetic storms can have an adverse impact on technology like
power systems, satellite operations and smartphones.
The new magnetometers mean we now have full coverage of magnetic field change across the UK.
Very large geomagnetic storms produce widespread aurora. While beautiful, they have the potential to be incredibly disruptive.
They could cause power disruption and affect essential services like satellite communications and transport.
Now that we have monitors in our blind spots, we will better understand in detail where and what ground effects can occur and understand why they happened.
Dr Ciarán Beggan, BGS Geophysicist.
Britain has had geomagnetic observatories in Shetland, Eskdalemuir and
Devon since 1908, covering the country from north to south; the three new observatories will improve the breadth of measurements from west to east.
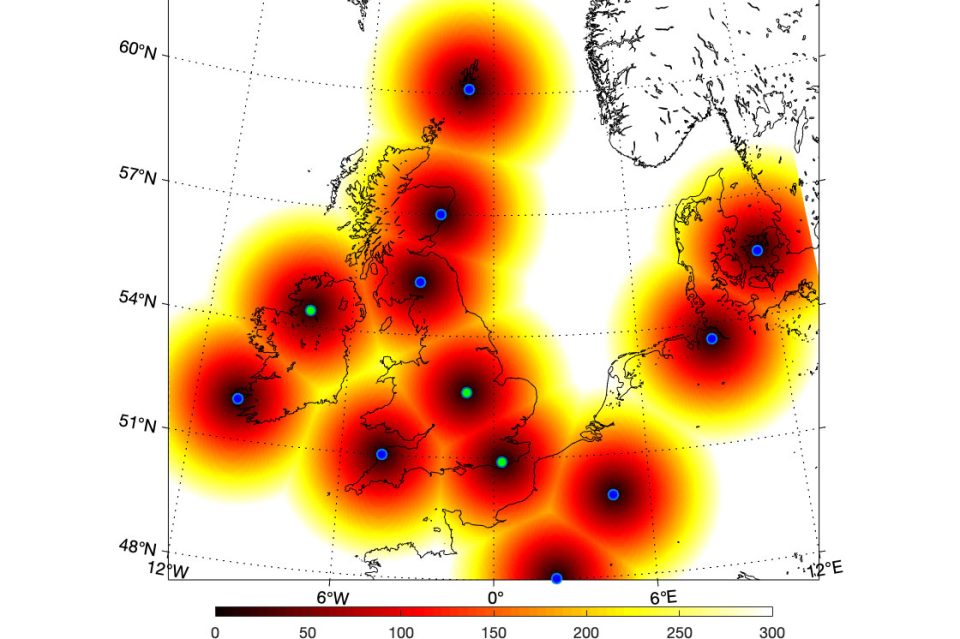
Zones of influence for the geomagnetic observatories.
The blue dots are existing observatories in the UK, Ireland and in northern Europe. The green dots are new UK observatories, three of which BGS installed in the past six months. The graded colouring from red to yellow shows the distance away from each location (up to 300 km away). No UK observatory is more than about 350 km (yellow colour) from its nearest neighbour and every part of the UK is within 200 km of an observatory.
The Aberdeen observatory is operated by Lancaster AuroraWatch, not BGS.
BGS © UKRI.
Mitigating a national risk
Severe space weather was included in the UK Government’s National Risk Register 2020.
Geomagnetic storms are one form of space weather. They interrupt essential
services by creating geoelectric fields in the subsurface, which then flow
into transformers, pipelines and railways, causing malfunctions.
Other effects include an increase in the density of the upper atmosphere (ionosphere), which disrupts radio waves passing through it. This leads to a loss of signal between the ground and satellites, affecting communications and the accuracy of global navigation satellite systems (GNSS). A huge number of technology systems rely on GNSS, including:
- phones
- trains
- self-driving vehicles
- timing for internet transactions
Major geomagnetic storms are relatively rare but, as Dr Beggan points out, they
have a pattern.
Major geomagnetic storms happen every 30 or 40 years in the UK, but we haven’t had a big one since 1989.
We live in a completely different society now, where we are all reliant on
continuous electricity supplies, smartphones and satellite communications — a major geomagnetic storm could significantly reduce those services.We’re currently moving into a stronger part of the solar cycle, which means the chance of large geomagnetic storms is greater.
Geomagnetic storms are currently hard to predict in terms of size or even arrival time from the Sun. Adding the new sensors means we are able to measure their effects on the ground in real-time and advise on the impact on technology.
Dr Ciarán Beggan, BGS Geophysicist.
Further reading
- Find out more about geomagnetism from BGS
Funding
The geomagnetic observatories were funded by UK Research and Innovation’s £20 million Space weather innovation, measurement, modelling and risk (SWIMMR) programme.
Relative topics
Media contact: Sarah McDaid (sarah@mcdaidpr.co.uk 07866789688)
How were the new sites selected?
Ciarán Beggan said: ‘We need a magnetically quiet, secure site. A magnetically quiet site must be at least 250 m from buildings, power lines and electric fences and 5 km from an electrified train line.
‘Ideally, it will have a south-facing aspect for the solar panel and 1 m of soil to allow the sensor to be buried. We ask permission from the landowner prior to installation. We want locations that are around 200–250 km from the existing observatories as this is the general “scale” of magnetic field changes during geomagnetic storms.
‘Fermanagh is the most westerly part of Northern Ireland. The Sussex site is relatively easterly and is part of an existing BGS facility at Herstmonceux. The Leicestershire site is approximately in the middle of England, equidistant between the observatories in Devon and Eskdalemuir.’
Examples of geomagnetic storms having adverse impact:
- 2022: Elon Musk’s SpaceX lost 40 satellites in one day as the result of a geomagnetic storm
- 2003: power outage in Sweden caused by geomagnetic storm
- 1989: Quebec 12-hour blackout caused by geomagnetic storm
- 1859: the ‘Carrington storm’, the biggest ever geomagnetic storm recorded, when people could see the northern lights in the tropics
- What if the Carrington storm happened today, in the satellite comms and smartphone era?
Related news

Funding awarded to UK/Canadian critical mineral research projects
08/07/2025
BGS is part of a groundbreaking science partnership aiming to improve critical minerals mining and supply chains.
Release of over 500 Scottish abandoned-mine plans
24/06/2025
The historical plans cover non-coal mines that were abandoned pre-1980 and are available through BGS’s plans viewer.

New collaboration aims to improve availability of real-time hazard impact data
19/06/2025
BGS has signed a memorandum of understanding with FloodTags to collaborate on the use of large language models to improve real-time monitoring of geological hazards and their impacts.

Modern pesticides found in UK rivers could pose risk to aquatic life
17/06/2025
New research shows that modern pesticides used in agriculture and veterinary medicines have been found for the first time in English rivers.

Goldilocks zones: ‘geological super regions’ set to drive annual £40 billion investment in jobs and economic growth
10/06/2025
Eight UK regions identified as ‘just right’ in terms of geological conditions to drive the country’s net zero energy ambitions.
Upgraded web portal improves access to geomagnetism data
02/06/2025
BGS’s geomagnetism portal, which holds data for over 570 observatories across the world, has received a significant update.
BGS digital geology maps: we want your feedback
29/05/2025
BGS is asking for user feedback on its digital geological map datasets to improve data content and delivery.

What is the impact of drought on temperate soils?
22/05/2025
A new BGS review pulls together key information on the impact of drought on temperate soils and the further research needed to fully understand it.

UK Minerals Yearbook 2024 released
21/05/2025
The annual publication provides essential information about the production, consumption and trade of UK minerals up to 2024.

BGS scientists join international expedition off the coast of New England
20/05/2025
Latest IODP research project investigates freshened water under the ocean floor.

New interactive map viewer reveals growing capacity and rare earth element content of UK wind farms
16/05/2025
BGS’s new tool highlights the development of wind energy installations over time, along with their magnet and rare earth content.

UKRI announce new Chair of the BGS Board
01/05/2025
Prof Paul Monks CB will step into the role later this year.




