New research reveals fresh insights into the role of karst in the Chalk aquifer
New research has thrown fresh light on what scientists understand about the role of karst in the Chalk aquifer, which provides public water supplies to millions of people, agriculture and industry, and sustains vital habitats.
20/12/2021 By BGS Press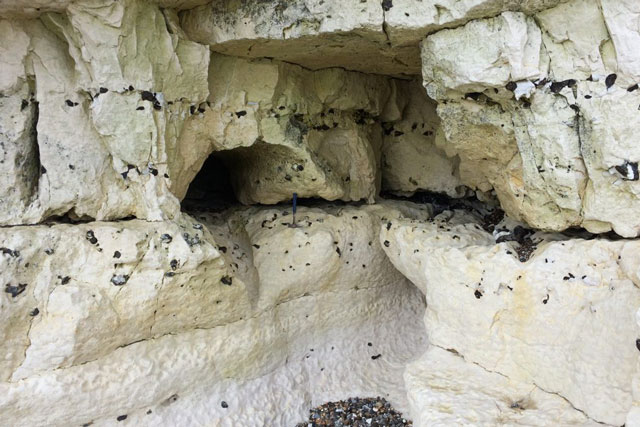
New research has thrown fresh light on what scientists understand about the role of karst in the Chalk Group aquifer, which provides public water supplies to millions of people, agriculture and industry, and sustains vital habitats. A study led by BGS, published in the Geological Society of London Special Publication SP517, The Chalk Aquifers of Europe, has compiled evidence showing that karst and rapid groundwater flow are much more widespread in the Chalk than previously thought.
The study will be of particular interest for regulators and water companies, both globally and in the UK, when planning future approaches to groundwater source protection and catchment management. Existing research shows that globally, around 20 to 25 per cent of people rely on karst groundwater for supply.
What is karst?
‘Karst’ is a geomorphological term that is applied to a type of landscape where erosion caused by dissolution, in other words the dissolving of bedrock, has resulted in fissures, sinkholes, sinking streams, ridges, caves, springs and other characteristic features. It is typically associated with soluble rock types such as limestone, marble and gypsum.
The Chalk is an unusual karst aquifer with limited cave development, but extensive networks of smaller solutional conduits and fissures that enable rapid groundwater flow. Small-scale karst features such as dolines, stream sinks, dissolution pipes and springs, are common.
This research is the culmination of many years work and is a step forward in our understanding of the Chalk aquifer. Our research presents evidence of the extent of karst in the Chalk throughout England, including almost 100 tracer connections demonstrating rapid groundwater flow.
We found high densities of stream sinks, and karstic conduits, springs, dolines and dissolution pipes are common.
We demonstrate that rapid groundwater flow and karst occur much more frequently than previously thought, which provides an important step forwards in our conceptual understanding of the Chalk and of global karst aquifers more generally.
Our work examines the implications of karst in the Chalk for groundwater protection and demonstrates how the evidence for karst should be central to future strategies for groundwater protection and management.
Louise Maurice, BGS Senior Hydrogeologist and lead author of the study.
Studying karst
Improved understanding of Chalk karst will expand understanding of similar karst aquifers with limited cave development that are globally widespread and provide vital public water resources to millions of people.
Such insights into the unique nature of Chalk karst may also help to advance understanding of classical karst aquifers, where major caves are often the main focus of research and fissures or smaller conduits are less understood.
The full study is titled Karst hydrogeology of the Chalk and implications for groundwater protection. The work is funded by the NERC knowledge Exchange fellowship scheme.
Other work in the Geological Society of London special publication also highlights the importance of karst in the Chalk, including a further BGS-led study, The genesis and evolution of karstic conduit systems in the Chalk.
Relative topics
Related news

Funding awarded to UK/Canadian critical mineral research projects
08/07/2025
BGS is part of a groundbreaking science partnership aiming to improve critical minerals mining and supply chains.
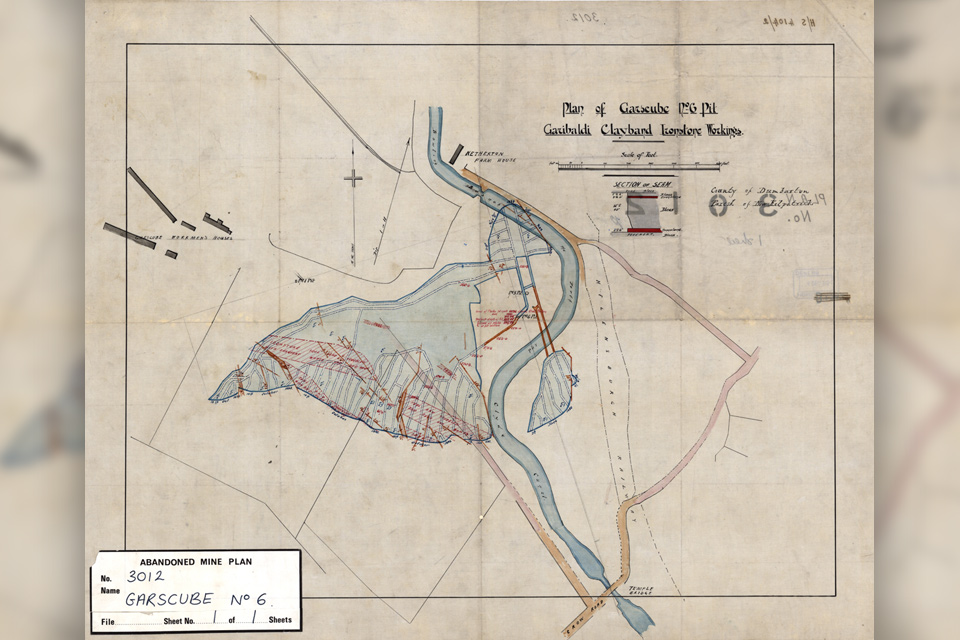
Release of over 500 Scottish abandoned-mine plans
24/06/2025
The historical plans cover non-coal mines that were abandoned pre-1980 and are available through BGS’s plans viewer.

New collaboration aims to improve availability of real-time hazard impact data
19/06/2025
BGS has signed a memorandum of understanding with FloodTags to collaborate on the use of large language models to improve real-time monitoring of geological hazards and their impacts.

Modern pesticides found in UK rivers could pose risk to aquatic life
17/06/2025
New research shows that modern pesticides used in agriculture and veterinary medicines have been found for the first time in English rivers.

Goldilocks zones: ‘geological super regions’ set to drive annual £40 billion investment in jobs and economic growth
10/06/2025
Eight UK regions identified as ‘just right’ in terms of geological conditions to drive the country’s net zero energy ambitions.
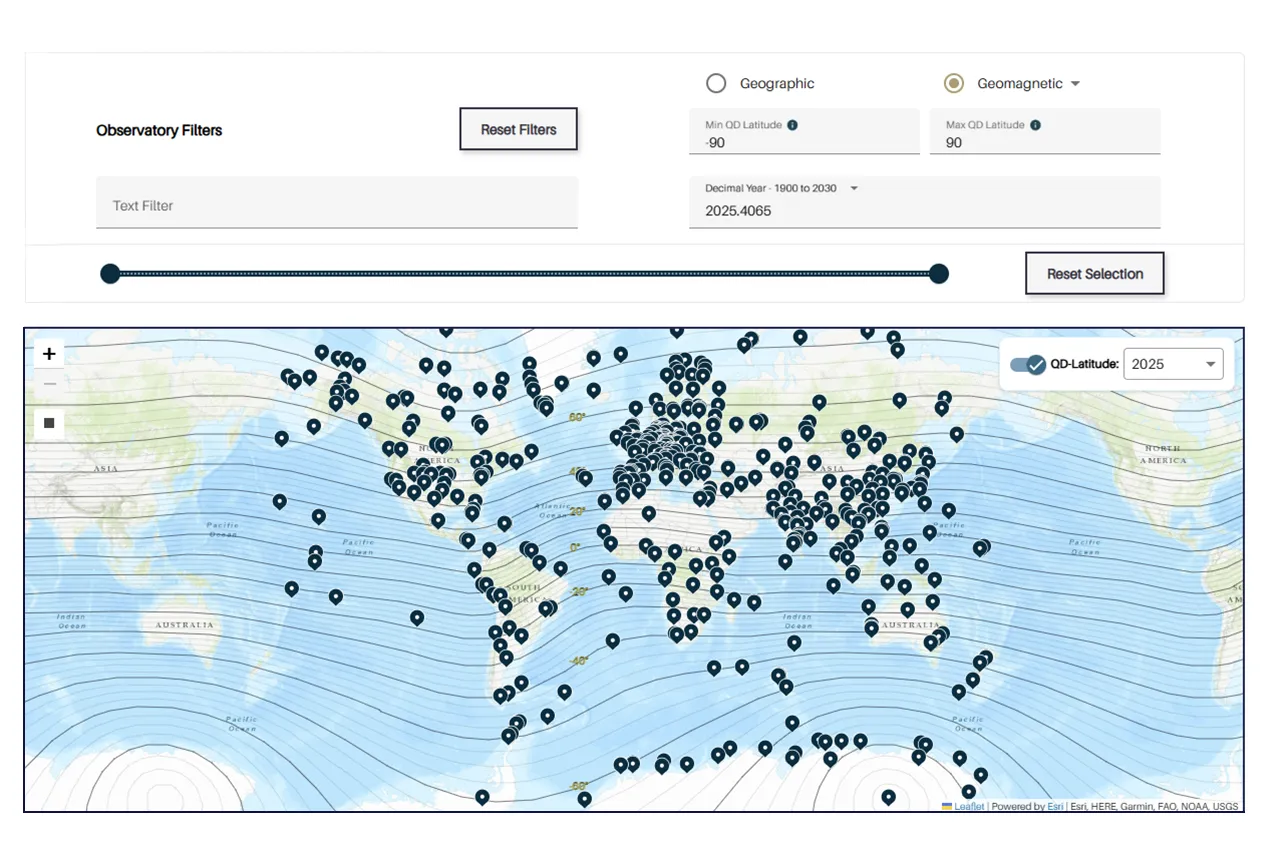
Upgraded web portal improves access to geomagnetism data
02/06/2025
BGS’s geomagnetism portal, which holds data for over 570 observatories across the world, has received a significant update.
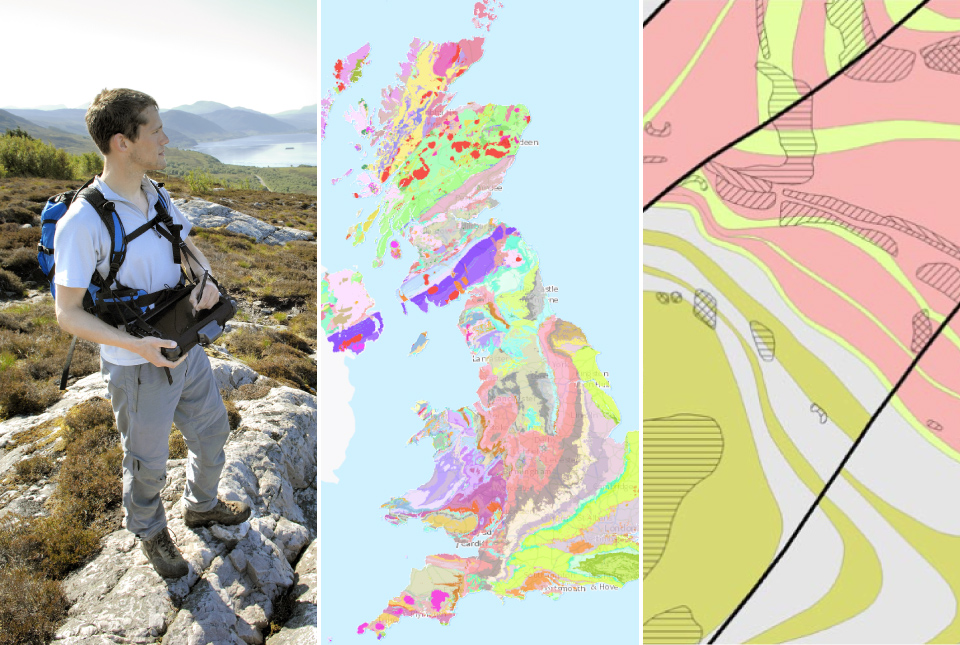
BGS digital geology maps: we want your feedback
29/05/2025
BGS is asking for user feedback on its digital geological map datasets to improve data content and delivery.

What is the impact of drought on temperate soils?
22/05/2025
A new BGS review pulls together key information on the impact of drought on temperate soils and the further research needed to fully understand it.

UK Minerals Yearbook 2024 released
21/05/2025
The annual publication provides essential information about the production, consumption and trade of UK minerals up to 2024.

BGS scientists join international expedition off the coast of New England
20/05/2025
Latest IODP research project investigates freshened water under the ocean floor.

New interactive map viewer reveals growing capacity and rare earth element content of UK wind farms
16/05/2025
BGS’s new tool highlights the development of wind energy installations over time, along with their magnet and rare earth content.

UKRI announce new Chair of the BGS Board
01/05/2025
Prof Paul Monks CB will step into the role later this year.



