UK’s new underground observatory open for research
The UK Geoenergy Observatory in Glasgow, which will give scientists an unprecedented look at the subsurface, holds its virtual opening.
07/12/2020 By BGS Press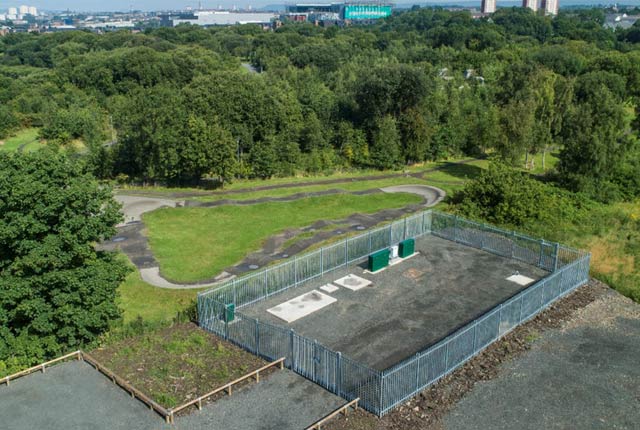
The UK Geoenergy Observatory in Glasgow, the first of two new underground laboratories that will give scientists an unprecedented look at the subsurface, had its virtual opening today, Monday 7 December.
The team behind the facility says it will contribute to the UK’s ambition to decarbonise its energy supply and achieve net zero by 2050.
Scientists around the world are now invited to apply to use the facility from March 2021, in line with COVID-19 restrictions.
The Glasgow Observatory comprises 12 boreholes, which are 16-199m deep and fitted with 319 state-of-the-art sensors.


Journey 90m below the surface of Glasgow, where historic mine workings now support research into sustainable use of mine water for heat and energy storage. Source: BGS © UKRI
Data from the Glasgow Observatory will help scientists understand the subsurface better, and how heat using warm water from abandoned mines could be used as a renewable energy source for homes and industry.
A second observatory is planned for a site in Cheshire.
Central Scotland, northern England and south Wales all have flooded, abandoned mines that could be tapped to supply local communities or industry with heat.
One problem with the take up of geothermal has been the risk involved: uncertainty over the resource available, high initial costs and long-term investments.
The UK Geoenergy Observatories will address those risks by providing fundamental information about the subsurface.
Together, the observatories represent a £31 million investment by the UK government through the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS).
They were commissioned by UK Research and Innovation’s (UKRI’s) Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) and delivered by the British Geological Survey (BGS), which will run the sites and manage their data.
The Glasgow Observatory was officially opened during a virtual event.
The Glasgow Observatory builds on the city’s industrial past.
The data from Glasgow’s abandoned mines will help us understand the processes and impacts of a mine water heat source and potential heat store as a sustainable way of heating homes and businesses in our cities.
Over the next 15 years, the network of boreholes will monitor any changes in the properties of the environment below the surface, and help close the knowledge gap we have on mine water heat energy and heat storage.
While today is the official opening, the Glasgow Observatory has been supplying scientists with open access data since drilling began in 2018.
There is no other publicly-funded observatory like this in the world, and it is very fitting that it is located in Glasgow, which will host COP 26 next year.
Dr Karen Hanghøj, Director of the British Geological Survey
The Glasgow Observatory is the first of our UK observatories that will create a high-resolution understanding of the underground system, providing a breakthrough in our knowledge of what lies beneath us.
Heat from mine water is one form of geothermal energy, and it has great potential to help the UK decarbonise its heat supply and meet net zero targets.
This £31 million investment is part of the UK’s national capability for world- class science, and will give the government, industry and regulators the knowledge required to understand how our underground might be used to power the future.
As we approach the COP26 summit in Glasgow in November 2021, today’s event demonstrates how UK research is bringing our communities together to create solutions to climate change and enable the UK to reach net zero by 2050.
Professor Sir Duncan Wingham, Executive Chair of the Natural Environment Research Council
It makes sense that the UK’s first geoenergy observatory is in Glasgow, given Scotland’s geology is world famous.
With the government’s target of achieving net zero emissions by 2050, emerging low carbon technologies may offer the best solutions to shaping future energy policy.
This observatory will be absolutely key for scientists to advance the study of renewable energy and is a great example of how Scotland is leading the way in energy innovation and investigating the viability of alternative energy sources.
Professor Dame Anne Glover, President of the Royal Society of Edinburgh
The Glasgow Observatory has already released 19 open data packs, giving scientists access to borehole information including optical images from up to 199m underground, environmental monitoring data and live seismic monitoring. For more information, or to view the data from the Glasgow Observatory, visit www.ukgeos.ac.uk

Welcome to UK Geoenergy Observatories: centres for world class research in Glasgow and Cheshire; on behalf of the research community, the Natural Environment Research Council and UK Research and Innovation. Source: BGS © UKRI
Where is the Glasgow Observatory?
Map here
About the 12 boreholes
The boreholes range in drilled length from 16 to 199m. They have been positioned so that scientists can:
- extract 180 m of rock core samples
- build up an accurate model of the geology below
- measure water temperature, flow and chemistry underground
- model the underground water systems
- measure the potential for mine water heat energy and heat storage
- provide baseline information on soil and surface water chemistry and ground gases nearby
Video here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gS2B3lBYdwI&feature=youtu.be
What information are the sensors collecting?
Seismic monitoring data since mid-2019
Available in 2021
- Groundwater logger data (water level, temperature, conductivity)
- Cross-borehole geo-electrical imaging baseline from electrical resistivity tomography sensors
- Direct temperature sensing baseline from fibre-optic downhole cables
- Scanning lasers monitoring near-surface CO2 and CH4, soil gas probes
- Weather station
What is geothermal energy?
Visit the BGS website for more info and videos: https://www.bgs.ac.uk/geology-projects/geothermal-energy/
The British Geological Survey (BGS) and Coal Authority have released maps which, for the first time, reveal the extent to which heat is stored in Britain’s abandoned coal mines.
https://www.bgs.ac.uk/news/new-maps-reveal-heat-stored-in-britains-abandoned-coal-mines/
What is net zero?
In 2019, the UK government became the first major economy to pass legislation committing to bring all greenhouse gas emissions to net zero by 2050.
Net zero means any emissions would be balanced by schemes to offset an equivalent amount of greenhouse gases from the atmosphere, such as planting trees or using technology like geothermal energy. Find out more here: https://www.gov.uk/government/news/uk-becomes-first-major-economy-to-pass-net-zero-emissions-law
Relative topics
Related news
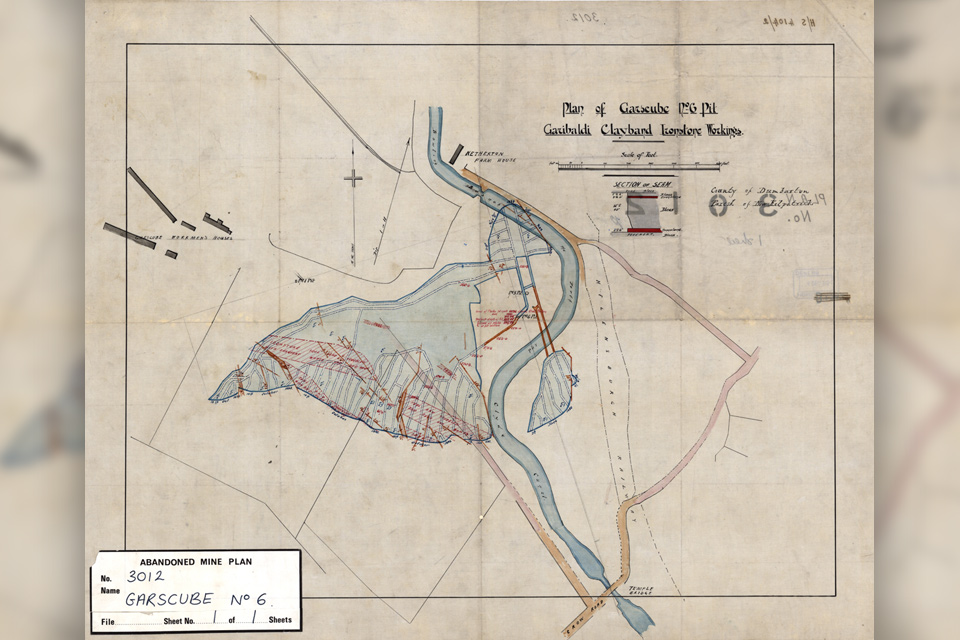
Release of over 500 Scottish abandoned-mine plans
24/06/2025
The historical plans cover non-coal mines that were abandoned pre-1980 and are available through BGS’s plans viewer.

New collaboration aims to improve availability of real-time hazard impact data
19/06/2025
BGS has signed a memorandum of understanding with FloodTags to collaborate on the use of large language models to improve real-time monitoring of geological hazards and their impacts.

Modern pesticides found in UK rivers could pose risk to aquatic life
17/06/2025
New research shows that modern pesticides used in agriculture and veterinary medicines have been found for the first time in English rivers.

Goldilocks zones: ‘geological super regions’ set to drive annual £40 billion investment in jobs and economic growth
10/06/2025
Eight UK regions identified as ‘just right’ in terms of geological conditions to drive the country’s net zero energy ambitions.
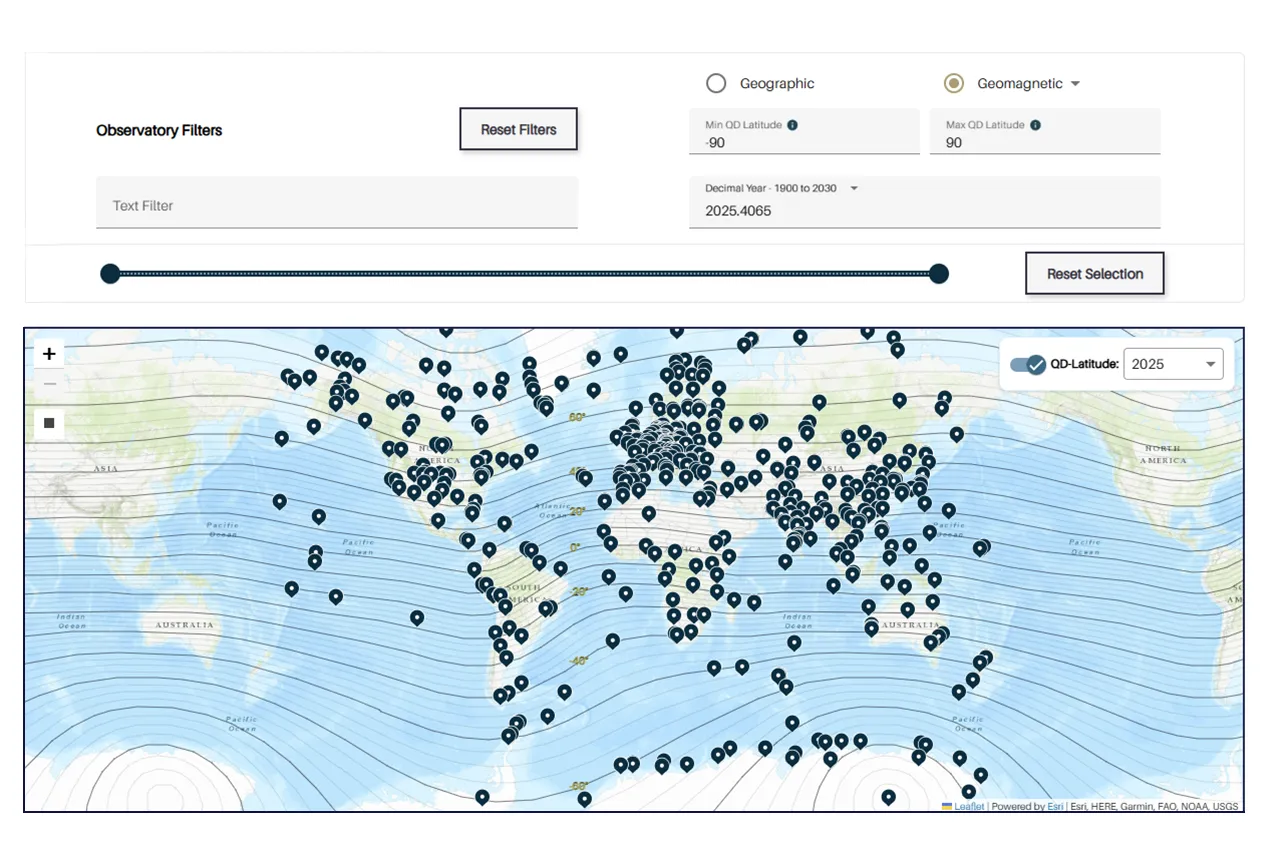
Upgraded web portal improves access to geomagnetism data
02/06/2025
BGS’s geomagnetism portal, which holds data for over 570 observatories across the world, has received a significant update.
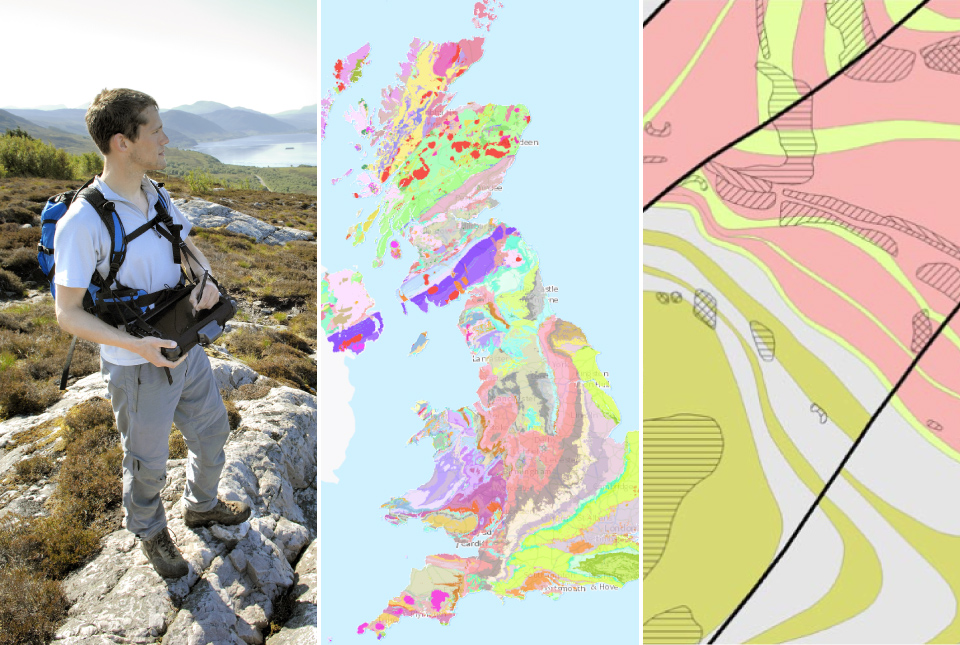
BGS digital geology maps: we want your feedback
29/05/2025
BGS is asking for user feedback on its digital geological map datasets to improve data content and delivery.

What is the impact of drought on temperate soils?
22/05/2025
A new BGS review pulls together key information on the impact of drought on temperate soils and the further research needed to fully understand it.

UK Minerals Yearbook 2024 released
21/05/2025
The annual publication provides essential information about the production, consumption and trade of UK minerals up to 2024.

BGS scientists join international expedition off the coast of New England
20/05/2025
Latest IODP research project investigates freshened water under the ocean floor.

New interactive map viewer reveals growing capacity and rare earth element content of UK wind farms
16/05/2025
BGS’s new tool highlights the development of wind energy installations over time, along with their magnet and rare earth content.

UKRI announce new Chair of the BGS Board
01/05/2025
Prof Paul Monks CB will step into the role later this year.

Latest mineral production statistics for 2019 to 2023 released
28/04/2025
More than 70 mineral commodities have been captured in the newly published volume of World Mineral Production.



