If ground collapse appears to have happened on or near your property, get specialist advice from a suitably qualified expert such as a chartered engineering geologist, geotechnical engineer or structural surveyor. Your local authority may also be able to offer information or advice. Inform your insurance company and mortgage lender, as appropriate.
If no collapse appears to have happened on the site, but there is thought to be potential for collapsible ground to be present, this potential should be taken into account when designing new buildings or making changes to land use.
- Take specialist advice before starting major building work.
- Maintain water pipes and drains in good condition, to avoid leaks.
- Direct surface water away from buildings in pipes or lined culverts.
- Avoid disposal of rain or other surface water in soakaways close to buildings.
- Avoid carrying out major irrigation or watering regimes without advice on their possible effects.
- Avoid increasing the loading on the ground without taking advice on its bearing capacity.
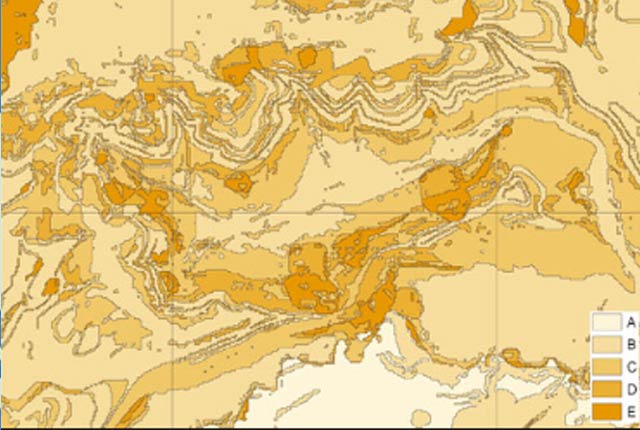
Hazard ratings and advice
| Hazard rating | Advice for public | Advice for specialist |
|---|---|---|
| A — deposits with potential to collapse when loaded and saturated are believed not to be present. | No actions required to avoid problems due to collapsible ground. | No special ground investigation required or increased construction costs or increased financial risk due to potential problems with collapsible ground. |
| B — deposits with potential to collapse when loaded and saturated are unlikely to be present. | No actions required to avoid problems due to collapsible ground. | No special ground investigation required or increased construction costs or increased financial risk due to potential problems with collapsible ground. |
| C — deposits with potential to collapse when loaded and saturated are possibly present in places. | Avoid large amounts of water entering the ground through pipe leakage or soakaways. Do not increase loading on existing foundations without technical advice. | Contact local authorities for information on local occurrence of damage due to collapsible ground.
New build — assess the possibility of collapsible (loessic) ground by ground investigation. If present do not exceed safe bearing capacity during or after construction and maintain site drainage, or carry out ground stabilisation. Existing property — possible increase in insurance risk if collapsible ground is present and if the load on the ground is increased or saturated by leakage or localised flooding. |
| D -— deposits with potential to collapse when loaded and saturated are probably present in places. | Avoid large amounts of water entering the ground through pipe leakage or soakaways. Do not increase loading on existing foundations without technical advice. | Contact local authorities for information on local occurrence of damage due to collapsible ground.
New build — assess the possibility of collapsible (loessic) ground by ground investigation. If present do not exceed safe bearing capacity during or after construction and maintain site drainage, or carry out ground stabilisation. Existing property — possible increase in insurance risk if collapsible ground is present and if the load on the ground is increased or saturated by leakage or localised flooding. |
| E — deposits with potential to collapse when loaded and saturated have been identified. | Avoid large amounts of water entering the ground through pipe leakage or soakaways. Do not increase loading on existing foundations without technical advice. | Contact local authorities for information on local occurrence of damage due to collapsible ground.
New build— assess the possibility of collapsible (loessic) ground by ground investigation. If present do not exceed safe bearing capacity during or after construction and maintain site drainage, or carry out ground stabilisation. Existing property — possible increase in insurance risk if collapsible ground is present and if the load on the ground is increased or saturated by leakage or localised flooding. |
You may also be interested in
BGS GeoSure
The BGS GeoSure datasets identify areas of potential hazard and, therefore, potential natural ground movement, in Great Britain.

BGS GeoSure: collapsible deposits
The potential for collapsible ground to be a hazard has been assessed using 1:50 000 scale digital maps of superficial deposits.