Climate change and human exploitation linked to historic decline in Atlantic salmon
New research reveals that both a change in climate and human exploitation played a role in a decline in North Atlantic salmon populations.
08/06/2022 By BGS Press
New research has revealed that an abrupt change in climate conditions in the North Atlantic around 800 years ago played a role in a decline in Atlantic salmon populations returning to rivers. Human exploitation reduced their populations still further.
Using state-of-the-art geochemistry, a team of scientists has discovered that large-scale changes in the marine habitat, brought on by a transition from a warm to a cold climate and what is now known as the Little Ice Age (approximately 1300 to 1850 CE), corresponded with a decline in salmon in the River Spey, Scotland. The study, published in the international journal The Holocene, was led by the University of Southampton, working with BGS.
These results can help us understand some of the controls on salmon populations prior to and during major human exploitation.
Our study shows that historically, beavers – common in Scotland hundreds of years ago – do not appear to have significantly impacted salmon numbers. This is very relevant today, as the animals are being reintroduced to UK rivers and a debate continues about their potential impact on migratory species like salmon.
Prof David Sear, professor of geography and environmental science at the University of Southampton and lead author of the study.
This research benefited from state-of-the-art geochemistry which enabled us to fingerprint salmon abundance over hundreds of years. We show that climate has been an important influence of salmon numbers, which is very relevant today due to the speed of climate change.
Prof Melanie Leng, BGS, co-author.
Atlantic salmon lay their eggs in the gravels of headwater streams, where their young live for a year or two before migrating out to sea. Here, they feed and grow into adults, eventually returning to the river to spawn, where many then die. The sperm, eggs and carcasses are rich in marine nutrients, which can be detected in sediment hundreds of years later.
Using core samples from Loch Insh on the River Spey, the scientists collected and measured marine-derived nutrients (MDNs), which give an understanding of the historic population levels of salmon. The team also examined a 150-year record of net-catch data from the lower Spey to help calibrate the MDN record.
The scientists were able to construct a 2000-year record of both salmon-derived nutrients and variations in climate conditions.
The findings show:
- bigger salmon populations (inferred from changes in MDNs) in the past reduced during a cooling climate at around the same time humans began to exploit them, leading to a major decline in the fish over the last 800 years
- larger salmon populations in the past occurred at a time when rivers were also inhabited by beavers, which suggests migratory fish are capable of co-existing with beavers; this is an important concern of anglers around current beaver reintroductions
- migratory fish, such as salmon, bring marine nutrients into our nutrient-poor upland rivers and probably represented a major boost to aquatic and wetland ecosystems in the past, with a decline in nutrients negatively affecting these ecosystems today
It is the first study to use MDNs to measure Atlantic salmon, although the method has previously been used for Pacific salmon in north-west USA and Canada.
Relative topics
Related news

Can sandstones under the North Sea unlock the UK’s carbon storage potential?
02/02/2026
For the UK to reach its ambitious target of storing 170 million tonnes of carbon dioxide per year by 2050, it will need to look beyond the current well-studied geographical areas.
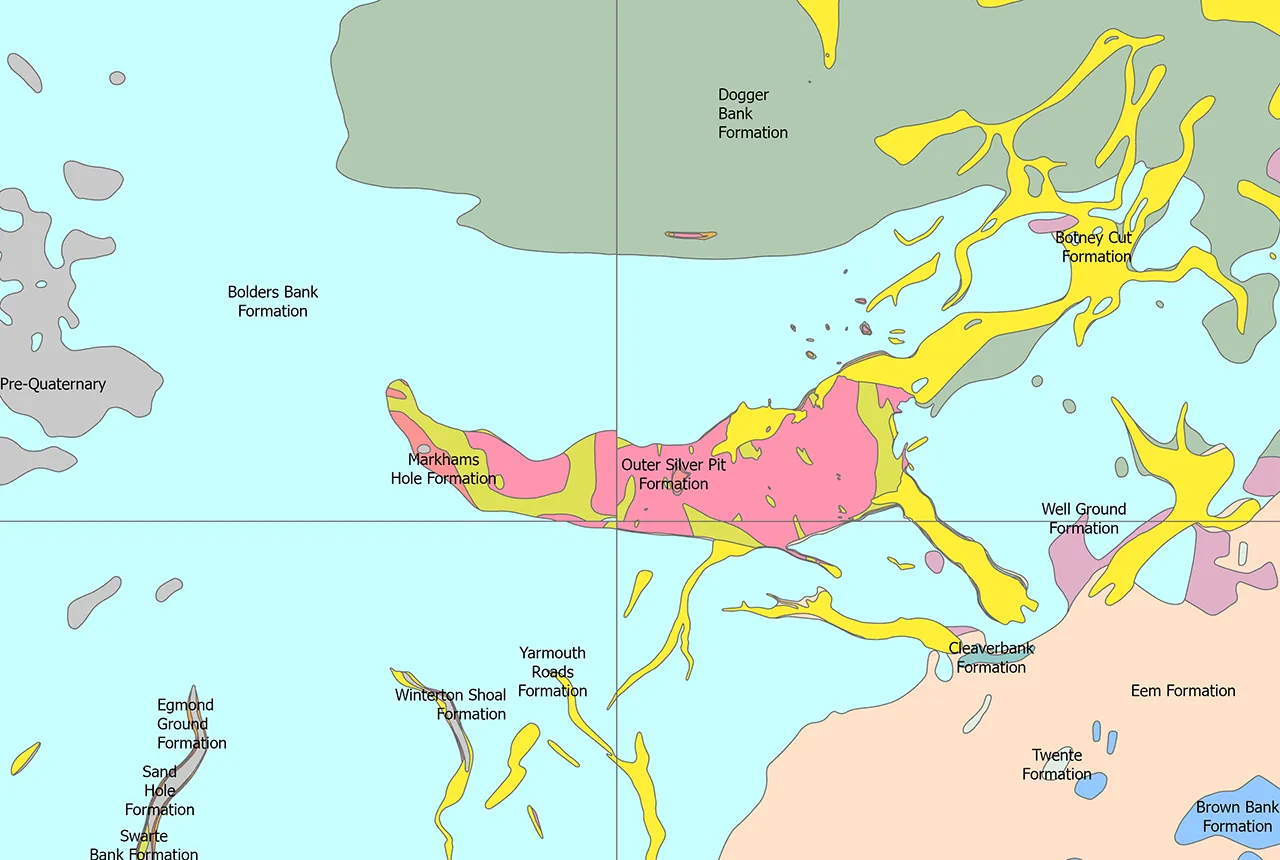
Quaternary UK offshore data digitised for the first time
21/01/2026
The offshore wind industry will be boosted by the digitisation of a dataset showing the Quaternary geology at the seabed and the UK’s shallow subsurface.

Suite of ten new soil reference materials released
02/01/2026
BGS has a longstanding track record of producing high-quality reference materials and has released ten new soil reference materials.
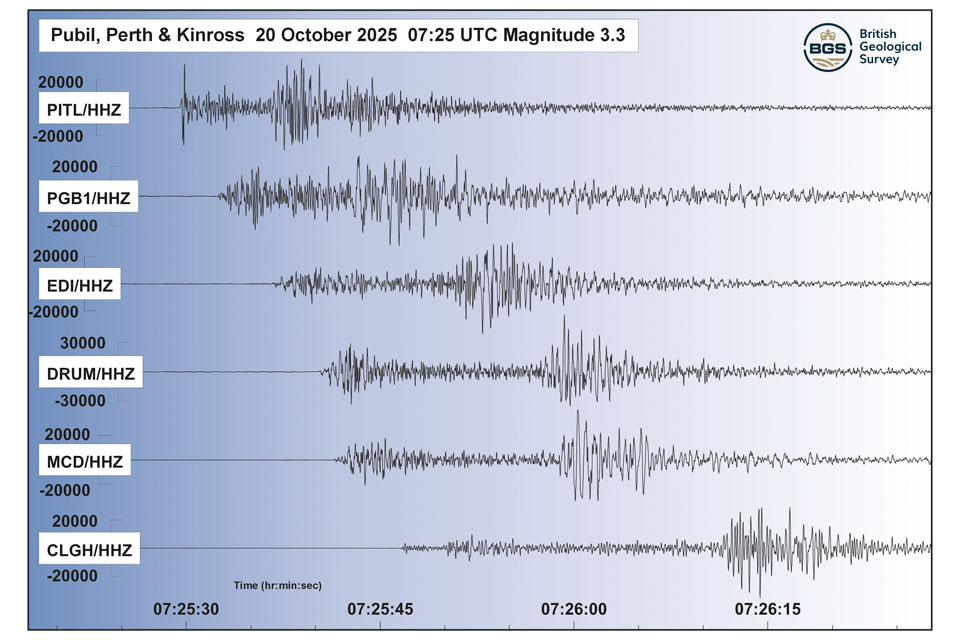
Perth and Kinross tops the UK’s earthquake activity charts for 2025
29/12/2025
Seismologists at BGS have published data on the number of seismic events over the past 12 months with over 300 earthquakes recorded.
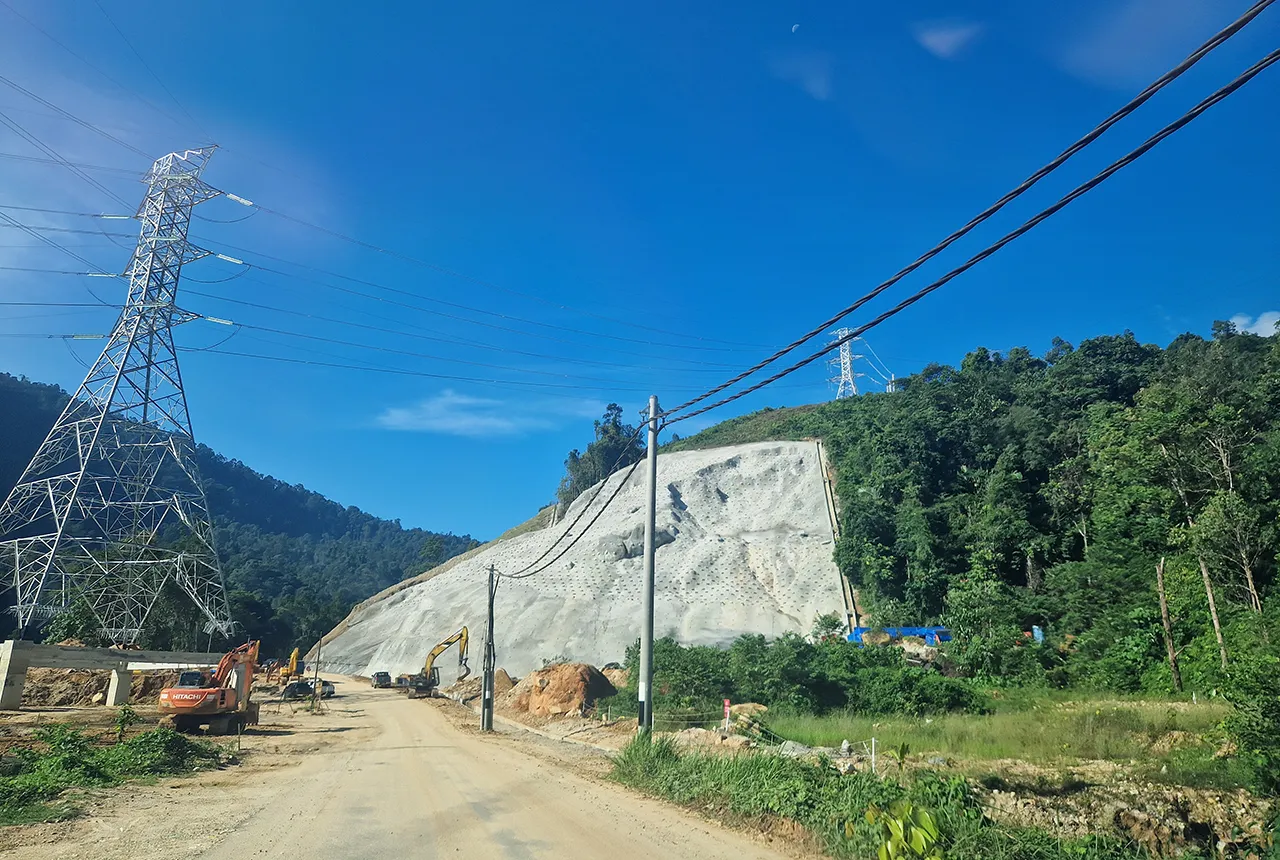

BGS awarded funding to support Malaysia’s climate resilience plan
17/12/2025
The project, funded by the Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office, will focus on minimising economic and social impacts from rainfall-induced landslides.
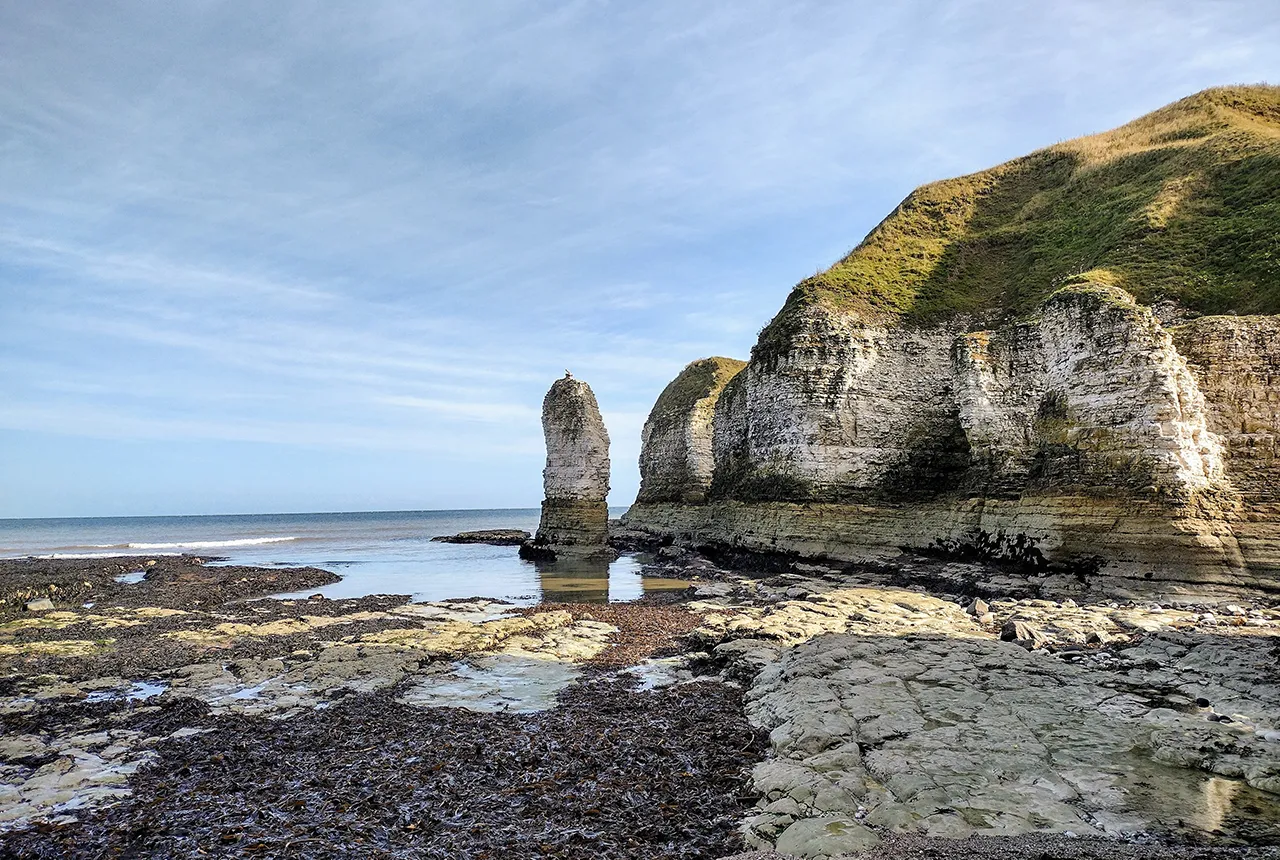

New geological maps of the Yorkshire Wolds to better inform groundwater management and policy decisions
17/12/2025
The new mapping provides crucial data on localised geological issues that may assist in protecting water supplies.

‘Three norths’ set to leave England and not return for hundreds of years
12/12/2025
The historic alignment of true, magnetic, and grid north is set to leave England, three years after they combined in the country for the first time since records began.

BGS agrees to establish collaboration framework with Ukrainian government
11/12/2025
The partnership will focus on joint research and data exchange opportunities with Ukrainian colleagues.

Making research matter: BGS joins leading research organisations in new national initiative
10/12/2025
A new alliance of 35 organisations has been formed that is dedicated to advancing science for the benefit of people, communities, the economy and national priorities.

New 3D model to help mitigate groundwater flooding
08/12/2025
BGS has released a 3D geological model of Gateshead to enhance understanding of groundwater and improve the response to flooding.

Scientists gain access to ‘once in a lifetime’ core from Great Glen Fault
01/12/2025
The geological core provides a cross-section through the UK’s largest fault zone, offering a rare insight into the formation of the Scottish Highlands.

New research shows artificial intelligence earthquake tools forecast aftershock risk in seconds
25/11/2025
Researchers from BGS and the universities of Edinburgh and Padua created the forecasting tools, which were trained on real earthquakes around the world.



