New method developed to identify wetland inhabitants
BGS-led research has helped develop a method to identify ancient human and animal wetland inhabitants.
01/11/2023 By BGS Press
A team of isotope scientists from BGS, along with Cardiff University, has led research that has developed a new analytical method to identify archaeological remains of humans and animals that once inhabited wetlands. The method provides an additional tool for archaeologists to explore human and animal mobility in the past.
Identifying human and animal movement has long been an important pursuit in archaeology. Isotope analysis provides direct data for this and is helpful in identifying non-local individuals and patterns of migration.
Our aim was to test the hypothesis that certain underlying rock types will produce low sulphur (sulfur; S) isotope values, which are transferred through the food chain and could therefore provide a means of identifying humans and animals raised in wetlands in the past.
Angela Lamb, BGS Isotope Geochemist.
The new research explored the potential of previously undiagnostic low, often negative, S-isotope values to identify wetland dwellers. This was carried out by testing the hypothesis that impervious clays, which often support wetlands, will produce low S-isotope values due to both the underlying substrate and redox conditions.
Collecting samples
To characterise the modern S-isotope biogeography of typical wetland environments, the researchers collected and analysed 58 modern plant samples taken from areas overlying Jurassic rocks in southern England. The sampling targeted archaeologically important areas of the Somerset Levels and the Cambridgeshire Fens. S-isotope ratios were also extracted from the bone collagen of 65 faunal fossil samples from archaeological sites in both regions and analysed to compare with modern data and test if this relationship held for archaeological samples. To understand if the plant signals were transferred up the food chain to the fauna, S-isotopes in modern bone collagen, extracted from nine farm animals raised in these areas, were also analysed.
An additional tool for archaeologists
Of the samples tested, 60 per cent gave a value below zero, with the modern plant datasets giving more negative values for the eastern regions of Cambridgeshire relative to Oxfordshire and Somerset. The plants showed a correlation between S-isotope composition and altitude, which supports the idea that low-lying wetlands supply the most negative values into the environment.
These results support the interpretation that relatively low or negative S-isotope values are indicative of vegetation and wildlife growing and grazing on wetland regions underlain by Jurassic clays. Data from this study formed part of a new BGS isotope domain map (see Figure 1).
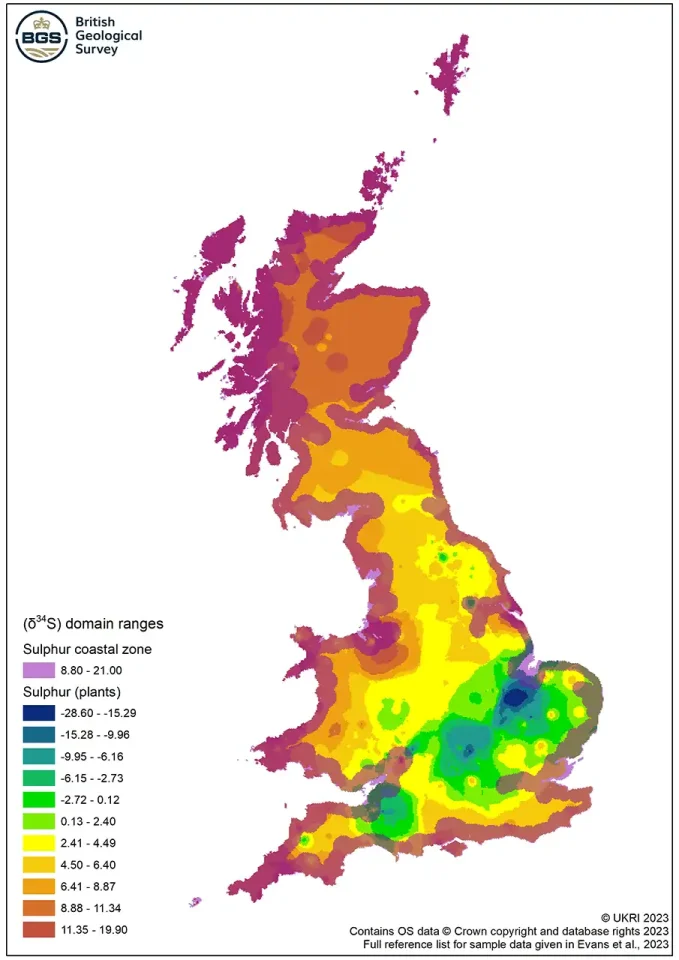
Figure 1 Map of S-isotope domain ranges for plants. BGS © UKRI.
Further work is needed to resolve regional differences in the altitude below which low S-isotope values occur and to understand S-isotope variability in higher altitude locations on the Jurassic clay, but this is a step forward in our understanding and therefore the application of low S- isotope ratios.
Angela Lamb
As a result, ancient humans and animals from wetlands, or that acquired their food from wetlands, may be identified using primary analytical methods. This provides an additional tool for archaeologists to explore animal management and human and animal mobility in the past.
More information
Read the research: Wet Feet: developing sulfur isotope provenance methods to identify wetland inhabitants
Evans, J A, Chenery, C A, Mee, K, and Marchant A P. 2023. Biosphere Isotope Domains GB (V2) [interactive website]. Available at https://www.bgs.ac.uk/datasets/biosphere-isotope-domains-gb/
Relative topics
Related news
Call for new members and Chair to join the NERC facilities steering committees
25/02/2026
New members are needed to join the committees over the next four years.

Your views wanted – developing a ‘Geothermal energy subsurface data portfolio’
24/02/2026
BGS is aiming to support the growth of the sector by providing the best-available, location-specific geothermal and ground source heat information as an accessible product or service.
Map of BGS BritPits showing the distribution of worked mineral commodities across the country
18/02/2026
BGS’s data scientists have generated a summary map of the most commonly extracted mineral commodities by local authority area, demonstrating the diverse nature of British mineral resources.

MARC Conference 2025: highlighting the importance of conferences to PhD students
16/02/2026
BGS and University of Nottingham PhD student Paulina Baranowska shares her experience presenting her research on nuclear forensics at her first international conference.

Funding awarded to map the stocks and flows of technology metals in everyday electronic devices
12/02/2026
A new BGS project has been awarded Circular Electricals funding from Material Focus to investigate the use of technology metals in everyday electrical items.

New UK/Chile partnership prioritises sustainable practices around critical raw materials
09/02/2026
BGS and Chile’s Servicio Nacional de Geología y Minería have signed a bilateral scientific partnership to support research into critical raw materials and sustainable practices.

Extensive freshened water confirmed beneath the ocean floor off the coast of New England for the first time
09/02/2026
BGS is part of the international team that has discovered the first detailed evidence of long-suspected, hidden, freshwater aquifers.

Funding secured to help mitigate ground risk in UK construction sector
05/02/2026
The BGS Common Ground project has been awarded new funding to help unlock the value of ground investigation data.

After-school kids’ clubs
Event from 25/02/2026 to 25/03/2026
An after school club for junior geology enthusiasts

Can sandstones under the North Sea unlock the UK’s carbon storage potential?
02/02/2026
For the UK to reach its ambitious target of storing 170 million tonnes of carbon dioxide per year by 2050, it will need to look beyond the current well-studied geographical areas.
Quaternary UK offshore data digitised for the first time
21/01/2026
The offshore wind industry will be boosted by the digitisation of a dataset showing the Quaternary geology at the seabed and the UK’s shallow subsurface.





