Airlines, shipping companies and sleigh drivers rush to update crucial navigation systems ahead of Christmas rush
Release of major upgrade to a new model tracking magnetic north prompts global reset of satellite tracking systems across trade and passenger transport routes.
17/12/2024 By BGS Press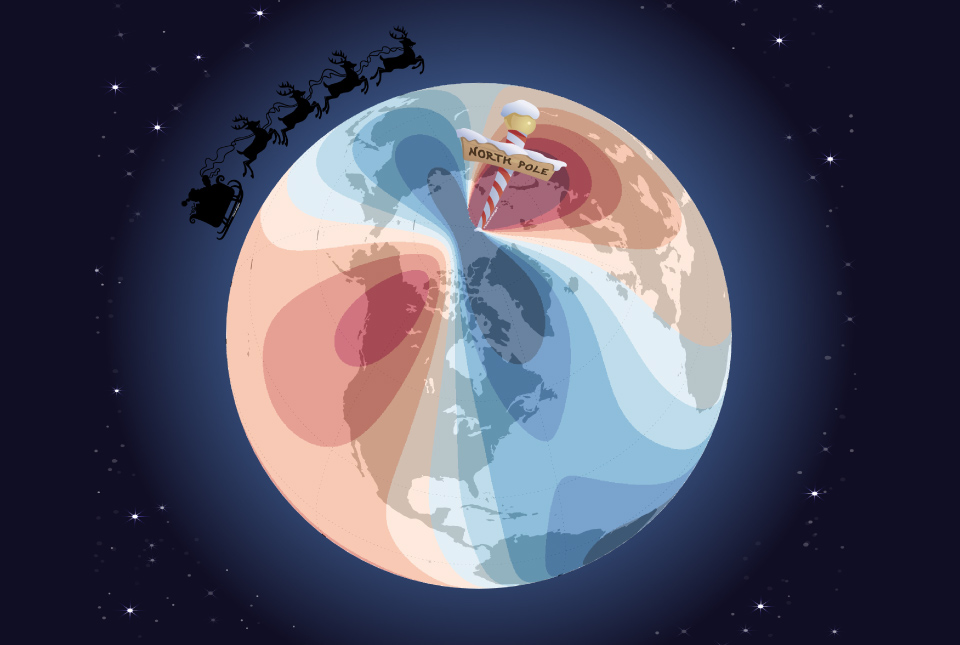
Hundreds of thousands of mariners, airline operators and North Pole-based gift distribution specialists will be rushing to update their navigation systems after the launch of a new model tracking magnetic north, which is crucial to the accuracy of global positioning systems (GPS) that are relied upon across the world.
In partnership with the UK Defence Geographic Centre and the US National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA), BGS and the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) have teamed up to update the World Magnetic Model (WMM).
The WMM is the standard model used by the United Kingdom and the United States governments, including the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration and the U.S. Department of Defense, as well as organizations with an international remit such as the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), the International Hydrographic Organization and the UK Hydrographic Office.
The model comprises a series of magnetic field maps that track changes in the magnetic field, such as the spot at which compass needles point in the northern hemisphere. To ensure pinpoint accuracy, it is crucial that the shifts in magnetic north, which are caused by flow of the liquid iron in the outer core of the Earth, are taken into account in the electronic equipment that is trusted to guide global trade and enable the safe transit of travellers across the planet. From GPS-enabled mobile phones to nuclear submarines, this improved resolution update will allow navigation with more accuracy than ever before to take place in the run up to Christmas — vital for all those who do not have a red nose to follow.
The WMM is officially released today, ensuring users can have the most up-to-date information so they can continue to navigate accurately for the next five years.
The current behaviour of magnetic north is something that we have never observed before. Magnetic north has been moving slowly around Canada since the 1500s but, in the past 20 years, it accelerated towards Siberia, increasing in speed every year until about five years ago, when it suddenly decelerated from 50 to 35 km per year, which is the biggest deceleration in speed we’ve ever seen.
Dr William Brown, global geomagnetic field modeller at BGS.
While each model predicts how magnetic north will shift over the five-year period to limit any error, the change will have an impact on travellers.
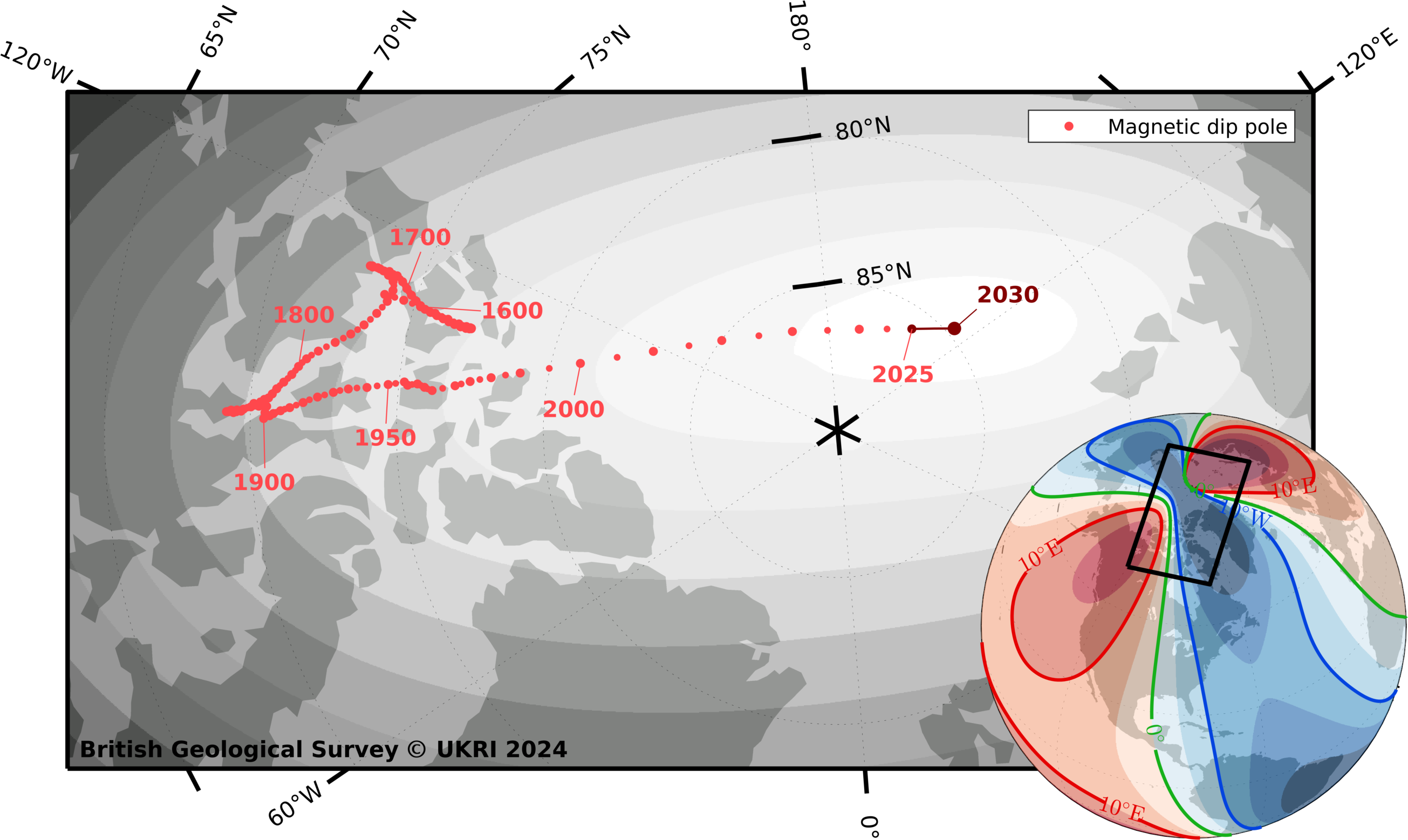
Magnetic north pole locations from 1590 to 2030. BGS © UKRI and © Wessel, P., and W. H. F. Smith (1996), A global, self-consistent, hierarchical, high-resolution shoreline database, J. Geophys. Res., 101(B4), 8741–8743, doi:10.1029/96JB00104. (v2.3.6).
Imagine someone was planning to travel by sleigh from a chimney top in South Africa to a snow covered-roof in the UK, a journey of around 8500 km. Using the previous WMM and setting off just one degree off-course, he would end up approximately 150 km away from where he should[1]. With a margin of error of only a few inches between chimney flues, this could cause significant issues.
Values from the updated model can now be calculated, and the WMMHR2025 and the WMM2025 are available for download.
More information
This year marks the first year that two versions of the model are being released. In addition to WMM2025, the 2025 update features the first-ever WMM High-Resolution 2025, which includes improved spatial resolution of approximately 300 km at the equator compared to the standard spatial resolution of 3300 km at the equator. Higher resolution provides greater directional accuracy through enhanced precision in the data.
Sponsored by NGA and the Defence Geographic Centre, the WMM is produced by BGS and NOAA’s National Centers for Environmental Information. It is the standard model used by the US Department of Defense, the UK Ministry of Defence, NATO and the International Hydrographic Organization for navigation, attitude and heading referencing systems using the geomagnetic field. It is also used widely in civilian navigation and heading systems. The WMM is updated every five years and its accuracy is validated annually to ensure it falls within the WMM military specification.
About NGA
NGA delivers world-class geospatial intelligence that provides a decisive advantage to policymakers, warfighters, intelligence professionals and first responders.
NGA is a unique combination of intelligence agency and combat support agency. It is the world leader in timely, relevant, accurate and actionable geospatial intelligence. NGA enables the US intelligence community and the Department of Defense to fulfill the president’s national security priorities to protect the nation.
For more information about NGA, visit us online at nga.mil, Instagram, LinkedIn, Facebook and X/Twitter
[1] It is believed that, while such a traveller may not rely primarily on satellite navigation, no logistical expert delivering hundreds of years of consistent service would not have such technology as a backup in case of emergency.
Relative topics
Related news
Call for new members and Chair to join the NERC facilities steering committees
25/02/2026
New members are needed to join the committees over the next four years.

Your views wanted – developing a ‘Geothermal energy subsurface data portfolio’
24/02/2026
BGS is aiming to support the growth of the sector by providing the best-available, location-specific geothermal and ground source heat information as an accessible product or service.
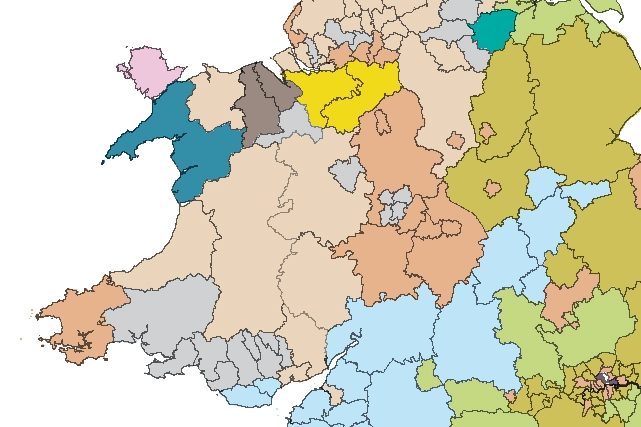
Map of BGS BritPits showing the distribution of worked mineral commodities across the country
18/02/2026
BGS’s data scientists have generated a summary map of the most commonly extracted mineral commodities by local authority area, demonstrating the diverse nature of British mineral resources.

Funding awarded to map the stocks and flows of technology metals in everyday electronic devices
12/02/2026
A new BGS project has been awarded Circular Electricals funding from Material Focus to investigate the use of technology metals in everyday electrical items.

New UK/Chile partnership prioritises sustainable practices around critical raw materials
09/02/2026
BGS and Chile’s Servicio Nacional de Geología y Minería have signed a bilateral scientific partnership to support research into critical raw materials and sustainable practices.

Extensive freshened water confirmed beneath the ocean floor off the coast of New England for the first time
09/02/2026
BGS is part of the international team that has discovered the first detailed evidence of long-suspected, hidden, freshwater aquifers.

Funding secured to help mitigate ground risk in UK construction sector
05/02/2026
The BGS Common Ground project has been awarded new funding to help unlock the value of ground investigation data.

Can sandstones under the North Sea unlock the UK’s carbon storage potential?
02/02/2026
For the UK to reach its ambitious target of storing 170 million tonnes of carbon dioxide per year by 2050, it will need to look beyond the current well-studied geographical areas.
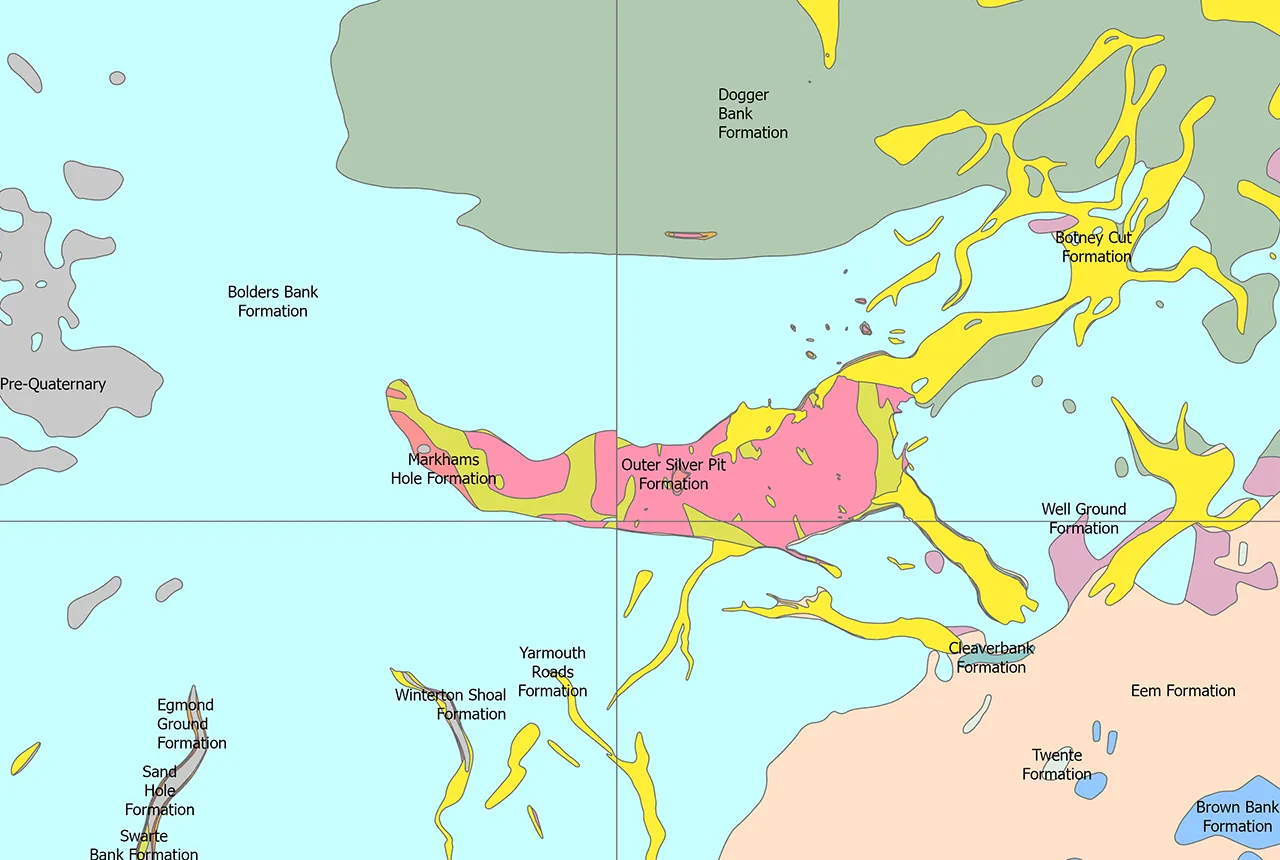
Quaternary UK offshore data digitised for the first time
21/01/2026
The offshore wind industry will be boosted by the digitisation of a dataset showing the Quaternary geology at the seabed and the UK’s shallow subsurface.
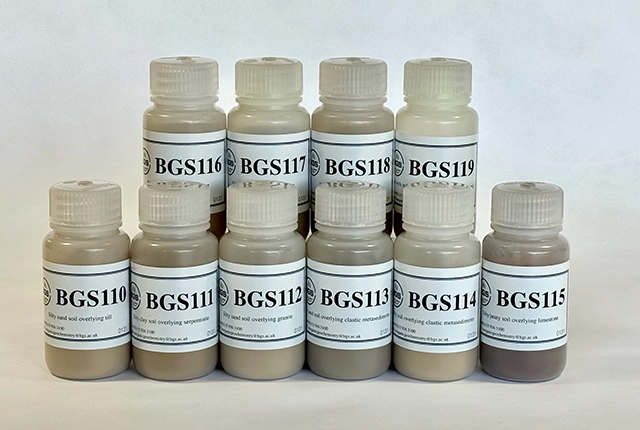

Suite of ten new soil reference materials released
02/01/2026
BGS has a longstanding track record of producing high-quality reference materials and has released ten new soil reference materials.
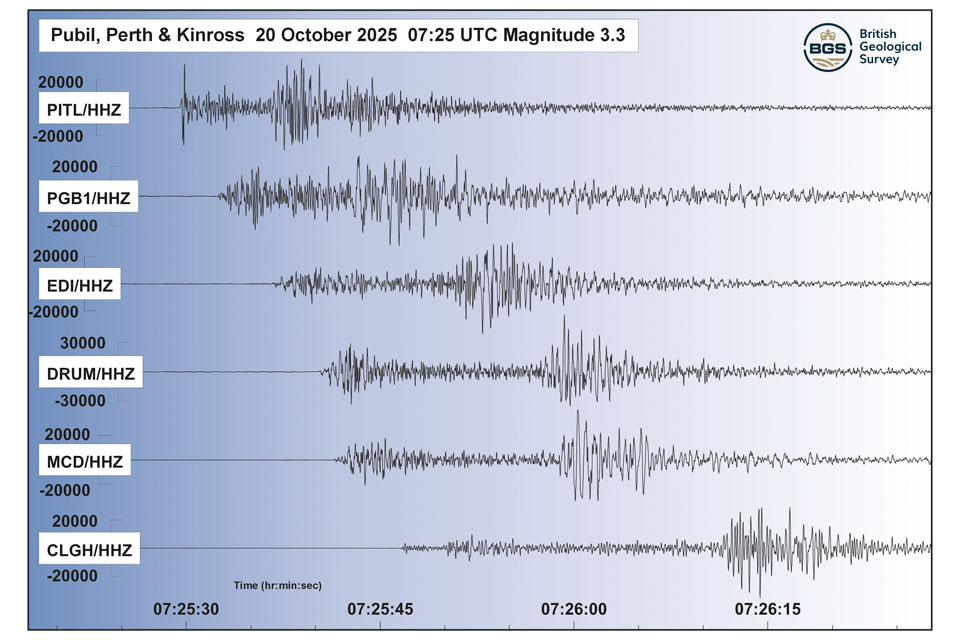
Perth and Kinross tops the UK’s earthquake activity charts for 2025
29/12/2025
Seismologists at BGS have published data on the number of seismic events over the past 12 months with over 300 earthquakes recorded.

BGS awarded funding to support Malaysia’s climate resilience plan
17/12/2025
The project, funded by the Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office, will focus on minimising economic and social impacts from rainfall-induced landslides.



