560-million-year-old fossil is first animal predator
The specimen is the first of its kind to be found and is related to the group that includes modern corals, jellyfish and anemones.
25/07/2022 By BGS Press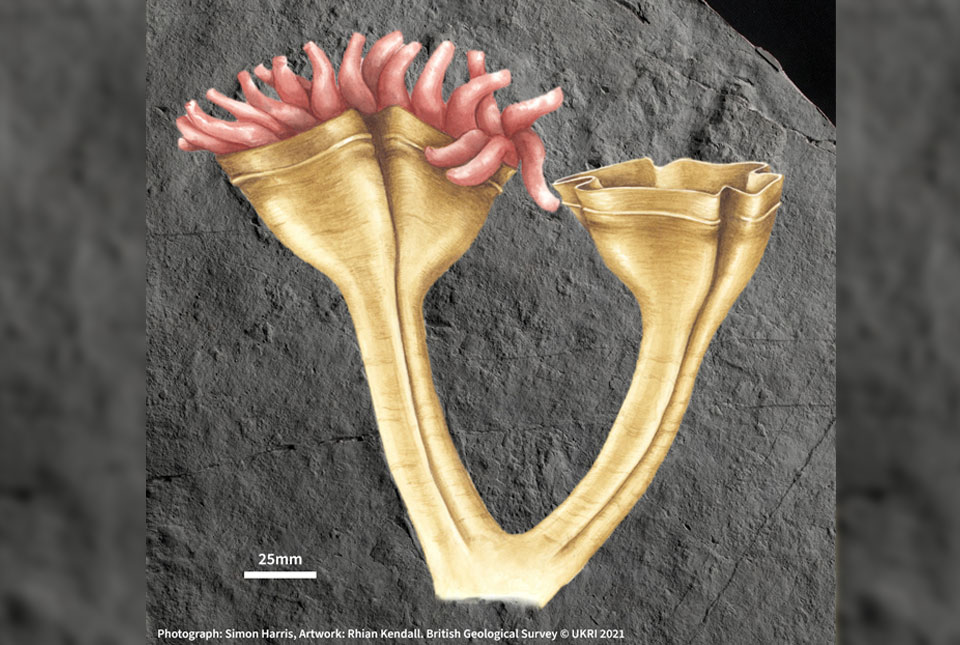
Geologists have found the fossil of the earliest known animal predator. The 560-million-year-old specimen is the first of its kind, but it is related to the group that includes corals, jellyfish and anemones living on the planet today.
The palaeontologists who discovered it have named it ‘Auroralumina attenboroughii‘ in honour of Sir David Attenborough. The first part of its name is Latin for ‘dawn lantern’, in recognition of its great age and resemblance to a burning torch.
It was found in Charnwood Forest, near Leicester in England, which is famous for its fossils. In 1957, a fern-like impression in stone turned out to be one of the oldest fossilised animals, Charnia masoni.
Sir David Attenborough ‘truly delighted’ with his new namesake
When I was at school in Leicester I was an ardent fossil hunter. The rocks in which Auroralumina has now been discovered were then considered to be so ancient that they dated from long before life began on the planet. So I never looked for fossils there.
A few years later a boy from my school found one and proved the experts wrong. He was rewarded by his name being given to his discovery. Now I have — almost — caught up with him and I am truly delighted.
Sir David Attenborough.
Sir David is referring to Roger Mason, after whom Charnia masoni was named.
When did modern groups appear?
The discovery of Auroralumina, reported in Nature Ecology and Evolution, throws into question when modern groups of animals appeared on Earth. Dr Phil Wilby, palaeontology lead at BGS, is one of the scientists who made the find.
It’s generally held that modern animal groups like jellyfish appeared 540 million years ago, in the Cambrian Explosion, but this predator predates that by 20 million years.
It’s the earliest creature we know of to have a skeleton. So far we’ve only found one, but it’s massively exciting to know there must be others out there, holding the key to when complex life began on Earth.
Dr Phil Wilby, BGS Palaeontology Lead.
When and where was it found?
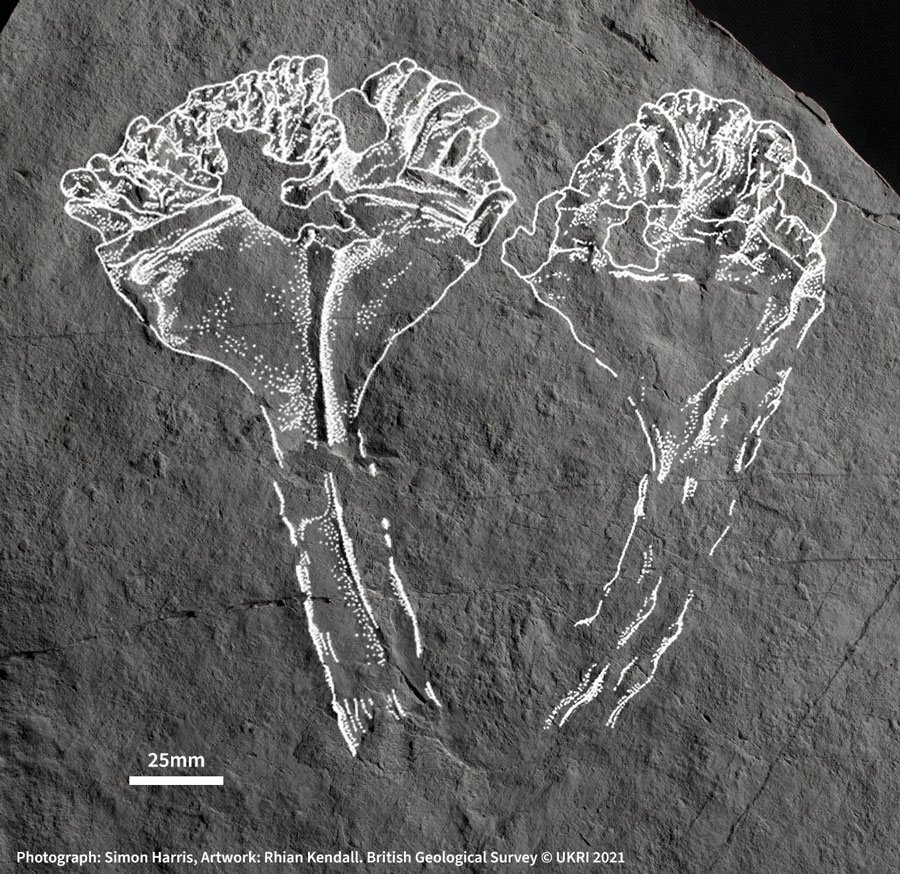
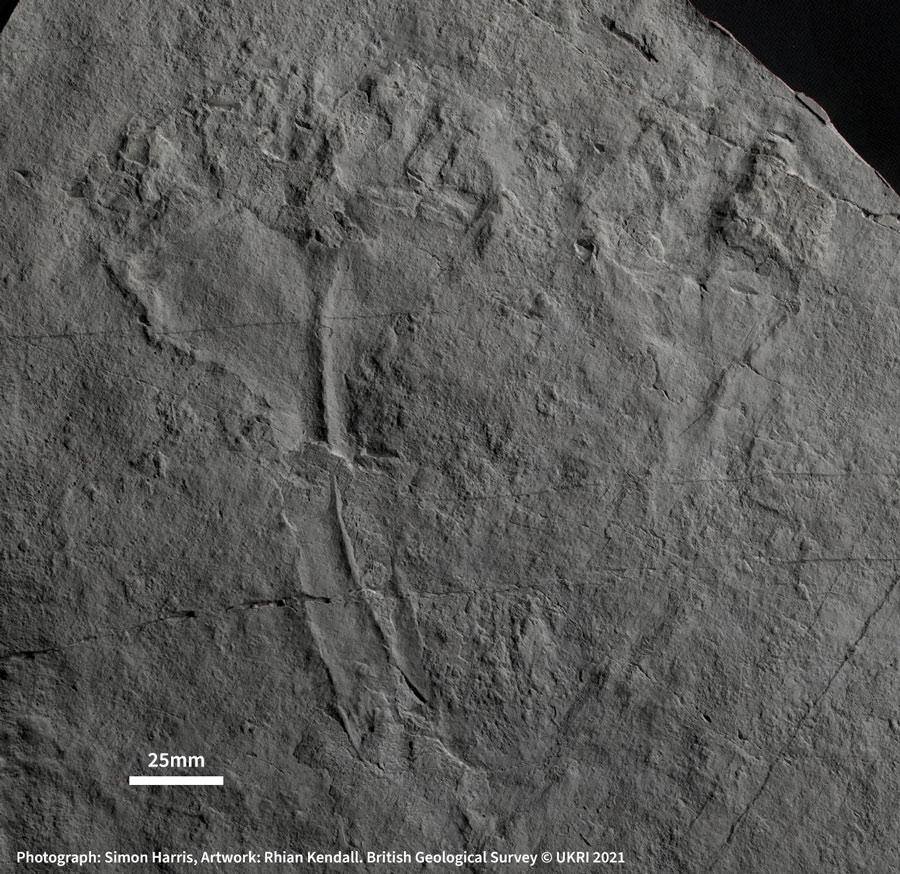
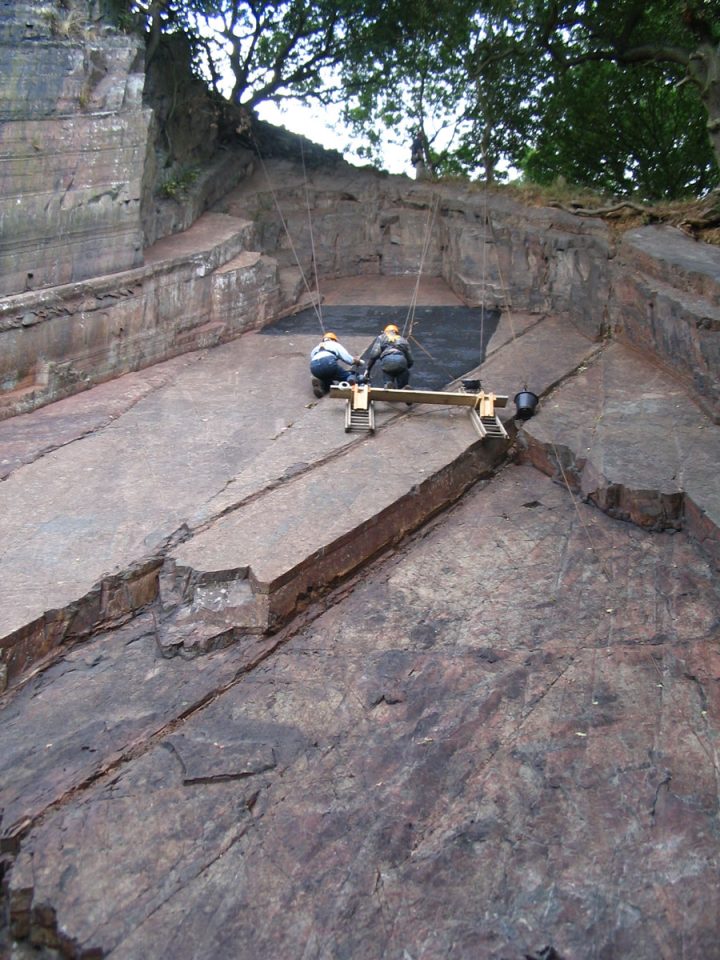
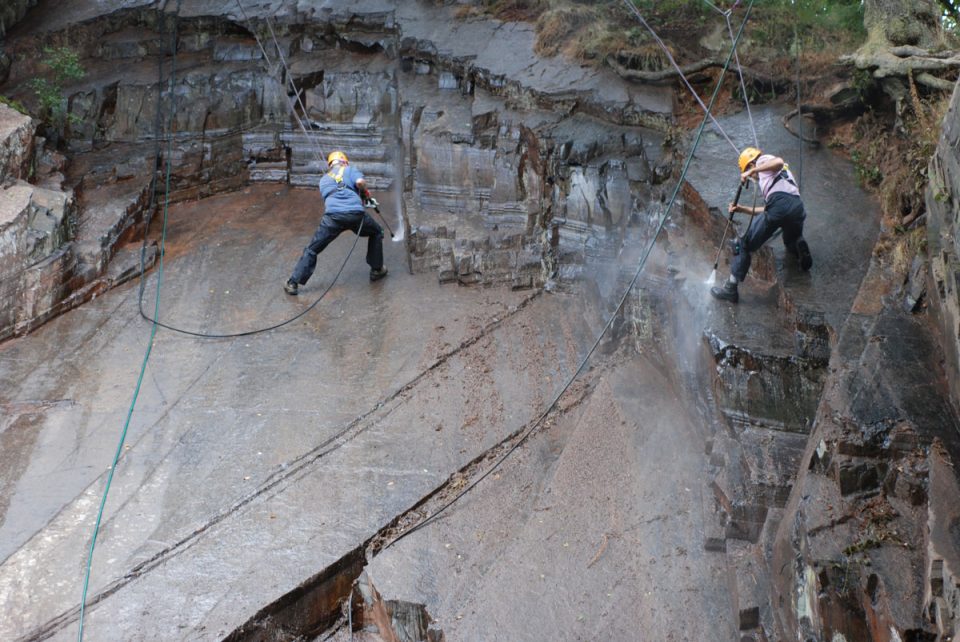
Palaeontologists still flock to the forest to examine its Ediacaran Period fossils, aged between 635 and 538.8 million years. In 2007, Phil Wilby and others from BGS spent over a week cleaning a 100 m-square rock surface with toothbrushes and pressure jets. They took a rubber mould of the whole surface and captured the impression of over 1000 fossils — and one stood out from the crowd.
Dr Frankie Dunn from the Oxford University Museum of Natural History carried out the detailed study.
This is very different to the other fossils in Charnwood Forest and around the world.
Most other fossils from this time have extinct body plans and it’s not clear how they are related to living animals. This one clearly has a skeleton, with densely packed tentacles that would have waved around in the water capturing passing food, much like corals and sea anemones do today.
It’s nothing like anything else we’ve found in the fossil record at the time.
Dr Frankie Dunn, Oxford University Museum of Natural History.
Dunn calls the specimen a ‘lonely little fossil’ and thinks it originated from shallower water than the rest of the fossils found in Charnwood.
The ancient rocks in Charnwood closely resemble ones deposited in the deep ocean on the flanks of volcanic islands, much like at the base of Montserrat in the Caribbean today.
All of the fossils on the cleaned rock surface were anchored to the sea floor and were knocked over in the same direction by a deluge of volcanic ash sweeping down the submerged foot of the volcano, except one: A. attenboroughii.
It lies at an odd angle and has lost its base, so appears to have been swept down the slope in the deluge.
Dr Frankie Dunn.
A. attenboroughii was dated at BGS’s headquarters in Keyworth, Nottingham, using zircons in the surrounding rock. Zircon is a tiny radioactive mineral that acts as a geological clock: it assesses how much uranium and lead are present. From that, geologists can determine precisely how old the rock is.
The ‘Cambrian Explosion’ was remarkable. It’s known as the time when the anatomy of living animal groups was fixed for the next half a billion years.
Our discovery shows that the body plan of the cnidarians [corals; jellyfish; sea anemones, etc.] was fixed at least 20 million years before this, so it’s hugely exciting and raises many more questions.
Dr Frankie Dunn.
Media contact: Sarah McDaid (sarah@mcdaidpr.co.uk/ 07866789688)
The new fossil’s name
The new fossil’s full name is Auroralumina attenboroughii.
About the Ediacaran Period
The Ediacaran Period immediately precedes the Cambrian Explosion and, for a long time, was thought not to contain fossils, although Darwin surmised that there must be a protracted history to life.
This all changed with the discovery of Charnia masoni and of similar fossils in rocks of the same age elsewhere in the world. Collectively, these strange fossils comprise the Ediacaran biota and include not only creatures that bear no resemblance to any subsequent life, but also the ancestors of modern animals. The planet at that time was a very different place, but these creatures helped shape the modern natural world.
Relative topics
Related news
Map of BGS BritPits showing the distribution of worked mineral commodities across the country
18/02/2026
BGS’s data scientists have generated a summary map of the most commonly extracted mineral commodities by local authority area, demonstrating the diverse nature of British mineral resources.

Funding awarded to map the stocks and flows of technology metals in everyday electronic devices
12/02/2026
A new BGS project has been awarded Circular Electricals funding from Material Focus to investigate the use of technology metals in everyday electrical items.

New UK/Chile partnership prioritises sustainable practices around critical raw materials
09/02/2026
BGS and Chile’s Servicio Nacional de Geología y Minería have signed a bilateral scientific partnership to support research into critical raw materials and sustainable practices.

Extensive freshened water confirmed beneath the ocean floor off the coast of New England for the first time
09/02/2026
BGS is part of the international team that has discovered the first detailed evidence of long-suspected, hidden, freshwater aquifers.

Funding secured to help mitigate ground risk in UK construction sector
05/02/2026
The BGS Common Ground project has been awarded new funding to help unlock the value of ground investigation data.

Can sandstones under the North Sea unlock the UK’s carbon storage potential?
02/02/2026
For the UK to reach its ambitious target of storing 170 million tonnes of carbon dioxide per year by 2050, it will need to look beyond the current well-studied geographical areas.
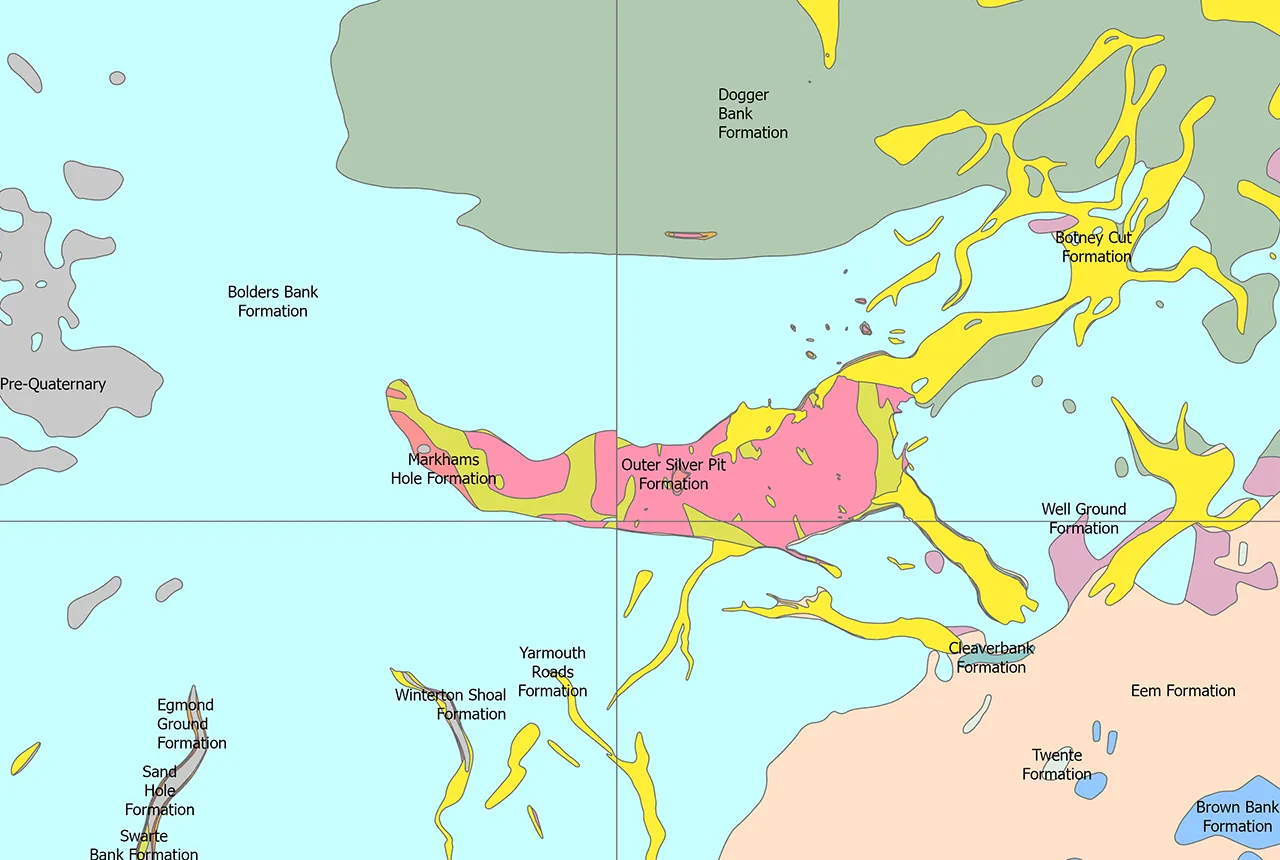
Quaternary UK offshore data digitised for the first time
21/01/2026
The offshore wind industry will be boosted by the digitisation of a dataset showing the Quaternary geology at the seabed and the UK’s shallow subsurface.

Suite of ten new soil reference materials released
02/01/2026
BGS has a longstanding track record of producing high-quality reference materials and has released ten new soil reference materials.
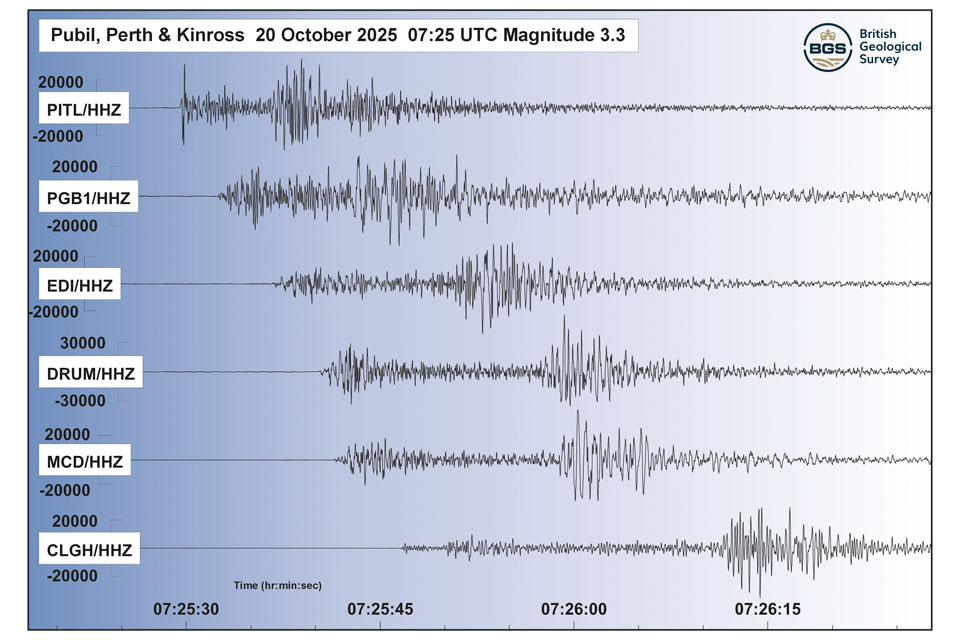
Perth and Kinross tops the UK’s earthquake activity charts for 2025
29/12/2025
Seismologists at BGS have published data on the number of seismic events over the past 12 months with over 300 earthquakes recorded.

BGS awarded funding to support Malaysia’s climate resilience plan
17/12/2025
The project, funded by the Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office, will focus on minimising economic and social impacts from rainfall-induced landslides.

New geological maps of the Yorkshire Wolds to better inform groundwater management and policy decisions
17/12/2025
The new mapping provides crucial data on localised geological issues that may assist in protecting water supplies.

‘Three norths’ set to leave England and not return for hundreds of years
12/12/2025
The historic alignment of true, magnetic, and grid north is set to leave England, three years after they combined in the country for the first time since records began.









