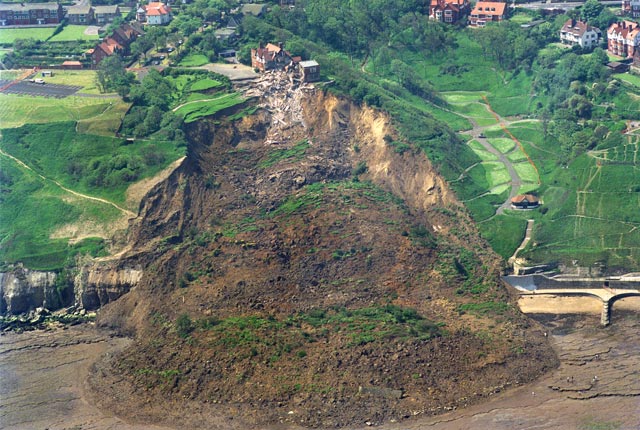
The Holbeck Hall landslide, south of Scarborough in North Yorkshire, attracted considerable interest when it destroyed the four-star Holbeck Hall Hotel between 3 and 5 June 1993. A rotational landslide involving about 1 million tonnes of glacial till cut back the 60 m-high cliff by 70 m. It flowed across the beach to form a semicircular promontory 200 m wide projecting 135 m outward from the foot of the cliff.
The landslide is National Landslide Database ID 10741/1.
Holbeck Hall location map. BGS © UKRI.


Holbeck Hall landslide aerial survey. Previously unseen aerial footage of the survey carried out by BGS of the landslide that affected the Holbeck Hall hotel in June 1993. BGS © UKRI.
Landslide details
The first signs of movement on the cliff were seen six weeks before the main failure, when cracks developed in the tarmac surface of footpaths running across the cliffs. These were filled to stop ingress of water to the cliff, but when the cracks reopened shortly before the main failure, the council closed the cliff paths below the hotel. At this time, a small part of the hotel garden was also observed to have suffered a minor movement.
There was originally 70 m of garden between the hotel and the cliff edge. At 6 am on 4 June, a guest saw that 55 m of the garden had disappeared. The hotel was evacuated and the landslide continued to develop, culminating in the collapse of the east wing of the hotel by the evening of 5 June.
The likely cause of the landslide was a combination of:
- rainfall of 140 mm in the two months before the slide took place
- issues related to the drainage of the slope
- pore water pressure build up in the slope
- geology
The landslide is a rotational landslide degrading to a mud/debris flow which covered the rocks on the beach (platform).
Geology
The cliff consists of glacial till (sandy, silty clay) resting on a low cliff of the Middle Jurassic Scalby Formation. The Scalby Formation comprises the Scalby Mudstone and the Moor Grit (sandstone).
References
Forster, A. 1993. Scarborough Landslip. Geoscientist, Vol. 3(5), 2–3.
Forster, A, and Culshaw, M. 2004. Implications of climate change for hazardous ground conditions in the UK, GeologyToday, Vol. 20(2), 61–66.
Lee, E M. 1999. Coastal planning and management: the impact of the 1993 Holbeck Hall landslide, Scarborough. East Midlands Geographer, Vol. 21(2) and Vol. 22(1), 78–91.
Blogs
Unseen video footage — the Holbeck Hall landslide 25 years on by Catherine Pennington. Looking back to the Holbeck Hall landslide with unseen video footage taken at the time from an aeroplane – drones hadn’t been invented yet…
Gallery
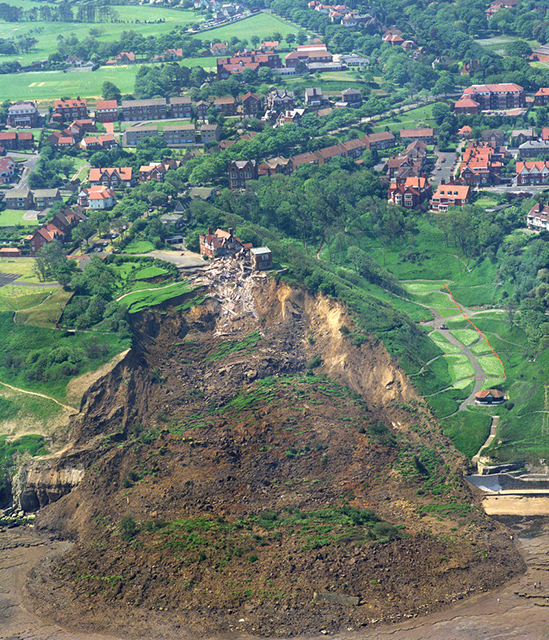

Holbeck Hall landslide from the air. BGS © UKRI.
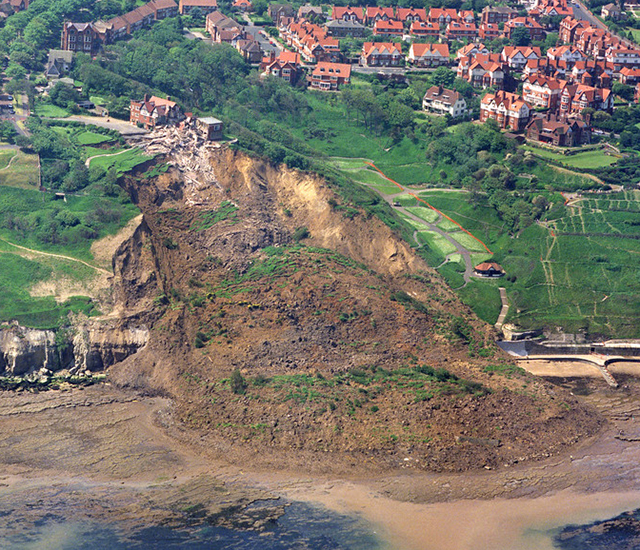

Holbeck Hall landslide from the air. BGS © UKRI.
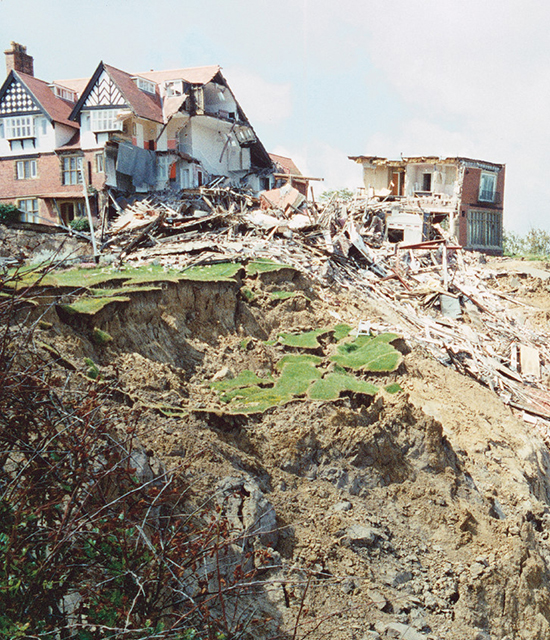

Top of the landslide showing damage to the Holbeck Hall Hotel. BGS © UKRI.
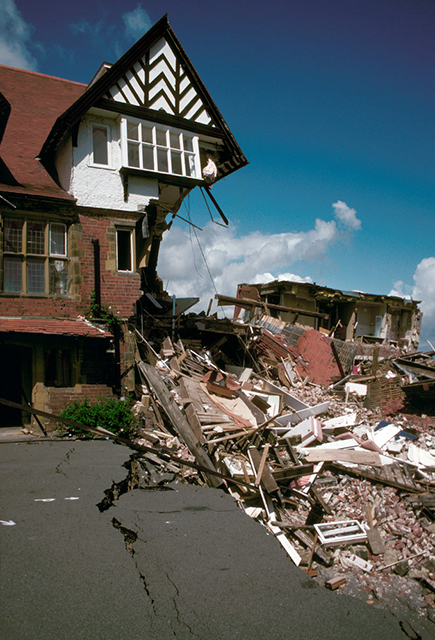

Damage to the hotel. BGS © UKRI.
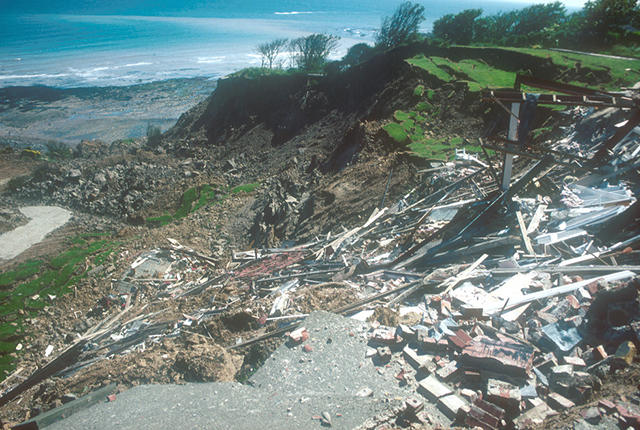

Looking down the landslide. BGS © UKRI.
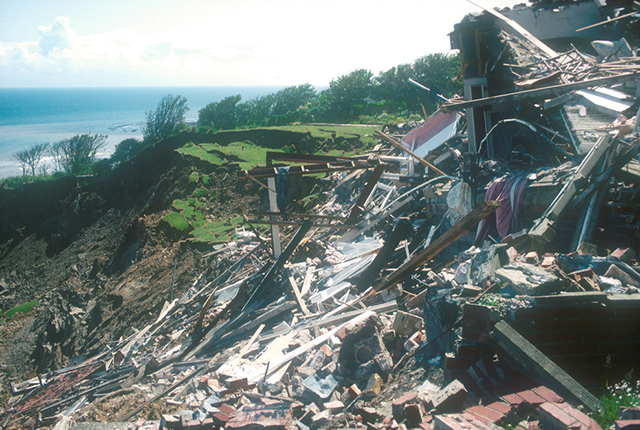

Debris from the hotel. BGS © UKRI.
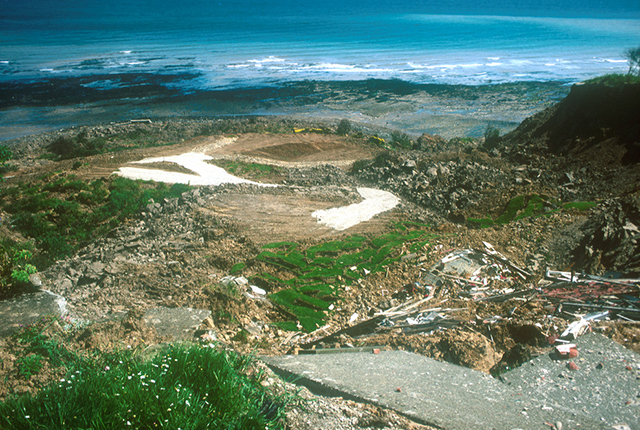

Looking down the landslide. BGS © UKRI.
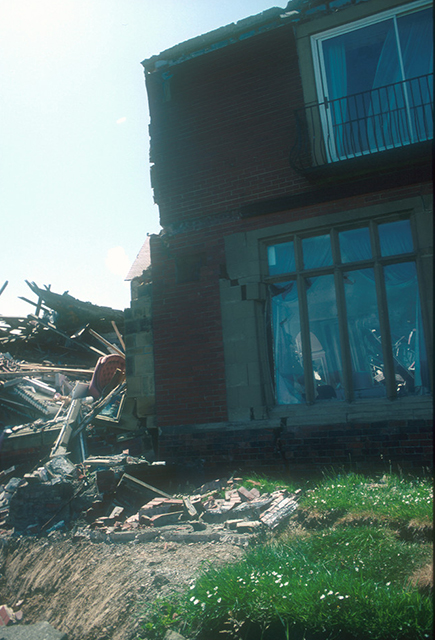

Damage to the hotel. BGS © UKRI.
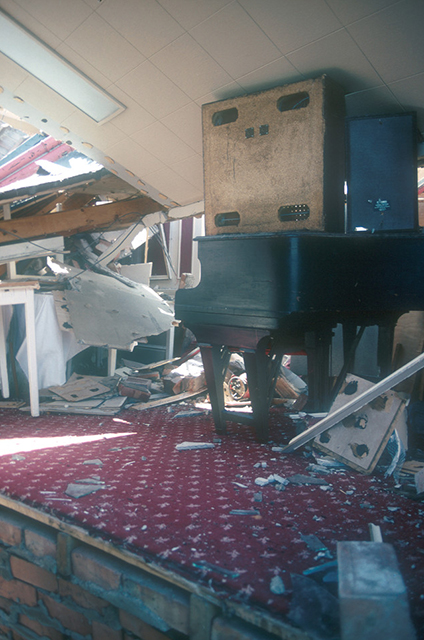

View of inside. BGS © UKRI.
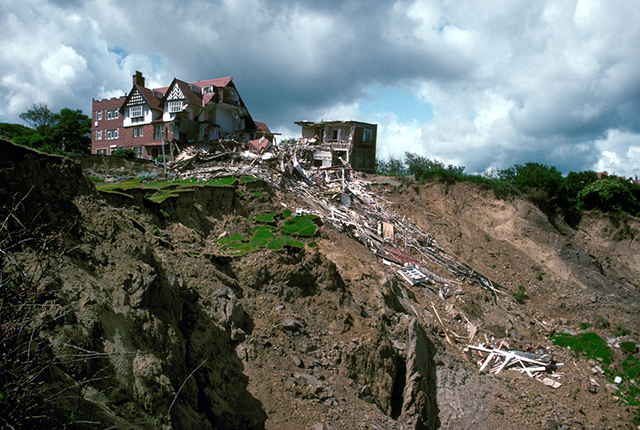

View of the Holbeck Hall Hotel and the top of the landslide. BGS © UKRI.
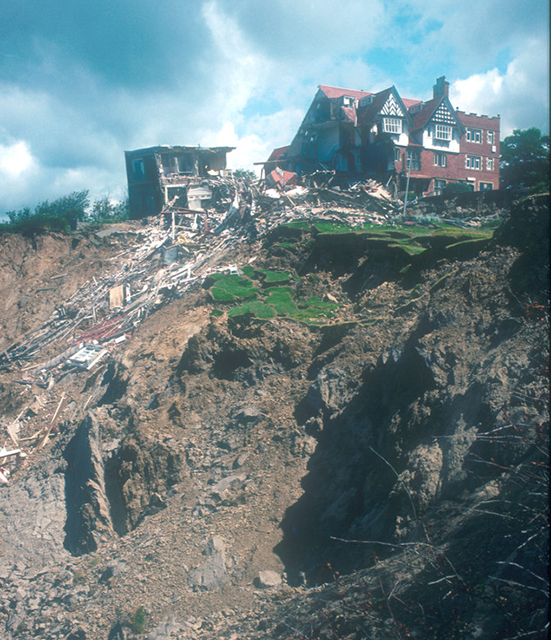

Holbeck Hall Hotel landslide. BGS © UKRI.
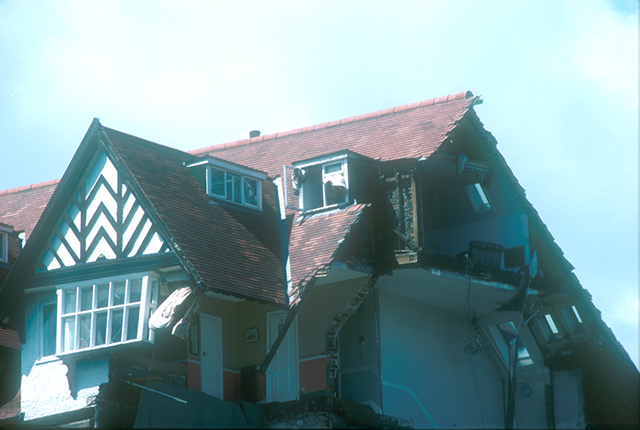

Damage to the roof. BGS © UKRI.
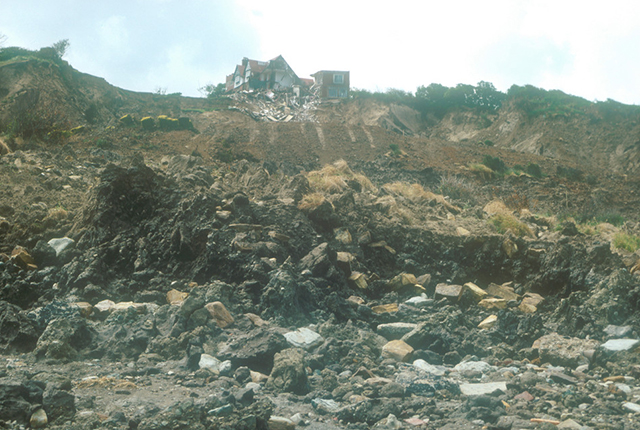

hotel from the bottom of the landslide looking up towards the hotel. BGS © UKRI.
You may also be interested in

Landslide case studies
The landslides team at the BGS has studied numerous landslides. This work informs our geological maps, memoirs and sheet explanations and provides data for our National Landslide Database, which underpins much of our research.

Understanding landslides
What is a landslide? Why do landslides happen? How to classify a landslide. Landslides in the UK and around the world.

How to classify a landslide
Landslides are classified by their type of movement. The four main types of movement are falls, topples, slides and flows.
Landslides in the UK and around the world
Landslides in the UK, around the world and under the sea.


