Data from the BGS Seismology team, led by Dr Brian Baptie, has helped to illustrate a dramatic reduction in seismic activity and earth vibrations — or ‘noise’ — during lockdown.
The data was transformed into an illustration as part of ‘Nature in Lockdown’, a Natural History Museum (NHM) public engagement initiative that crowdsourced research ideas to discover which environmental impacts of COVID-19 people were most interested in.
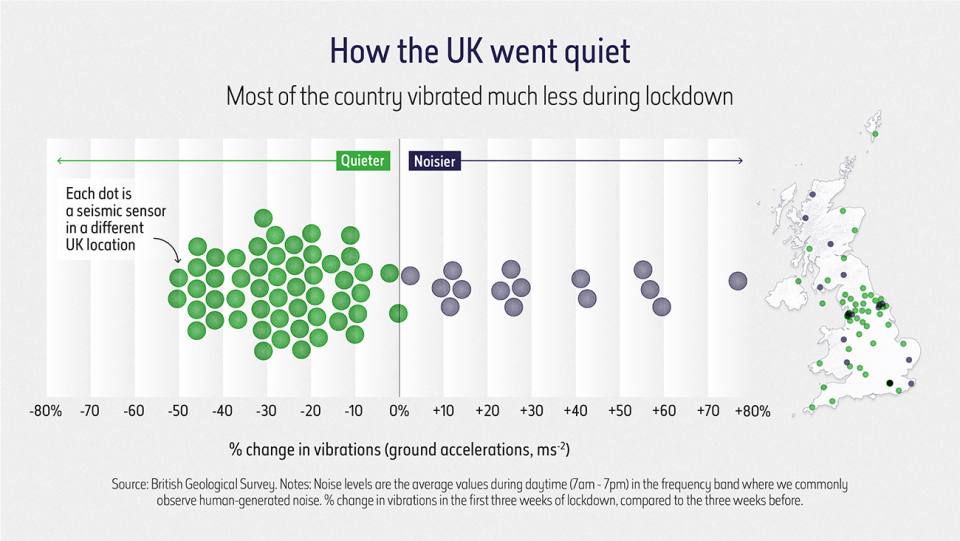
How the UK went quiet, copyright Natural History Museum.
As part of the initiative, NHM collaborated with data visualisation company Beyond Words, who approached BGS to help illustrate some of the environmental changes wrought by lockdown.
The seismic data was brought to their attention when BGS seismologists observed a drop in seismic activity throughout March 2020 in some locations across the UK.
Some areas of the UK were noisier during lockdown, but most of the country vibrated less; a pattern also noted by scientists in locations across Europe when entire countries were brought to a standstill.
We compared the average daytime noise levels at seismic stations in the UK in the two week period since the start of the COVID-19 lockdown with the average noise levels for the beginning of the year. The results show reductions in noise levels at most of our stations of between 10 and 50 per cent.
We see that some of the biggest noise reductions are at sites closest to sources of human-generated noise. Much of our understanding about the Earth comes from observations of earthquakes. So in theory, this could lead to new insights about our planet.
Brian Baptie, BGS Seismologist.
The Nature in Lockdown initiative drew on a variety of open-source data and scientific databases and documented the dramatic drop in driving and public transport use, and the changes to sightings of both animals and birds.
The project, which received funding from the Natural Environment Research Council, culminated in a live interactive virtual ‘Lates’ event on Friday 25 September, during which audiences posed questions to young and emerging researchers about those topics.
These fascinating visualisations, the result of a collaboration between scientists, our digital teams and Beyond Words, bring to life some of the astonishing impacts lockdown has had on our environments and how we noticed and experienced nature in a new and different way.
Clare Matterson, NHM’s executive director of engagement.
You can view the illustrations on The Natural History Museum website.
Find out more about how the BGS collects data to improve our understanding of earthquake hazards.
Relative topics
Related news
Call for new members and Chair to join the NERC facilities steering committees
25/02/2026
New members are needed to join the committees over the next four years.

Your views wanted – developing a ‘Geothermal energy subsurface data portfolio’
24/02/2026
BGS is aiming to support the growth of the sector by providing the best-available, location-specific geothermal and ground source heat information as an accessible product or service.
Map of BGS BritPits showing the distribution of worked mineral commodities across the country
18/02/2026
BGS’s data scientists have generated a summary map of the most commonly extracted mineral commodities by local authority area, demonstrating the diverse nature of British mineral resources.

Funding awarded to map the stocks and flows of technology metals in everyday electronic devices
12/02/2026
A new BGS project has been awarded Circular Electricals funding from Material Focus to investigate the use of technology metals in everyday electrical items.

New UK/Chile partnership prioritises sustainable practices around critical raw materials
09/02/2026
BGS and Chile’s Servicio Nacional de Geología y Minería have signed a bilateral scientific partnership to support research into critical raw materials and sustainable practices.

Extensive freshened water confirmed beneath the ocean floor off the coast of New England for the first time
09/02/2026
BGS is part of the international team that has discovered the first detailed evidence of long-suspected, hidden, freshwater aquifers.
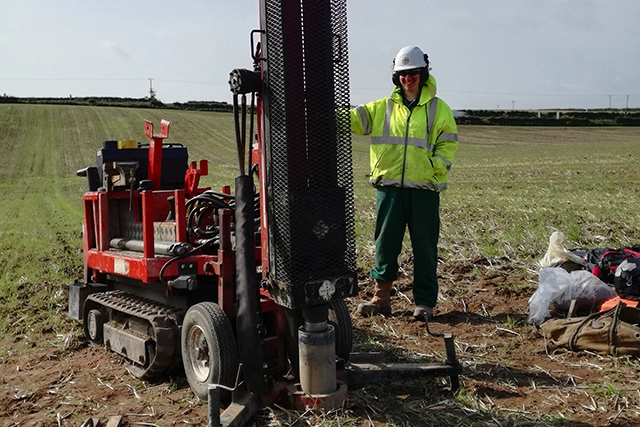

Funding secured to help mitigate ground risk in UK construction sector
05/02/2026
The BGS Common Ground project has been awarded new funding to help unlock the value of ground investigation data.
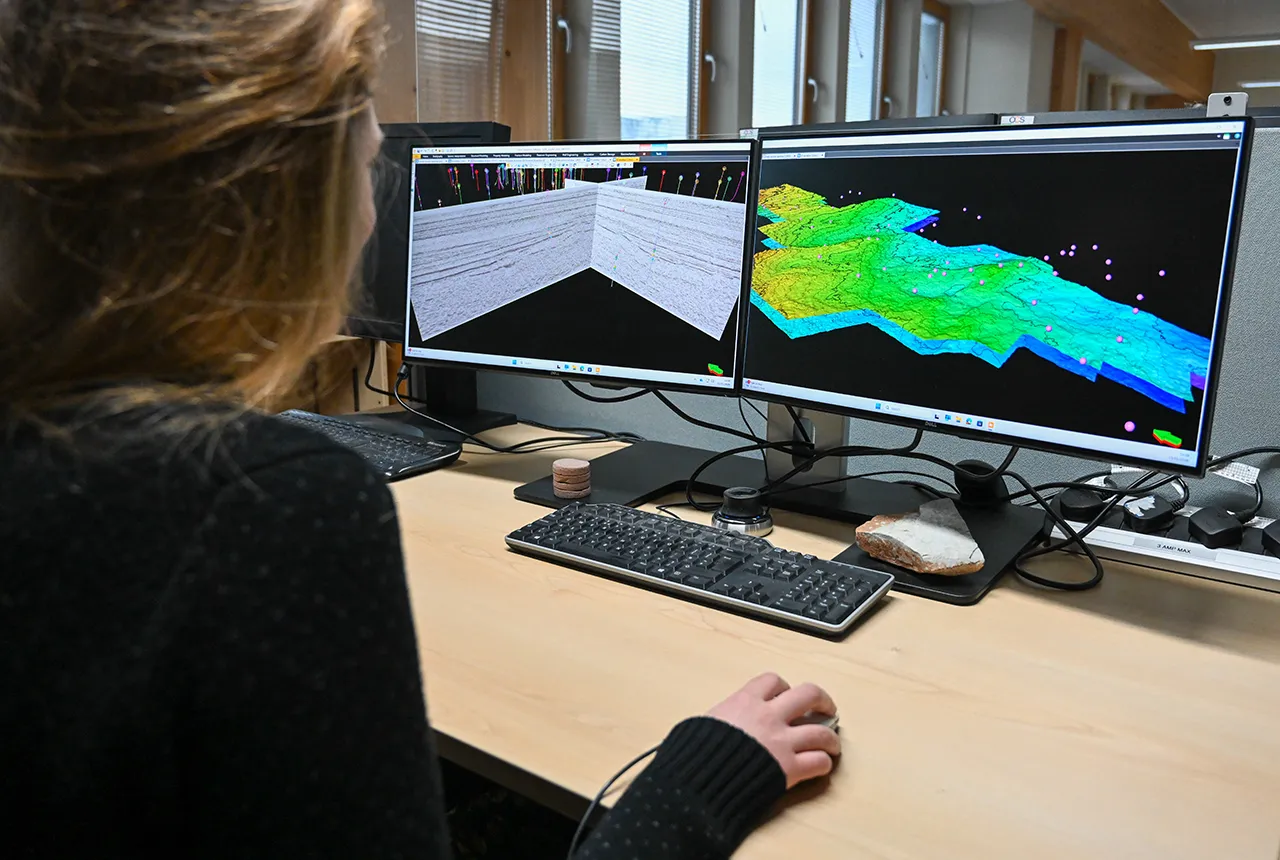

Can sandstones under the North Sea unlock the UK’s carbon storage potential?
02/02/2026
For the UK to reach its ambitious target of storing 170 million tonnes of carbon dioxide per year by 2050, it will need to look beyond the current well-studied geographical areas.
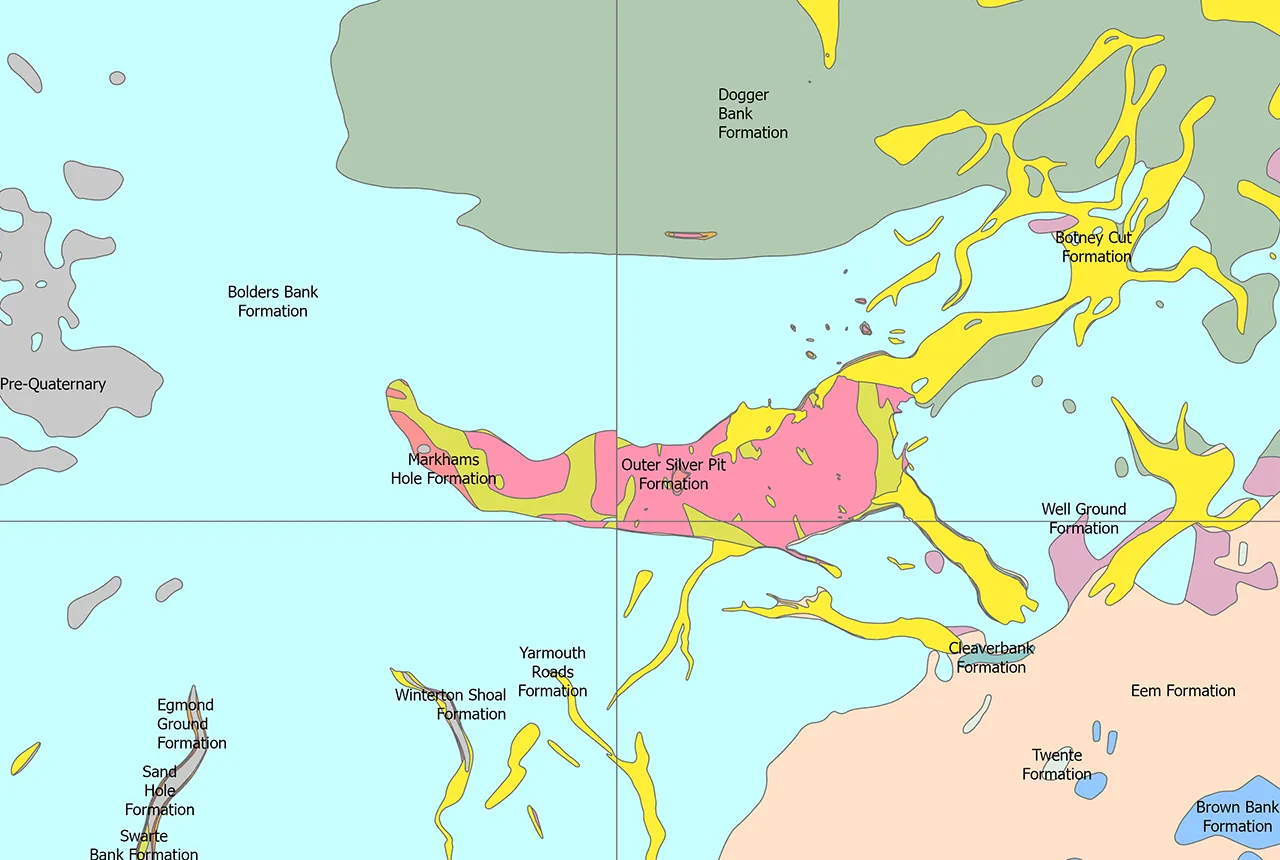
Quaternary UK offshore data digitised for the first time
21/01/2026
The offshore wind industry will be boosted by the digitisation of a dataset showing the Quaternary geology at the seabed and the UK’s shallow subsurface.
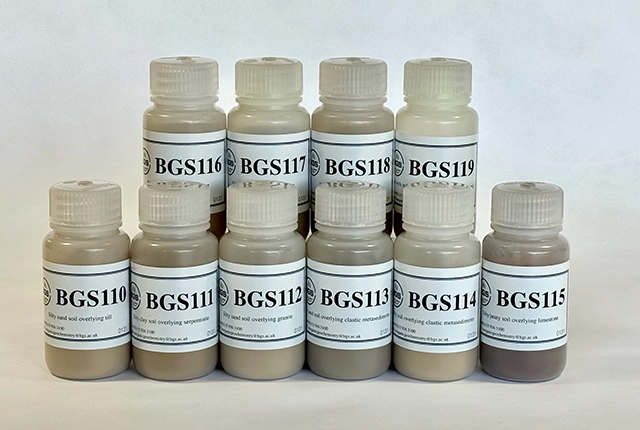

Suite of ten new soil reference materials released
02/01/2026
BGS has a longstanding track record of producing high-quality reference materials and has released ten new soil reference materials.
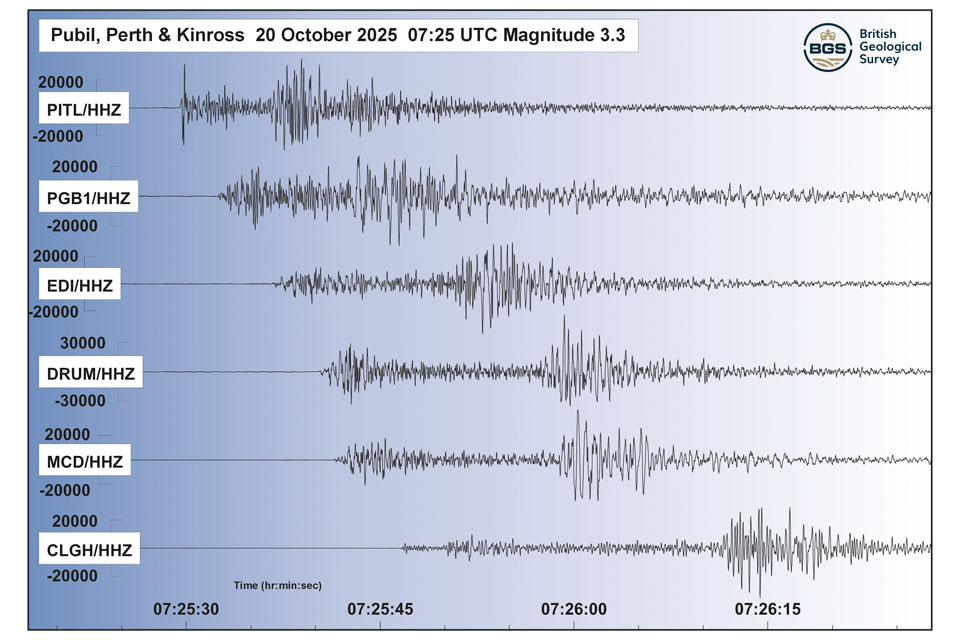
Perth and Kinross tops the UK’s earthquake activity charts for 2025
29/12/2025
Seismologists at BGS have published data on the number of seismic events over the past 12 months with over 300 earthquakes recorded.
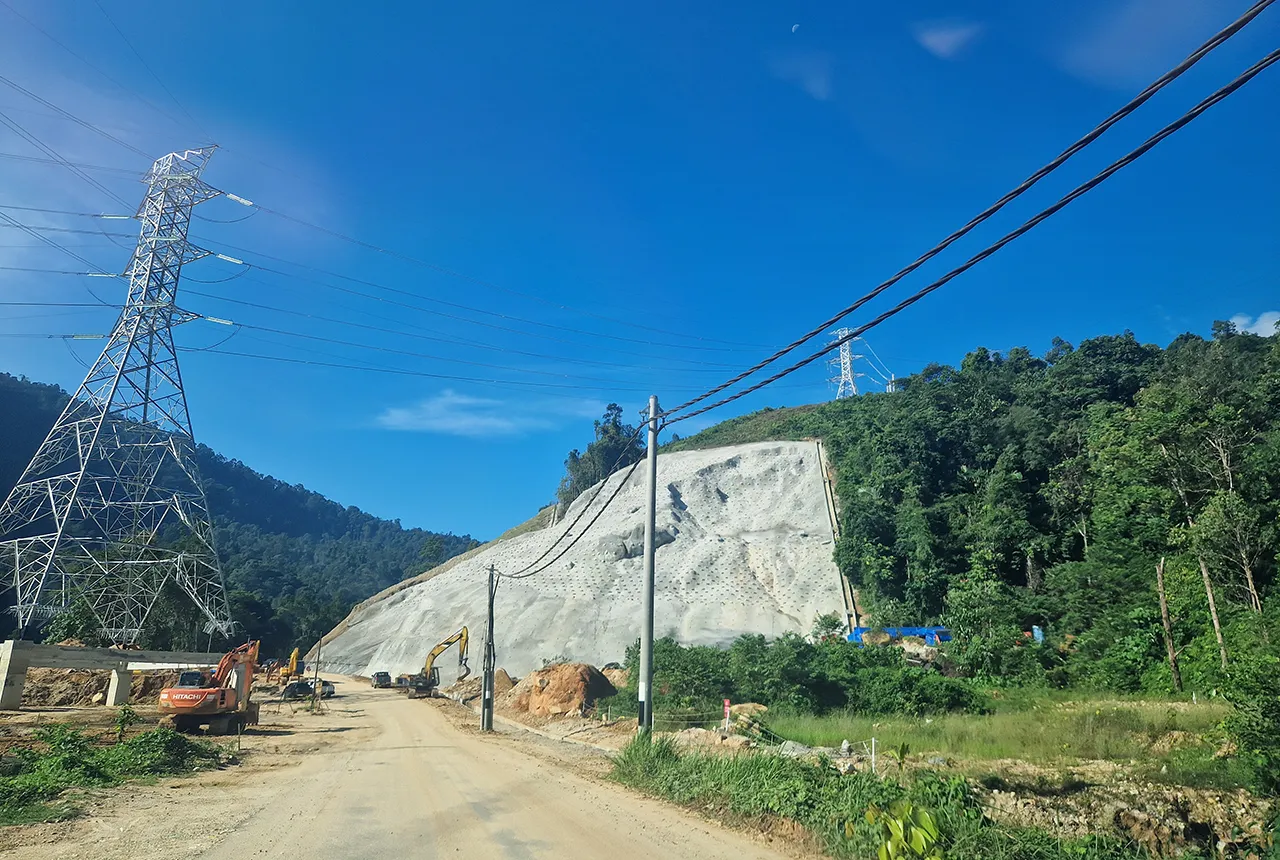

BGS awarded funding to support Malaysia’s climate resilience plan
17/12/2025
The project, funded by the Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office, will focus on minimising economic and social impacts from rainfall-induced landslides.




