What lies beneath Loch Lomond?
BGS geoscientists have visualised what lies beneath the waves of Loch Lomond, revealing an image of the loch bed and various sedimentary features of the subsurface.
17/10/2023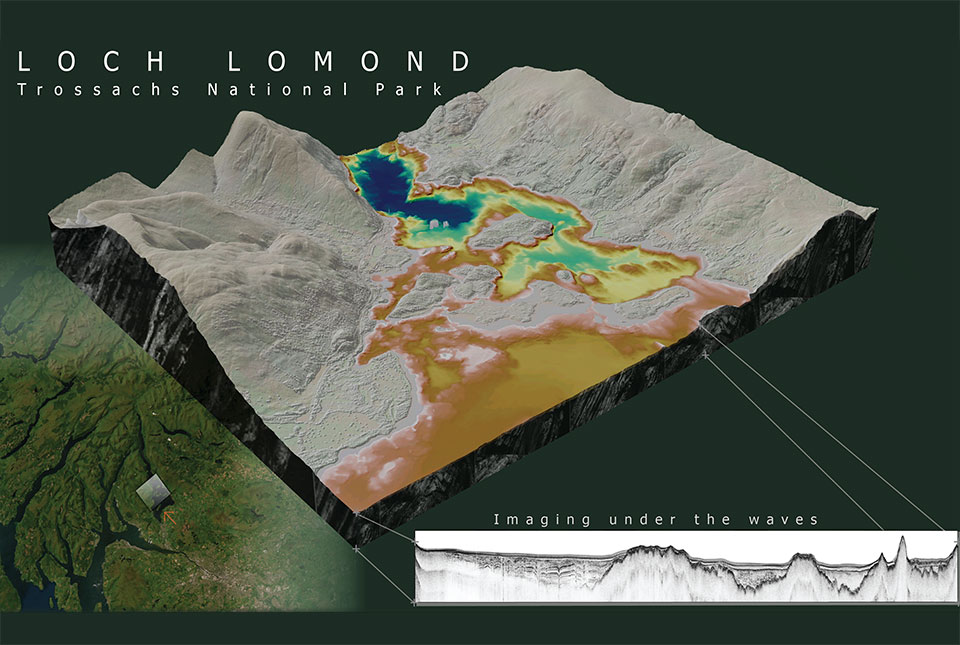
Loch Lomond is a freshwater lake at the heart of the Loch Lomond and Trossachs National Park in the south-west highlands of Scotland. It is surrounded by beautiful landscapes and vistas influenced by past ice ages.
Using seismic data, marine geoscientists at BGS have discovered a new sedimentary unit buried in deposits beneath the loch, giving new insights into its past glacial history.
Scotland in the last ice age
Much of the highlands of Scotland were covered by an extensive mountain ice cap 12 900 to 11 700 years ago, during the last period of cold climate (known as the Younger Dryas or the Loch Lomond Stadial). Decades of onshore research have shown how past ice ages have shaped the landscape of Loch Lomond, including carving of the present-day loch itself and its surroundings through processes such as erosion and deposition. However, this new dataset provides an interpretation of the stratigraphy now buried beneath the loch.
Mapping the loch bed and subsurface features
BGS used multibeam bathymetry surveys to gather detailed information about the features on the loch bed. The data revealed a series of flat-topped and prograding features (or the growth of a river delta further out into the sea over time) and ancient glacial geomorphological features. These features include drumlins, which are oval-shaped hills largely composed of glacial drift that form parallel to the direction of ice flow, and streamlined bedrock, created by glacial restructuring of hard beds that produces a collection of extended rock landforms, interpreted as showing the direction of the palaeo-ice advance.
It’s been incredibly exciting to have had the opportunity to interpret these datasets and present the loch surface and subsurface in a way we’ve never seen before. The seismic mapping and interpretation of the Inchmurrin Formation helps us understand past landscapes and geological events that are now buried under the loch bed. We are keen to undertake further research in and around the area, building on the seismostratigraphical framework that we observe in Loch Lomond.
Nicola Dakin, BGS marine geoscientist.
BGS geoscientists used seismic data to map the subsurface of the loch. Seismic data uses sound waves, which travel through buried layers of sediment, forming an acoustic image based on density variations between different sediment types. We interpreted the acoustic signature, linking sedimentary processes and depositional environments to past climatic cycles. This provided a framework to create an updated chronostratigraphy within the loch.
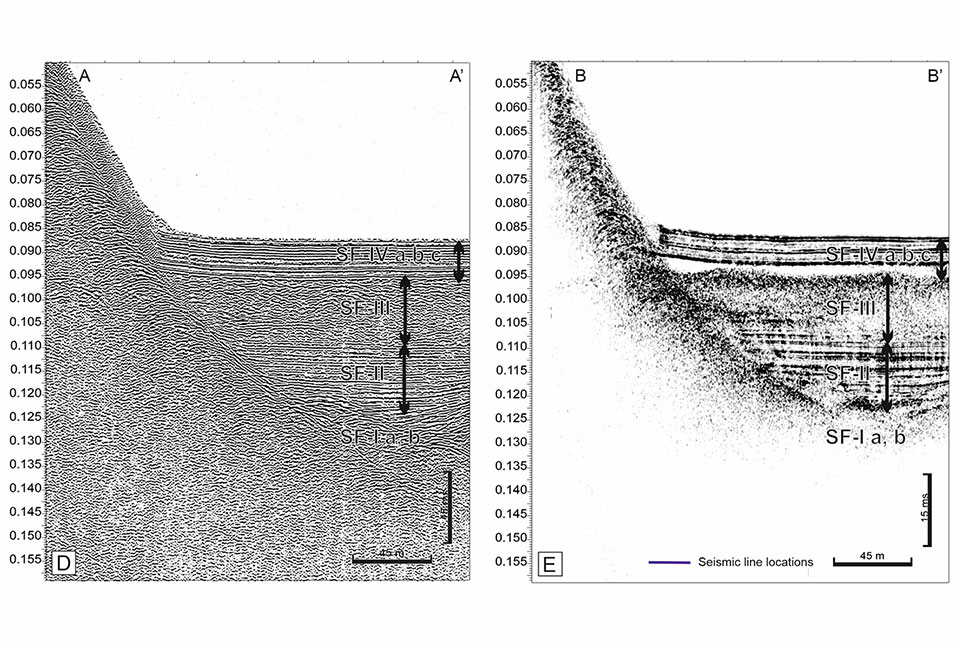
(A) Boomer and (B) EdgeTech data enabled a visual comparison of the stratigraphy imaged by different acquisition systems BGS © UKRI.
What did the survey reveal?
- during glacier advance associated with the cold Younger Dryas climate, glacial landforms were shaped underneath the ice; these can now be identified at the base of the sedimentary succession, up to 60 m below the loch bed surface
- as the ice retreated, vast volumes of water and sediment were released into the loch, leaving a sequence of layered sediments up to 44 m thick
- immediately after deglaciation of the area, exposure of steep loch margins likely resulted in landslides into the loch, producing a unit that is shown as a transparent layer in the seismic data and can represent up to 50 per cent of the sediment fill in places — we have named this new unit the ‘Inchmurrin Formation’
- as the climate transitioned from the early Holocene to the present day, a final phase of lacustrine sedimentation followed, depositing up to 127 m of the youngest, layered, grey-brown lake sediments
Global value of this work
Work is continuing to build understanding of other lochs in the area. The Loch Lomond dataset is a valuable resource that could enable BGS to offer insights into the extent and rates of landscape adjustment that accompanied the transition from glacial to non-glacial conditions. Such findings are of global importance when considering landscape stability and potential future geohazards in regions that are undergoing rapid deglaciation, such as around the European Alps, Himalayas and New Zealand’s Southern Alps.
About the author

Nicola Dakin
Marine geoscientist
Relative topics
Related news
Call for new members and Chair to join the NERC facilities steering committees
25/02/2026
New members are needed to join the committees over the next four years.

Your views wanted – developing a ‘Geothermal energy subsurface data portfolio’
24/02/2026
BGS is aiming to support the growth of the sector by providing the best-available, location-specific geothermal and ground source heat information as an accessible product or service.
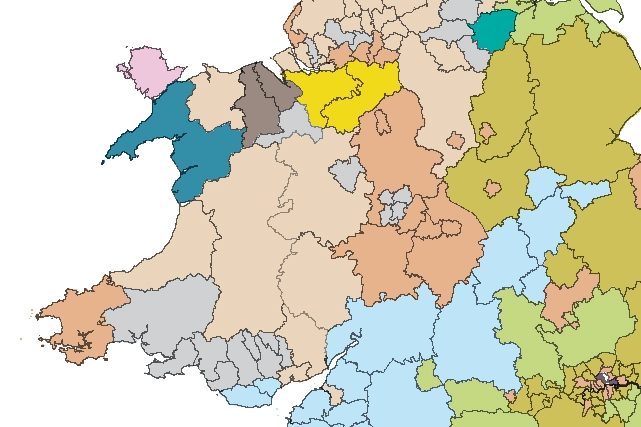
Map of BGS BritPits showing the distribution of worked mineral commodities across the country
18/02/2026
BGS’s data scientists have generated a summary map of the most commonly extracted mineral commodities by local authority area, demonstrating the diverse nature of British mineral resources.

MARC Conference 2025: highlighting the importance of conferences to PhD students
16/02/2026
BGS and University of Nottingham PhD student Paulina Baranowska shares her experience presenting her research on nuclear forensics at her first international conference.

Funding awarded to map the stocks and flows of technology metals in everyday electronic devices
12/02/2026
A new BGS project has been awarded Circular Electricals funding from Material Focus to investigate the use of technology metals in everyday electrical items.

New UK/Chile partnership prioritises sustainable practices around critical raw materials
09/02/2026
BGS and Chile’s Servicio Nacional de Geología y Minería have signed a bilateral scientific partnership to support research into critical raw materials and sustainable practices.

Extensive freshened water confirmed beneath the ocean floor off the coast of New England for the first time
09/02/2026
BGS is part of the international team that has discovered the first detailed evidence of long-suspected, hidden, freshwater aquifers.

Funding secured to help mitigate ground risk in UK construction sector
05/02/2026
The BGS Common Ground project has been awarded new funding to help unlock the value of ground investigation data.

After-school kids’ clubs
Event from 25/02/2026 to 25/03/2026
An after school club for junior geology enthusiasts

Can sandstones under the North Sea unlock the UK’s carbon storage potential?
02/02/2026
For the UK to reach its ambitious target of storing 170 million tonnes of carbon dioxide per year by 2050, it will need to look beyond the current well-studied geographical areas.
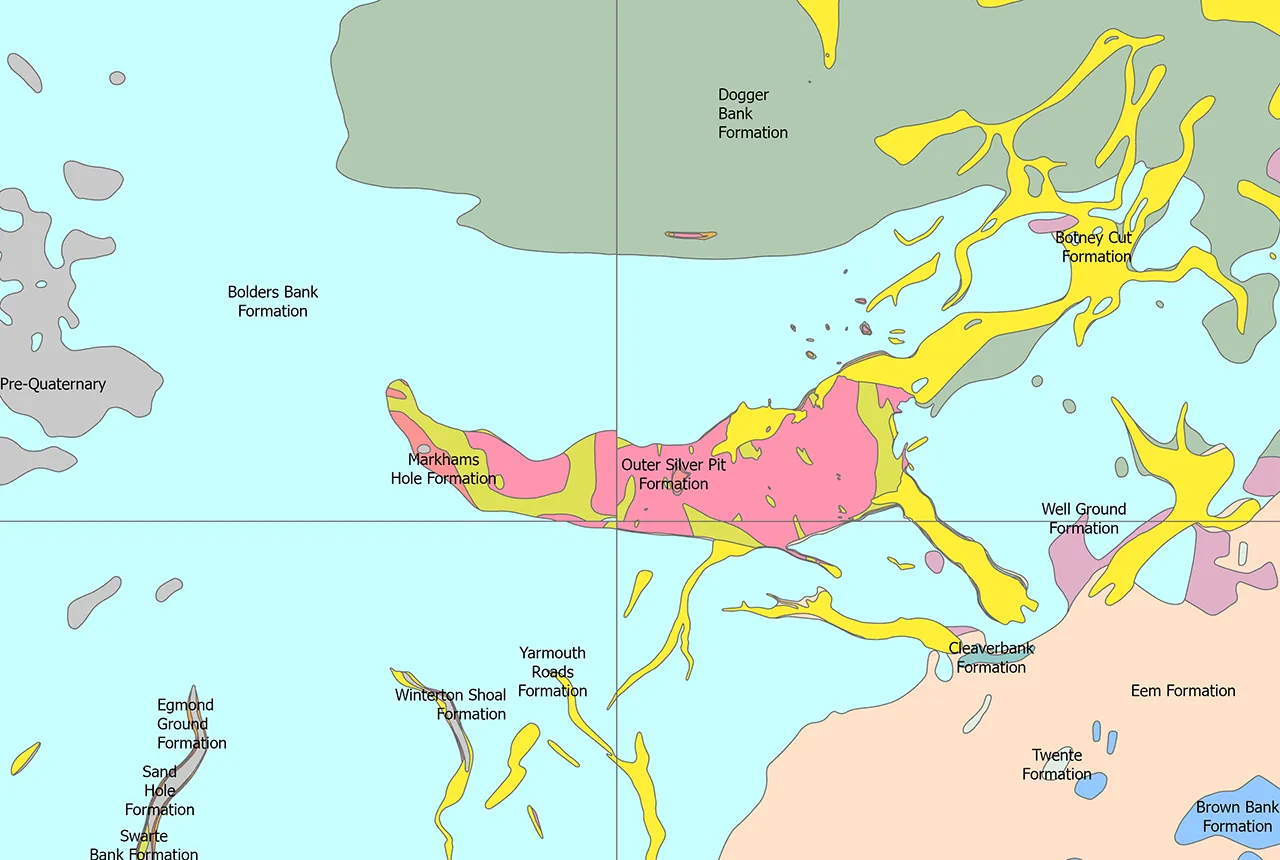
Quaternary UK offshore data digitised for the first time
21/01/2026
The offshore wind industry will be boosted by the digitisation of a dataset showing the Quaternary geology at the seabed and the UK’s shallow subsurface.





