‘Significant opportunity’ for engineering geologists to increase influence on global sustainable development
Engineering geologists have an essential role to play in meeting the UN's Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
15/03/2022 By BGS Press
Engineering geologists do not just bridge the gap between earth sciences and engineering but have an essential role to play in meeting the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), a new study by geologists at Arup and BGS highlights.

The UN’s 17 Sustaianable Development Goals. © United Nations 2022.
Crucially, their knowledge, skills and understanding around the interfaces between science and engineering and the natural and built environments past, present and future mean that engineering geologists offer a unique perspective to help build resilience to natural hazards, solve environmental problems caused by human activities and reduce the cost and risk of building and infrastructure construction.
Engineering geologists and, more broadly, geoscientists possess deep domain knowledge of natural systems and processes that makes them very well placed to tackle both environmental and socio-economic challenges covered by the UN SDGs.
Despite their unique skills and knowledge, geoscientists have historically been underrepresented in the global debate on sustainable development.
A significant opportunity therefore exists for geoscientists and engineering geologists especially to increase their influence and enhance their impact.
Marcus Dobbs, senior engineering geologist at BGS and contributor to the study.
To fully understand the current contribution of engineering geologists to the UN SDGs and where this could be enhanced, scientists at Arup and BGS undertook a mapping exercise to systematically review all 169 SDG targets and related indicators against typical engineering geology knowledge, skills and activities.
They concluded that engineering geology knowledge, skills and activities can be linked (directly or indirectly) to 107 of the 169 targets (63 per cent).
Engineering geology makes the strongest overall contribution to 5 of the 17 SDGs:
- SDG 7 (affordable and clean energy): linked to 100 per cent of targets
- SDG 9 (industry, innovation and infrastructure): linked to 88 per cent of targets
- SDG 12 (responsible consumption and production): linked to 82 per cent of targets
- SDG 11 (sustainable cities and communities): linked to 80 per cent of targets
- SDG 13 (climate action): linked to 80 per cent of targets
The mapping exercise shows that engineering geologists clearly have an important role to play in achieving sustainable development globally, primarily through their role in infrastructure development, building resilience and disaster risk reduction and environmental protection as well as in building equitable communities and through collaborative and strong partnerships.
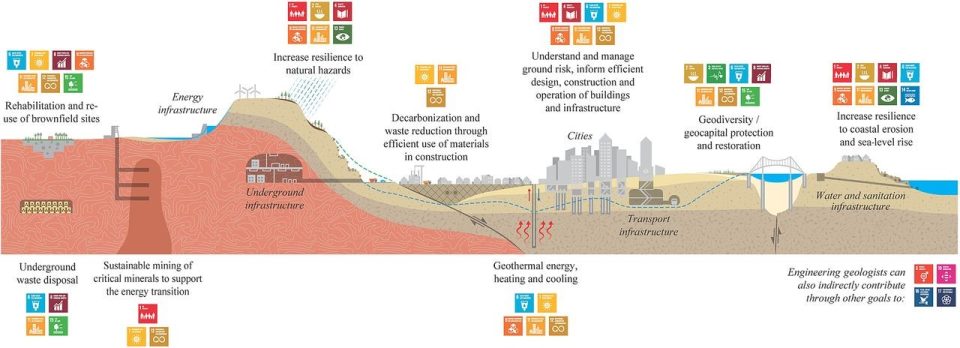
For over 20 years, BGS engineering geology research has:
- generated a wealth of data and information on the properties and behaviour of geological formations that are strategically important to critical infrastructure development in the UK
- undertaken research to enhance societal resilience to shallow geohazards by developing and communicating a better understanding of their distribution, character, susceptibility and triggering, and potential impacts, with much of this research specifically focused on landslides and landslide processes both in the UK and internationally
- made significant advances in the field of urban geoscience to specifically support decision makers in the planning and construction sector to optimise the use of the subsurface to make cities and communities inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable
- contributed to the developed national-scale engineering geology and geohazard datasets to support sustainable and resilient land use, planning and development
In addition to the existing contribution of engineering geology to the SDGs, the Arup and BGS study also identified opportunities for engineering geologists to strengthen contribution to all 17 of the UN SDGs, with the greatest of these being to:
- SDG 7 (affordable and clean energy): 100 per cent of targets were identified;
- SDG 12 (responsible consumption and production): 55 per cent of targets were identified
- SDG 16 (peace, justice and strong institutions): 50 per cent of targets were identified
- SDG 17 (partnerships for the goals): 41 per cent of targets were identified
These opportunities include:
- extending influence across the project life cycle and to policymaking
- greater consideration of options for decarbonisation
- the impacts of climate change
- the value of geocapital and geodiversity
- training in geoethics
- a greater emphasis on diversity, inclusion and equity within the profession
- increased collaboration and knowledge sharing globally through cross- and multidisciplinary partnerships, and between industry and academia
In recent years, engineering geologists within BGS have been engaged in a range of multidisciplinary research studies to address some of these challenges, including:
- building multidisciplinary, international partnerships to improve the characterisation of multi-hazard relationships and help inform risk management in the context of sustainable development
- exploring the application of shallow geothermal energy technologies for both heating and cooling
- the potential for fault reactivation in deep geothermal reservoirs
- assessing potential viability of reusing depleted oil reservoirs for carbon capture and sequestration
- examining the physical properties and behaviour of geological materials to inform the development of the safe subsurface disposal of radioactive waste
- identifying and characterising marine geohazards and marine geohazard processes to support the development of large-scale offshore wind-farms
- working with industry and academia, through the Engineering Group of the Geological Society, to document and publicise good working practice for offshore exploration, survey and development
We hope these findings will enable and empower engineering geologists globally to better communicate the value of their contribution to society, the environment and the economy and identify opportunities to increase that impact.
Marcus Dobbs.
BGS is keen to broaden its research partnerships to include a greater diversity of collaborators and stakeholders from government, academia, industry and the not-for-profit sectors. Anyone interested in working with BGS on sustainable engineering geology research can contact Marcus Dobbs.
Gill, J C, Malamud, B D, Barillas, E M, and Noriega, A G. 2020. Construction of regional multi-hazard interaction frameworks, with an application to Guatemalaional multi-hazard interaction frameworks. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, Vol. 20(1), 149–180.
Tomorrow’s Cities — an interdisciplinary research hub working globally to bring multi-hazard disaster risk management to the centre of urban policy and practice.
Relative topics
Related news
Call for new members and Chair to join the NERC facilities steering committees
25/02/2026
New members are needed to join the committees over the next four years.

Your views wanted – developing a ‘Geothermal energy subsurface data portfolio’
24/02/2026
BGS is aiming to support the growth of the sector by providing the best-available, location-specific geothermal and ground source heat information as an accessible product or service.
Map of BGS BritPits showing the distribution of worked mineral commodities across the country
18/02/2026
BGS’s data scientists have generated a summary map of the most commonly extracted mineral commodities by local authority area, demonstrating the diverse nature of British mineral resources.

Funding awarded to map the stocks and flows of technology metals in everyday electronic devices
12/02/2026
A new BGS project has been awarded Circular Electricals funding from Material Focus to investigate the use of technology metals in everyday electrical items.

New UK/Chile partnership prioritises sustainable practices around critical raw materials
09/02/2026
BGS and Chile’s Servicio Nacional de Geología y Minería have signed a bilateral scientific partnership to support research into critical raw materials and sustainable practices.

Extensive freshened water confirmed beneath the ocean floor off the coast of New England for the first time
09/02/2026
BGS is part of the international team that has discovered the first detailed evidence of long-suspected, hidden, freshwater aquifers.

Funding secured to help mitigate ground risk in UK construction sector
05/02/2026
The BGS Common Ground project has been awarded new funding to help unlock the value of ground investigation data.

Can sandstones under the North Sea unlock the UK’s carbon storage potential?
02/02/2026
For the UK to reach its ambitious target of storing 170 million tonnes of carbon dioxide per year by 2050, it will need to look beyond the current well-studied geographical areas.
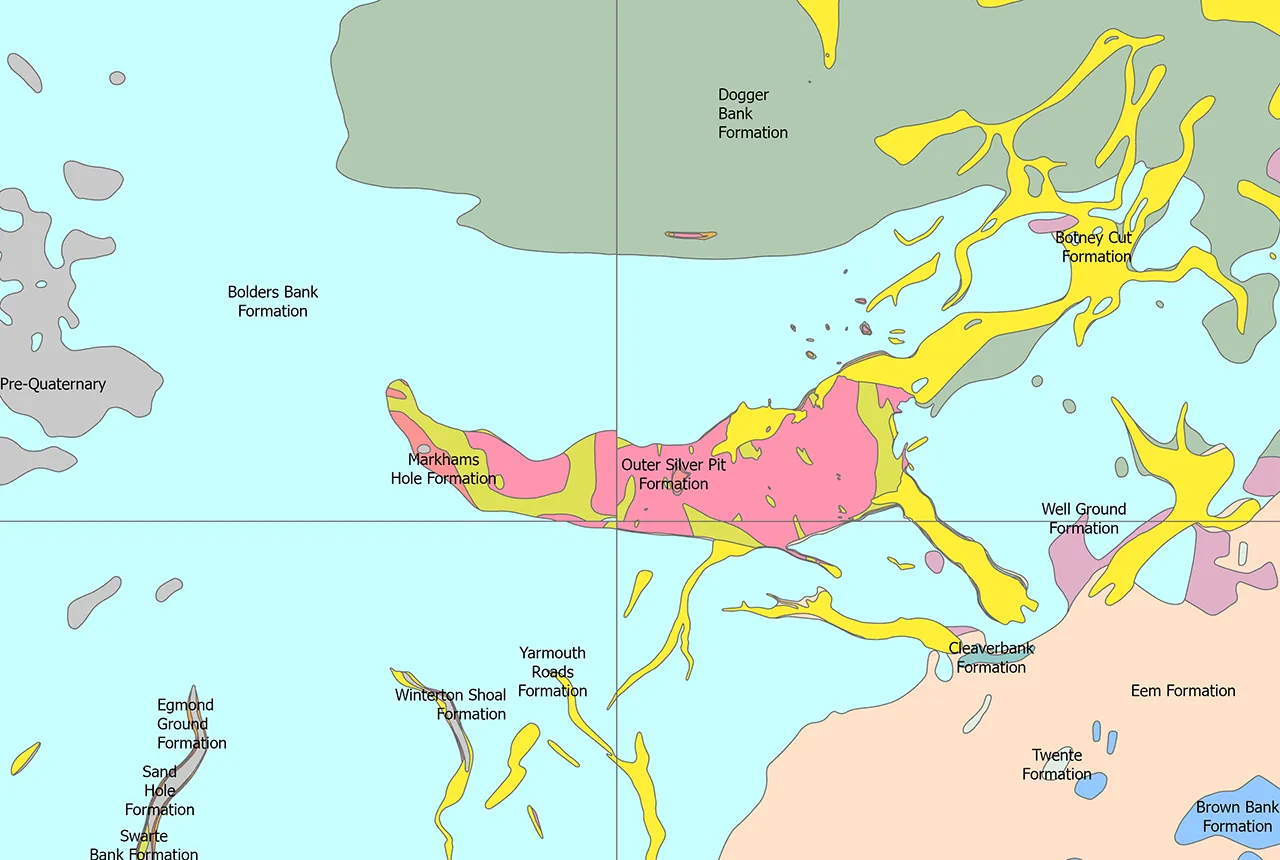
Quaternary UK offshore data digitised for the first time
21/01/2026
The offshore wind industry will be boosted by the digitisation of a dataset showing the Quaternary geology at the seabed and the UK’s shallow subsurface.
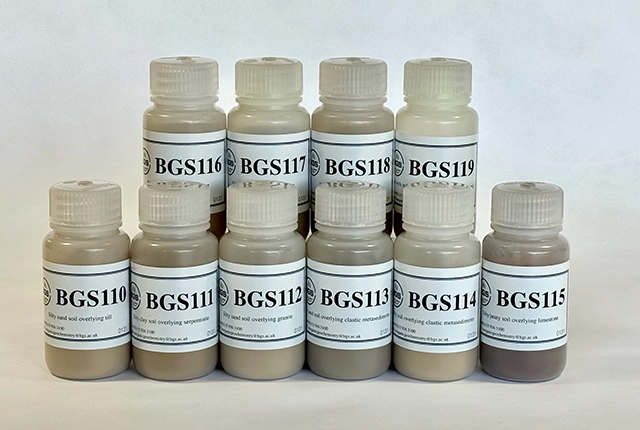

Suite of ten new soil reference materials released
02/01/2026
BGS has a longstanding track record of producing high-quality reference materials and has released ten new soil reference materials.
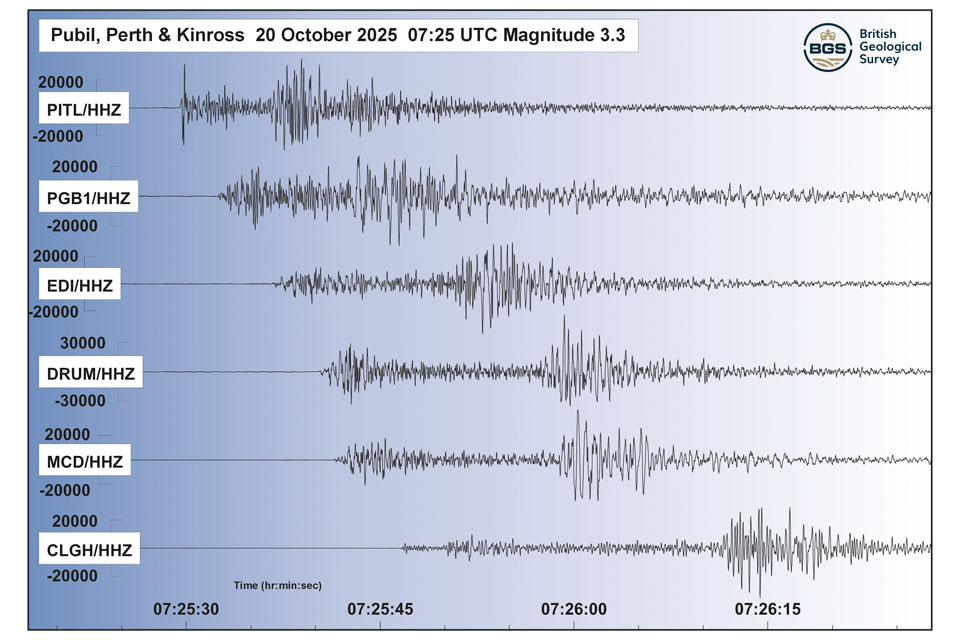
Perth and Kinross tops the UK’s earthquake activity charts for 2025
29/12/2025
Seismologists at BGS have published data on the number of seismic events over the past 12 months with over 300 earthquakes recorded.

BGS awarded funding to support Malaysia’s climate resilience plan
17/12/2025
The project, funded by the Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office, will focus on minimising economic and social impacts from rainfall-induced landslides.




