‘First of its kind’ online tool created to help tackle pollution in London
The new Road Pollution Solutions tool predicts pollution levels from road runoff and suggests nature-based solutions to combat it.
04/09/2023 By BGS Press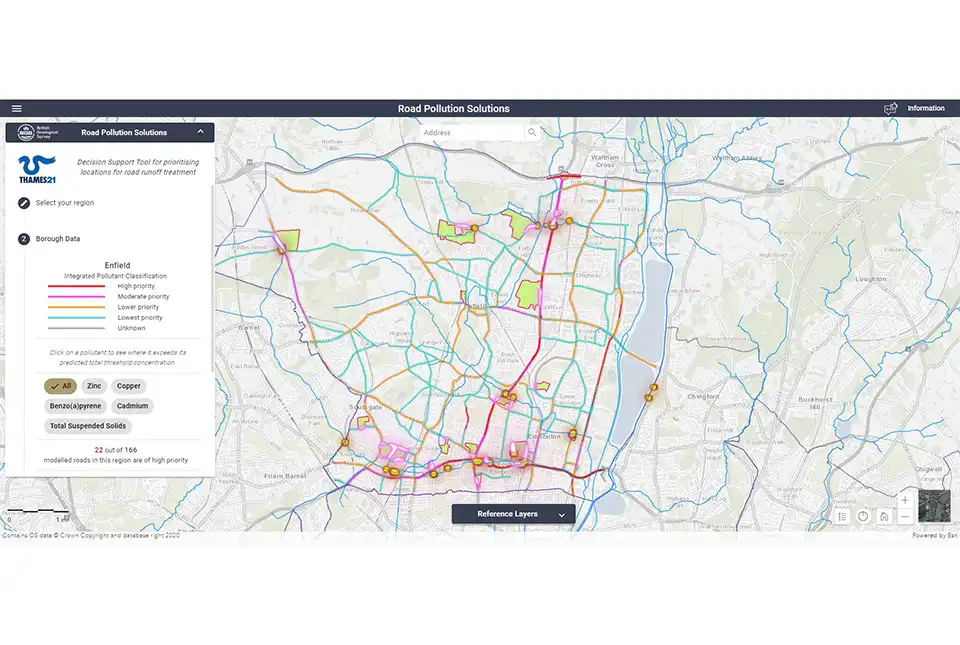
BGS’s new, first of its kind online tool, Road Pollution Solutions, has gone live today (4 September 2023) and predicts which roads in London create the most runoff pollutants and how this can be tackled with nature-based solutions. The tool will help local authorities to prioritise water-quality improvement interventions at roads where major road runoff pollution is occurring and in the greenspaces that lie between the roads and the rivers.
Road runoff pollution in rivers and streams comes from oil, diesel and petrol spills as well as the wearing of roads, tyres and braking systems. These all leave residues and sediment that are washed off the roads and into waterways by rain. Roads where heavy goods vehicles regularly apply their brakes are often the worst affected.
Modelling shows that more than 2400 road sections covering a total of 451 km of London’s major roads pose a high risk of causing road runoff pollution. These roads are the priority for treatment, with natural barriers, such as wetlands, being used to help capture and prevent some of this road runoff pollution from entering rivers and streams.
The London boroughs ‘predicted’ to have the most polluting roads include:
- Barking and Dagenham
- Barnet
- Havering
- Haringey
- Waltham Forest
We have been delighted to work with Thames21 and its partners to create the Road Pollution Solutions tool. It will help local authorities and anyone seeking to improve our water environment to quickly identify the major sources of pollution from roads and to prioritise interventions to tackle them. Nature-based solutions have multiple benefits and we expect the tool to speed up their implementation.
Chris Jackson, BGS Head of Environmental Modelling
Road Pollution Solutions is built on years of research by environmental charity Thames21 and its partner Middlesex University, as well as the South East Rivers Trust. The charity started its initial road runoff project identifying key polluting London roads in 2019, with funding help from the Greater London Authority, Transport for London and the Environment Agency.
Additional support for the creation of the tool was provided by the UKRI/NERC-funded CAMELLIA project.
- Project delivered by:
- researchers:
- Thames21
- Middlesex University
- South East Rivers Trust
- funders:
- Environment Agency
- Transport for London
- Greater London Authority
- Project supported by:
- Middlesex University
- Zoological Society of London (ZSL)
- CAMELLIA
- Built by: BGS
- researchers:
This study uses numbers of vehicles and vehicle types to predict the amount of pollution deposited on roads and then predicts the degree of damage these contaminants could cause to our rivers. The modelling for this project only applies to the major roads in outer London for which Transport for London has modelled or observed data around vehicle movements. All the roads assessed have potential for damaging river health.
The project assessed six pollutants, five of which have environment quality standards (zinc, cadmium, copper, total suspended solids and benzo(a)pyrene). Pyrene was also modelled as an important indicator of road runoff, though it does not yet have an environment quality standard.
About BGS
The British Geological Survey (BGS) is a world-leading geological survey that undertakes strategic science for the benefit of society. BGS is part of UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) and a research centre within the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC).
BGS delivers research, products and services for the UK, and operates internationally to maximise the impact of its science and to contribute to the UK’s international priorities. BGS is the national centre of geological data and information and undertakes monitoring and analytical research programmes. These enable the timely and authoritative provision of impartial and independent information and advice to governments, industry and civil society.
The new BGS Strategy for 2023 to 2028, ‘Understanding our Earth’, sets out its four priority science areas for the next five years, helping to deliver the necessary geological data and knowledge for a sustainable future. See www.bgs.ac.uk.
Related news
Call for new members and Chair to join the NERC facilities steering committees
25/02/2026
New members are needed to join the committees over the next four years.

Your views wanted – developing a ‘Geothermal energy subsurface data portfolio’
24/02/2026
BGS is aiming to support the growth of the sector by providing the best-available, location-specific geothermal and ground source heat information as an accessible product or service.
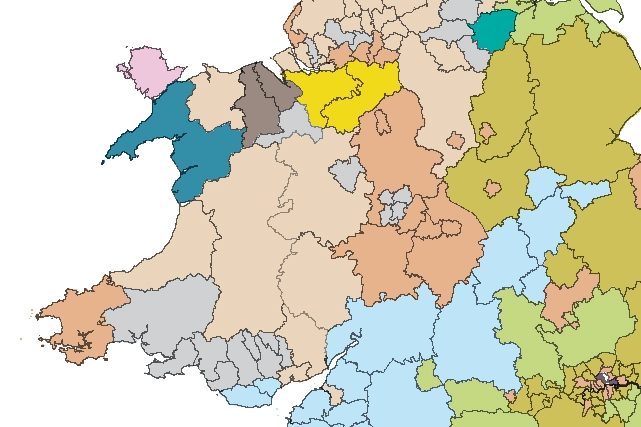
Map of BGS BritPits showing the distribution of worked mineral commodities across the country
18/02/2026
BGS’s data scientists have generated a summary map of the most commonly extracted mineral commodities by local authority area, demonstrating the diverse nature of British mineral resources.

MARC Conference 2025: highlighting the importance of conferences to PhD students
16/02/2026
BGS and University of Nottingham PhD student Paulina Baranowska shares her experience presenting her research on nuclear forensics at her first international conference.

Funding awarded to map the stocks and flows of technology metals in everyday electronic devices
12/02/2026
A new BGS project has been awarded Circular Electricals funding from Material Focus to investigate the use of technology metals in everyday electrical items.

New UK/Chile partnership prioritises sustainable practices around critical raw materials
09/02/2026
BGS and Chile’s Servicio Nacional de Geología y Minería have signed a bilateral scientific partnership to support research into critical raw materials and sustainable practices.

Extensive freshened water confirmed beneath the ocean floor off the coast of New England for the first time
09/02/2026
BGS is part of the international team that has discovered the first detailed evidence of long-suspected, hidden, freshwater aquifers.

Funding secured to help mitigate ground risk in UK construction sector
05/02/2026
The BGS Common Ground project has been awarded new funding to help unlock the value of ground investigation data.

After-school kids’ clubs
Event from 25/02/2026 to 25/03/2026
An after school club for junior geology enthusiasts

Can sandstones under the North Sea unlock the UK’s carbon storage potential?
02/02/2026
For the UK to reach its ambitious target of storing 170 million tonnes of carbon dioxide per year by 2050, it will need to look beyond the current well-studied geographical areas.
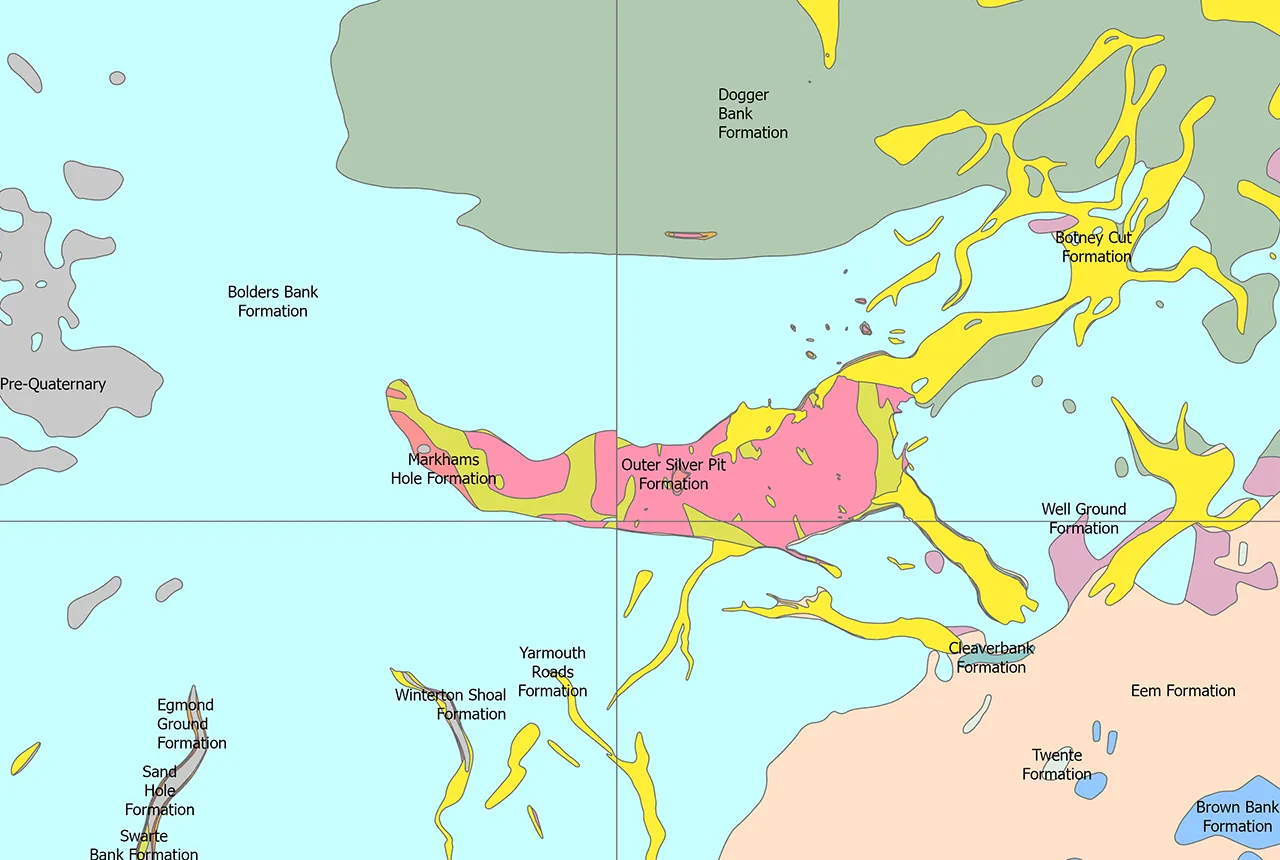
Quaternary UK offshore data digitised for the first time
21/01/2026
The offshore wind industry will be boosted by the digitisation of a dataset showing the Quaternary geology at the seabed and the UK’s shallow subsurface.




