Discovering Geology

Discovering Geology introduces a range of geoscience topics to school-age students and learners of all ages. Explore these pages to discover the fascinating processes and properties that shape our dynamic planet.
The Earth has been cooling down since it formed 4.6 billion years ago. Over that time, its surface has changed constantly, driven by the movement of magma deep within the planet and aided by the processes of erosion, deposition and weathering. New oceans have appeared as tectonic plates move apart, great mountain ranges have formed as tectonic plates crash together, valleys have been created as glaciers move and the wind has carried sediment particles over great distances to form new landscapes.
Discovering Geology explores the processes that have shaped current and past landscapes and how our planet’s diverse range of rocks and minerals formed. We also investigate how rocks and fossils can be used to explain the changing climates of the past and why learning from the past is the key to understanding our sustainable future.
Throughout Discovering Geology, we link topics with the scientific research and monitoring work that we carry out at the BGS. From investigating natural earth hazards to understanding past environments, our research aims to offer geoscientific solutions for a safer, more sustainable and prosperous planet.
Start discovering geology!

Discovering Geology: climate change
What is the difference between weather and climate? what causes the Earth’s climate to change and what are the impacts? Find out more with our Discovery Geology climate change resources.

Rocks and minerals
Find out more about the differences between rocks and minerals and how they are formed.

Geological processes
Planet Earth is dynamic with a surface that is always changing. Find out about the processes that cause these changes.
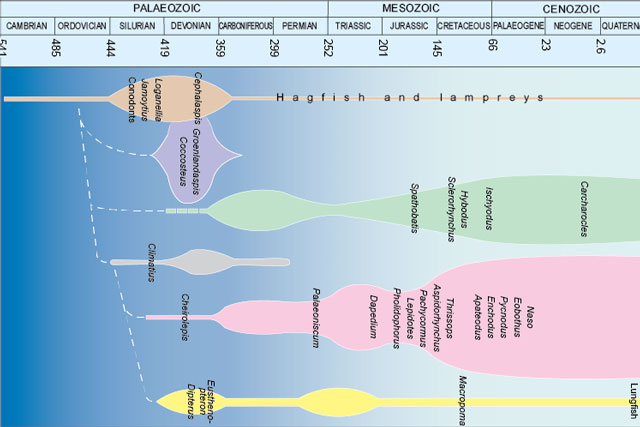
Fossils and geological time
Take a look at the history of the Earth, from its formation over four and a half billion years ago to present times.

Earth hazards
The Earth beneath our feet is constantly shifting and moving, and violently with catastrophic and immediate results. Find out more about earth hazards.
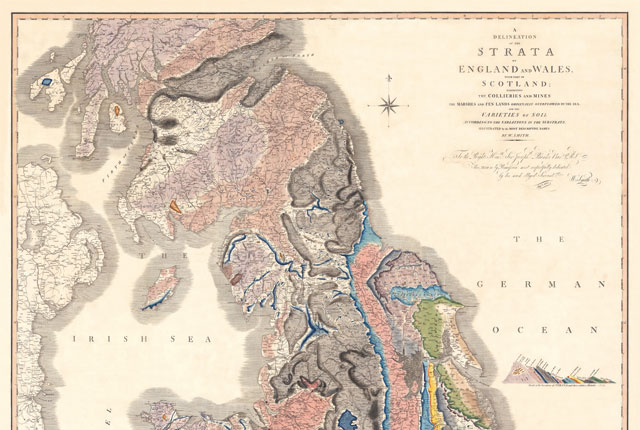
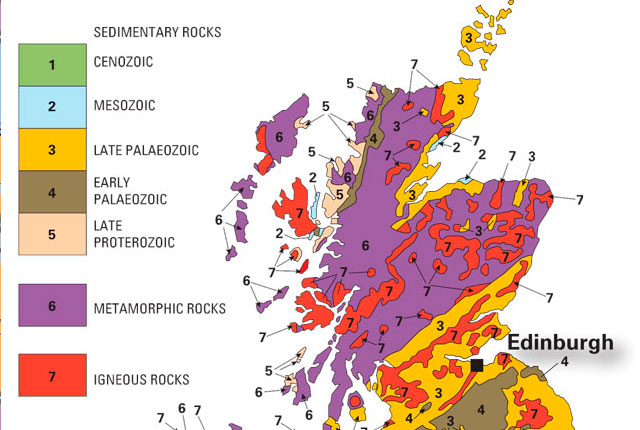
Maps and resources
Download and print free educational resources.
Classroom activities, lesson plans and other resources

Critical minerals resources
Our modern lives rely on a whole host of metals and minerals that are extracted from the ground. Available resources include classroom activities and a touring festival stand.

The CheMUDstry Investigation
Our CheMUDstry investigation makes use of mud pies and uses them in different activities to look at soil chemistry. Use the observation booklet to practise taking soil samples and make observations of soil samples and their environment.
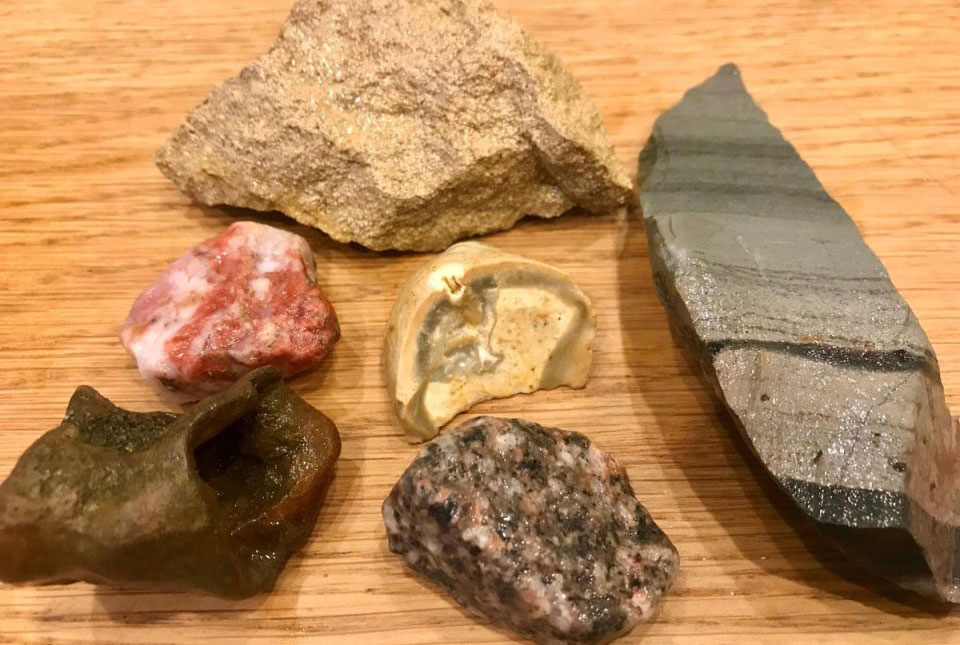

Rock observation resources
Activities to help budding geologists identify rocks and minerals. Available resources include grain size charts, rock loan kits, and classroom activites.

Energy resources
Complete lesson plans with videos and worksheets on geothermal energy, energy storage and future energy planning.
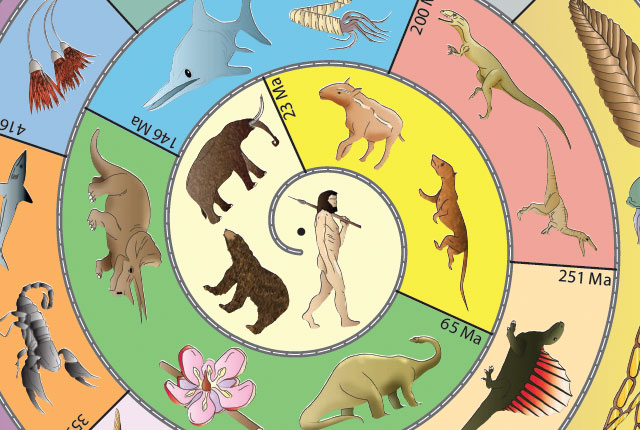

Fossils and geological time resources
You can download, print and make a number of paper dinosaur puppets to play with or colour-in a geological timeline to hang in your bedroom or classroom.
Climate change
Our climate is intimately connected to the evolution of life, to the erosion and formation of rocks, and even to the generation of mountains.

The carbon story
The carbon cycle describes the process in which carbon atoms continually travel from the atmosphere into the Earth, then released back into the atmosphere.

The greenhouse effect
Gases in the Earth’s atmosphere act as an insulating blanket around the planet, trapping more of the Sun’s heat.
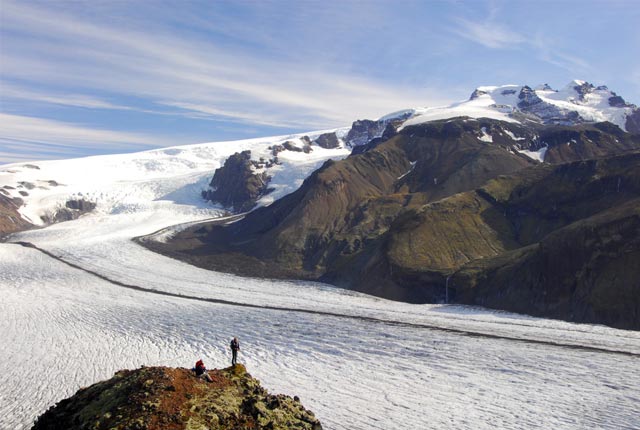

What causes the Earth’s climate to change?
Geological records demonstrate that there have been a number of large variations in Earth’s climate in the past.
Earth hazards
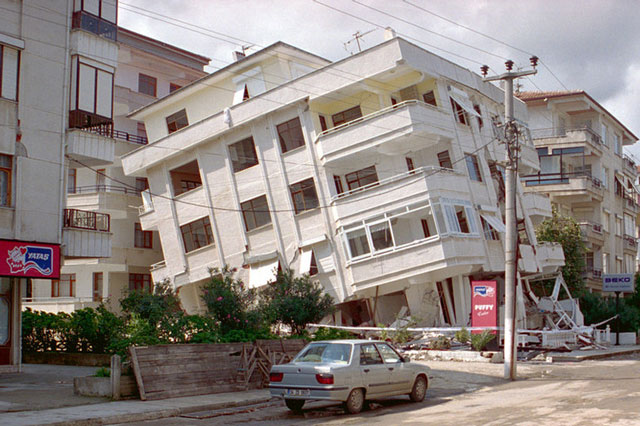

Earthquakes
Earthquakes are among the most deadly natural hazards. They strike without warning and many earthquake zones coincide with areas of high population density.
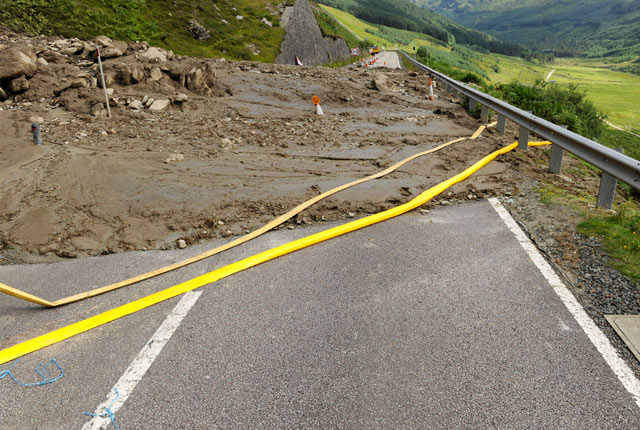

Understanding landslides
What is a landslide? Why do landslides happen? How to classify a landslide. Landslides in the UK and around the world.
Rocks and minerals

Rocks and minerals
Find out more about the differences between rocks and minerals and how they are formed.
Landforms and processes
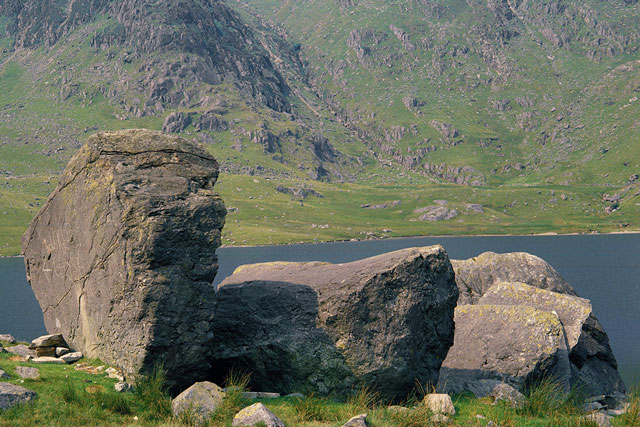

Deposition
Deposition is the laying down of sediment carried by wind, water, or ice.
Fossils and geological time

Fossils and geological time
Take a look at the history of the Earth, from its formation over four and a half billion years ago to present times.